W . d e l l . c o m s u p p o r t . d e l l . c o m
Service Tag
Diagnostic lights
CD or DVD eject button CD or DVD activity light
October YH242
Contents
Cleaning the Computer, Keyboard, and Monitor
Program is designed for an earlier Windows operating system
100
Using Microsoft Windows XP System Restore
Resolving Software and Hardware Incompatibilities
101
106
104
105
107
137
Support.dell.com
Warranty information
Finding Information
Updates
Use the Service Tag to
When you use
Appropriate for your configuration, providing critical
Click the topic that describes your problem
How to work with programs and files
How to personalize my desktop
How to reinstall my operating system
Finding Information
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Front View of the Computer
Vents and any object near the vents
Computer. Instead, perform an operating system shutdown
Back View of the Computer
Computer
Back Panel Connectors
Green a good connection exists between a 10-Mbps network
Ensure reliable operation
Connecting Monitors
Surround sound setup
TV-OUT connector
Connecting Two Monitors With VGA Connectors
One DVI Connector
VGA connector blue
Connecting a Television TV
Changing the Display Settings
For dual-monitor capable cards with two DVI connectors
Setting Up a Printer
Connecting a USB Printer
Printer Cable
Connecting to the Internet
Setting Up Your Internet Connection
Setting Up a Home and Office Network
Connecting to a Network Adapter
Transferring Information to a New Computer
Network Setup Wizard
Network adapter connector
Computer Network cable
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Playing CDs and DVDs
Playing a CD or DVD
DVD player includes the following basic buttons
Copying CDs and DVDs
Adjusting the Volume
Adjusting the Picture
How to Copy a CD or DVD
Using Blank CDs and DVDs
Helpful Tips
Media Type Read Write Rewritable
SmartMedia SMC MultiMediaCard MMC
Using a Media Card Reader Optional
XD-Picture Card Memory Stick MS/MS Pro
Ieee 1394 Optional
Power Management
Standby Mode
Overview
Power Schemes Tab
Hibernate Mode
Power Options Properties
Advanced Tab
Cleaning Your Computer
Cleaning the Computer, Keyboard, and Monitor
Hibernate Tab
