CHAPTER 2: ELECTRICAL BACKGROUND
In a
In modern digital meters, Blondell's Theorem is still applied to obtain proper metering. The difference in modern meters is that the digital meter measures each phase voltage and current and calculates the
Some digital meters calculate the individual phase power values one phase at a time. This means the meter samples the voltage and current on one phase and calculates a power value. Then it samples the second phase and calculates the power for the second phase. Finally, it samples the third phase and calculates that phase power. After sampling all three phases, the meter combines the three readings to create the equivalent
More advanced meters actually sample all three phases of voltage and current simultaneously and calculate the individual phase and
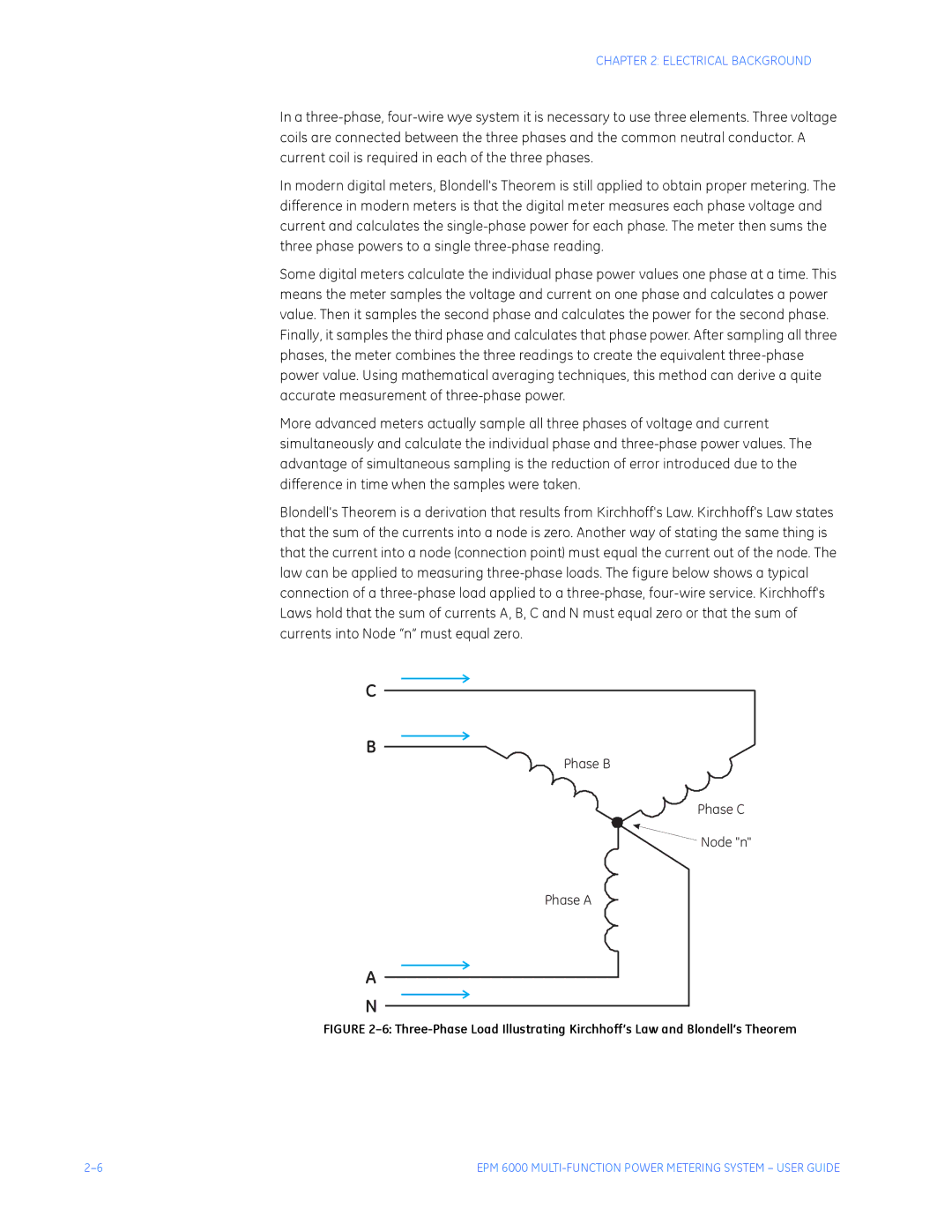
Blondell's Theorem is a derivation that results from Kirchhoff's Law. Kirchhoff's Law states that the sum of the currents into a node is zero. Another way of stating the same thing is that the current into a node (connection point) must equal the current out of the node. The law can be applied to measuring
C
B
Phase B
Phase C
 Node "n"
Node "n"
Phase A
A
N
FIGURE 2–6: Three-Phase Load Illustrating Kirchhoff’s Law and Blondell’s Theorem
EPM 6000 |