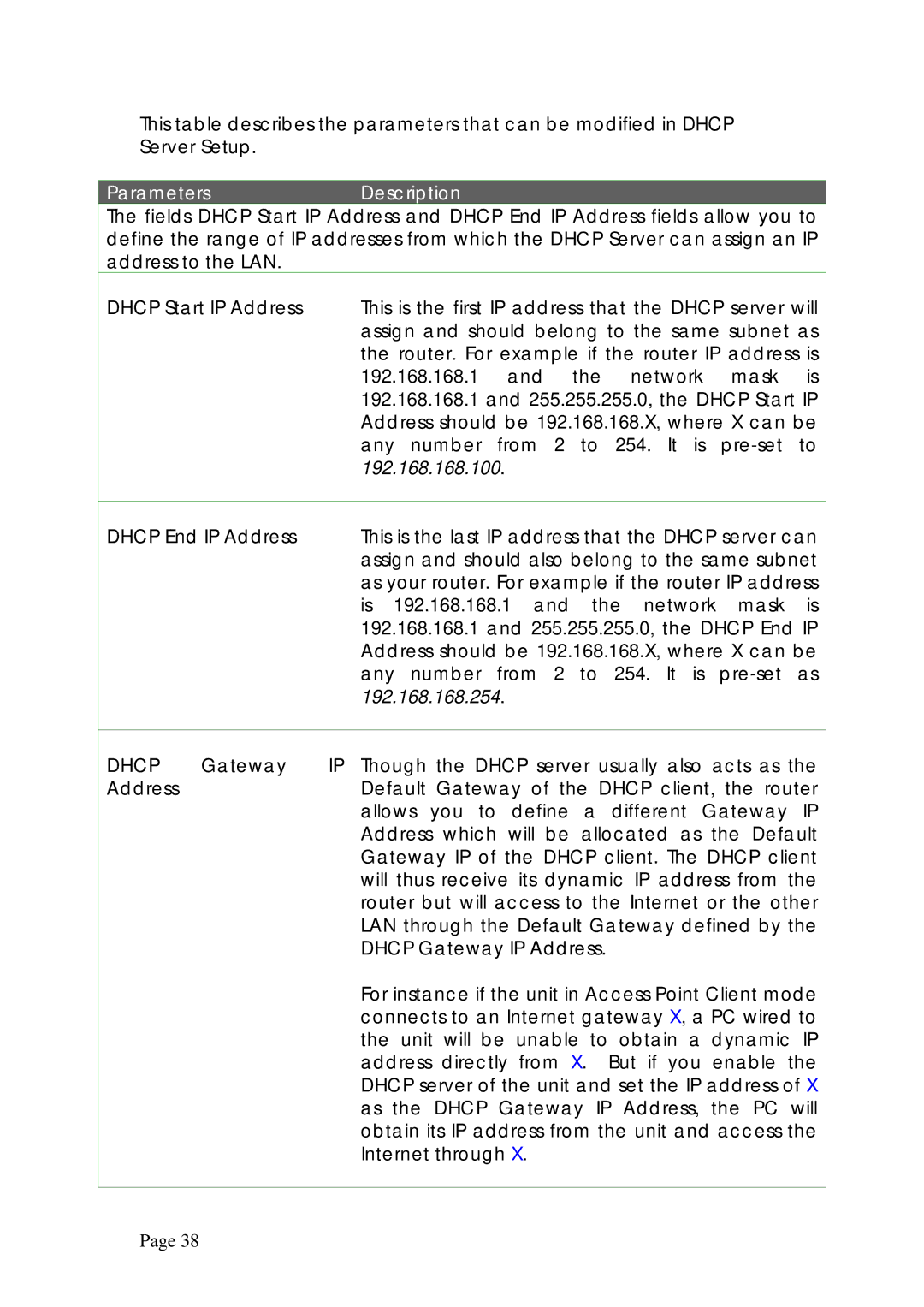
This table describes the parameters that can be modified in DHCP Server Setup.
Parameters | Description |
The fields DHCP Start IP Address and DHCP End IP Address fields allow you to | |
define the range of IP addresses from which the DHCP Server can assign an IP address to the LAN.
DHCP Start IP Address |
| This is the first IP address that the DHCP server will | |
|
|
| assign and should belong to the same subnet as |
|
|
| the router. For example if the router IP address is |
|
|
| 192.168.168.1 and the network mask is |
|
|
| 192.168.168.1 and 255.255.255.0, the DHCP Start IP |
|
|
| Address should be 192.168.168.X, where X can be |
|
|
| any number from 2 to 254. It is |
|
|
| 192.168.168.100. |
|
|
| |
DHCP End IP Address |
| This is the last IP address that the DHCP server can | |
|
|
| assign and should also belong to the same subnet |
|
|
| as your router. For example if the router IP address |
|
|
| is 192.168.168.1 and the network mask is |
|
|
| 192.168.168.1 and 255.255.255.0, the DHCP End IP |
|
|
| Address should be 192.168.168.X, where X can be |
|
|
| any number from 2 to 254. It is |
|
|
| 192.168.168.254. |
|
|
|
|
DHCP | Gateway | IP | Though the DHCP server usually also acts as the |
Address |
|
| Default Gateway of the DHCP client, the router |
|
|
| allows you to define a different Gateway IP |
|
|
| Address which will be allocated as the Default |
|
|
| Gateway IP of the DHCP client. The DHCP client |
|
|
| will thus receive its dynamic IP address from the |
|
|
| router but will access to the Internet or the other |
|
|
| LAN through the Default Gateway defined by the |
|
|
| DHCP Gateway IP Address. |
|
|
| For instance if the unit in Access Point Client mode |
|
|
| connects to an Internet gateway X, a PC wired to |
|
|
| the unit will be unable to obtain a dynamic IP |
|
|
| address directly from X. But if you enable the |
|
|
| DHCP server of the unit and set the IP address of X |
|
|
| as the DHCP Gateway IP Address, the PC will |
|
|
| obtain its IP address from the unit and access the |
|
|
| Internet through X. |
|
|
|
|
Page 38