Cleaning CDs and DVDs
Cleaning the Mouse
Cleaning the Floppy Drive
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Optimizing Performance
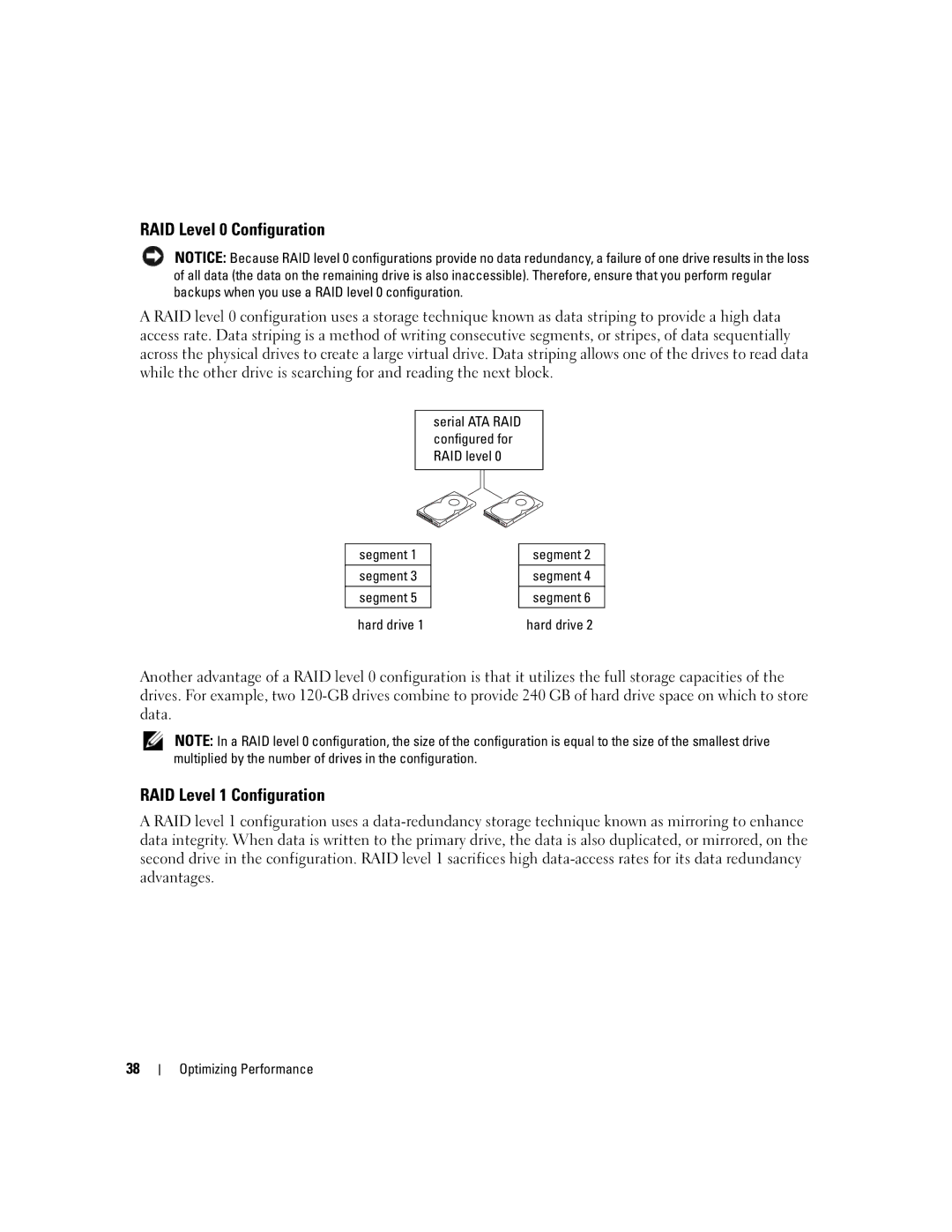
About Your RAID Configuration
Hyper-Threading
Segment Hard drive
RAID Level 0 Configuration
RAID Level 1 Configuration
Configuring Your Computer for RAID
Setting Your Computer to RAID-Enabled Mode
Using the Intel RAID Option ROM Utility
Creating a RAID Level 0 Configuration
Creating a RAID Level 1 Configuration
Deleting a RAID Volume
Using the Intel Application Accelerator
Creating a RAID Level 1 Configuration
Migrating to a RAID Level 0 Configuration
Migrating to a RAID Level 1 Configuration
Rebuilding a Degraded RAID Level 1 Configuration
Creating a Spare Hard Drive
Intel Viiv Technology Optional
Using Intel Viiv Quick Resume Technology QRT
Dell DataSafe Optional
Enabling the QRT Feature in System Setup
Enabling the QRT Feature in the Operating system
Optimizing Performance
Solving Problems
Troubleshooting Tips
Battery Problems
Drive Problems
CD and DVD drive problems
Problems writing to a CD/DVD-RW drive
Mail, Modem, and Internet Problems
Hard drive problems
Solving Problems
Error Messages
Use these characters in filenames
Media Card Reader Problems
Keyboard Problems
Computer stops responding
Lockups and Software Problems
Computer does not start up
Program stops responding
Solid blue screen appears
Other software problems
Program is designed for an earlier Windows operating system
Memory Problems
Mouse Problems
Network Problems
Power Problems
Printer Problems
Scanner Problems
Sound and Speaker Problems
No sound from speakers
Screen is blank
Video and Monitor Problems
No sound from headphones
Screen is difficult to read
Solving Problems
Troubleshooting Tools
Diagnostic Lights
Light Pattern Problem Description
If available, install properly working
Light Pattern Problem Description Suggested Resolution
Identified a faulty module or
If the problem persists, contact Dell
Installed. If the computer starts
For memory module/connector
Placement exist see Memory on
Memory on
Dell Diagnostics
Tab Function
Dell Diagnostics Main Menu
Option Function
Identifying Drivers
What Is a Driver?
Drivers
Windows XP
Manually Reinstalling Drivers
Reinstalling Drivers
Using Windows XP Device Driver Rollback
Restoring Your Operating System
Using Microsoft Windows XP System Restore
Resolving Software and Hardware Incompatibilities
Enabling System Restore
Creating a Restore Point
Undoing the Last System Restore
Restoring the Computer to an Earlier Operating State
Using Dell PC Restore by Symantec
Removing Dell PC Restore
Troubleshooting Tools
Recommended Tools
Removing and Installing Parts
Before You Begin
Turning Off Your Computer
Removing the Computer Cover
Before Working Inside Your Computer
Cover release latch Computer cover
CD or DVD drive Processor fan
Power supply System board Hard drive Card fan
Inside View of Your Computer
Processor
FlexBay USB connector Clear Cmos jumper
Battery socket Battery Sata Connectors SATA0
Front panel I/O connector Main power connector
System Board Components
Memory Overview
Connector
Memory
PCI Express x16 card
Installing Memory
Addressing Memory With 4-GB Configurations
Crossbar Removing and Installing Parts
Cutouts Memory module
Removing Memory
PCI Cards
Installing a PCI Card
Cards
Release tabs Filler bracket
Release tab
Fully seated card Not fully seated card
Alignment bar Alignment guide
Removing a PCI Card
PCI Express Cards
Filler bracket Alignment guide Alignment bar
Installing a PCI Express Card
Card retention door Release tabs
Release tab
PCI Express x16 card slot
PCI Express x1 card PCI Express x1 card slot
Fully seated card Not fully seated card
Release tab
Removing a PCI Express Card
Release tab
Removing and Installing Parts
100
Drive Panels
Removing the Drive Panel
Sliding plate Sliding plate lever
Drive panel Drive-panel insert tab
Removing the Drive-Panel Insert
101
Center drive-panel tab Drive panel
Replacing the Drive-Panel Insert
102
Drive-panel insert
103
Drives
Replacing the Drive Panel
104
General Installation Guidelines
Hard Drive
105
Power cable
Removing a Hard Drive
Tabs
Installing a Hard Drive
106
Adding a Second Hard Drive
107
108
109
Floppy Drive
Removing a Floppy Drive
Power cable Floppy drive cable Sliding plate lever
110
Floppy drive
Installing a Floppy Drive
111
112
Media Card Reader
Removing a Media Card Reader
Media Card Reader not
Present on all computers Removing and Installing Parts
113
114
Media Card Reader
Installing a Media Card Reader
115
Media Card Reader optional
CD/DVD Drive
116
117
CD/DVD drive cable Power cable
Removing a CD/DVD Drive
Sliding plate
Installing a CD/DVD Drive
118
CD/DVD drive
CD/DVD cable Power cable
119
120
Battery
Replacing the Battery
121
Battery Tab
Replacing the Computer Cover
122
Specifications
123
Expansion Bus
124
Audio
Drives
Connectors
125
126
127
System Setup
Entering System Setup
Environmental
System Setup Screens
128
System Setup Options
129
130
Video
131
Security
132
Boot Sequence
Option Settings
133
Changing Boot Sequence for the Current Boot
Changing Boot Sequence for Future Boots
Clearing Forgotten Passwords
134
Dell Technical Support Policy U.S. Only
Clearing Cmos Settings
Definition of Dell-Installed Software and Peripherals
135
FCC Class B
FCC Notice U.S. Only
Definition of Third-Party Software and Peripherals
136
Contacting Dell
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
Website support.ap.dell.com
152
Called from within Singapore or Malaysia only
153
154
155
Printers, and Projectors for Relationship
156
157
158
159
Glossary
160
161
162
163
164
NIC See network adapter
165
166
167
168
169
170
Index
Index 171
172 Index
Index 173
USB
174 Index