Hp procurve series 2500 switches
Page
Management and Configuration Guide
HP ProCurve Switches 2512
Publication Number
Preface
Use of This Guide and Other ProCurve Switch Documentation
Preface
Page
Contents
Tasks for Your First HP Web Browser Interface Session
Using a Standalone Web Browser in a PC or Unix Workstation
Globally Assigned IP Network Addresses
Viii
Chapter Contents Overview
Menu Viewing and Configuring IP Authorized Managers
Web Displaying and Configuring Port Security Features
Web Configuring IP Authorized Managers
Operating and Troubleshooting Notes
Rmon Support Extended Rmon
Advanced Management Rmon and HP Extended
Another Stack Monitoring Stack Status
Vlan Support and the Default Vlan
Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast Igmp
Igmp Operating Features
10-9
10-8
Using the Event Log To Identify Problem Sources
Daylight Savings Time on HP ProCurve Switches
Xvi
Selecting a Management Interface
Chapter Contents
Understanding Management Interfaces
Overview
Selecting a Management Interface
Selecting a Management Interface
Menu interface also provides access for
Advantages of Using the Menu Interface
Enables Telnet in-band access to the menu functionality
Advantages of Using the Menu Interface
HP2512config#
Advantages of Using the CLI
CLI Usage
HP2512
Advantages of Using the HP Web Browser Interface
Advantages of Using the HP Web Browser Interface
Advantages of Using HP TopTools for Hubs & Switches
Advantages of Using HP TopTools for Hubs & Switches
Interface
Selecting a Management Interface
Screen Structure and Navigation
Using the Menu Interface
Starting and Ending a Menu Session
Using the Menu Interface
Configure these features
Using
Menu Interface
Starting and Ending a Menu Session
Starting and Ending a Menu Session
Menu Interaction with Other Interfaces
Password
How To Start a Menu Interface Session
HP2512# menu Enter
Results
Main Menu with Manager Privileges
How To End a Menu Session and Exit from the Console
Using the Menu Interface
Main Menu Features
Main Menu Features
Using the Menu Interface
Screen Structure and Navigation
Screen Structure and Navigation
TaskActions
How To Navigate in the Menu Interface
Example Showing How To Display Help
Rebooting the Switch
Rebooting the Switch
Reboot Switch option
Indication of a Configuration Change Requiring a Reboot
Logout
Menu Features List
Menu Features List
Option Where To Turn
Where To Go From Here
Using the Menu Interface
Displaying Help for an Individual Command
Use Tab To Search for or Complete a Command Word
Conventions for Command Option Displays
CLI commands are not case-sensitive
Accessing the CLI
Using the CLI
Privilege Levels at Logon
Using the CLI
Operator Privileges
Location, such as a locked wiring closet
Privilege Level Operation
HP2512config# vlan HP2512vlan-10#
HP2512 Enable
Manager Privileges
Manager prompt
Enable
Setup
Privilege Level Hierarchy
Menu
Change in Levels Example of Prompt , Command, and Result
How To Move Between Levels
? at the Operator level produces this listing
Listing Commands and Command Options
Listing Commands Available at Any Privilege Level
Typing ? at the Manager level produces this listing
Example of the Manager-Level Command Listing
HP2512config# portTab HP2512config# port-security
Command Option Displays
Displaying CLI Help
Example of How To List the Options for a Specific Command
Interface CLI
Example of Context-Sensitive Command-List Help
HP2512# interface help Invalid input interface
Configuration Commands and the Context Configuration Modes
HP2512eth-5-8# ?
10. Context-Specific Commands Affecting Port Context
HP2512vlan-100# ?
HP2512config# vlan
HP2512vlan-100#
CLI Control and Editing
Tasks for Your First HP Web Browser Interface Session
Using the HP Web Browser Interface
HP Web Browser Interface
Agent Enabled parameter setting to No
Using Using the HP Web Browser Interface
General Features
General Features
PCs
Web Browser Interface Requirements
Platform Entity and OS Version Minimum Recommended
PCs
Enable Java and Enable JavaScript options
Using a Standalone Web Browser in a PC or Unix Workstation
Http
Using HP TopTools for Hubs & Switches
Example of Status Overview Screen
Window displayed for the selected device, as shown in figure
Tasks for Your First HP Web Browser Interface Session
Viewing the First Time Install Window
Tasks for Your First HP Web Browser Interface Session
HP Web Browser
Creating Usernames and Passwords in the Browser Interface
String
Device Passwords Window
If You Lose a Password
Using the Passwords
Using the User Names
Server URL on
Online Help for the HP Web Browser Interface
Support/Mgmt URLs Feature
Support/Mgmt URLs Feature
If Online Help Fails To Operate. Do one of the following
Support URL
Help and the Management Server URL
How To Access Web Browser Interface Online Help
Overview Window
Status Reporting Features
Status Reporting Features
Port Utilization
Port Utilization and Status Displays
10. Changing the Graph Area Scale
Port Status
12. The Port Status Indicators and Legend
Sorting the Alert Log Entries
Alert Log
Each alert has the following fields of information
Alert The specific event identification
Alert String Alert Description
Alert Types
Alert Strings and Descriptions
Console interface
Viewing Detail Views of Alert Log Entries
Color Switch Status
Status Indicator Key
Status Bar
Blue
16. The Fault Detection Window
Setting Fault Detection Policy
Using the HP Web Browser Interface
Using
Interface Access Console/Serial Link, Web
IP Addressing Access,
IP Configuration Features
IP Configuration
IP Configuration
Feature Default Menu
Remove it from the switch
HP2512# setup
Just Want a Quick Start?
IP Addressing with Multiple VLANs
IP Addressing in a Stacking Environment
Switch Configuration IP Configuration
To Configure IP Addressing
From the Main Menu, Select
Following screen
Show ip
IP Commands Used in This Section
Address Ip default-gateway Ip ttl No ip timep
Syntax show ip
HP2512config# ip ttl
How IP Addressing Affects Switch Operation
Web Configuring IP Addressing
Configure the Optional Timep Server
Click on the Configuration tab
Features Available Without an IP Address
DHCP/Bootp Operation
Network
Servers
Process immediately
Address received via Dhcp or Bootp
Reply
Is the IP address to be assigned to the switch or Vlan
J2512switch
Network Preparations for Configuring DHCP/Bootp
Company Name/Address
Globally Assigned IP Network Addresses
Country
Locked environment
Interface Access Features
Switch Configuration System Information
Menu Modifying the Interface Access
To Access the Interface Access Parameters
Interface Access Commands Used in This Section
CLI Modifying the Interface Access
To re-enable web browser access
To disable web browser access
Configuration will take effect
Two parameters
Configuring Interface
Example of Executing a Series of Console Commands
At last Power reset
System Information Features
System Information
System Information
On configuration options for these features
Menu Viewing and Configuring System Information
Press E for Edit. The cursor moves to the System Name field
Enter, then press S for Save and return to the Main Menu
System information settings
CLI Viewing and Configuring System Information
System Information Commands Used in This Section
HP2512config# mac-age-time
For example, to configure the age interval to seven minutes
For example, to set the switch to 345 p.m. on October 1
Web Configuring System Parameters
HP2512config# time 1545 10/01/00
Configure System Parameters in the Web Browser Interface
Configuring Interface
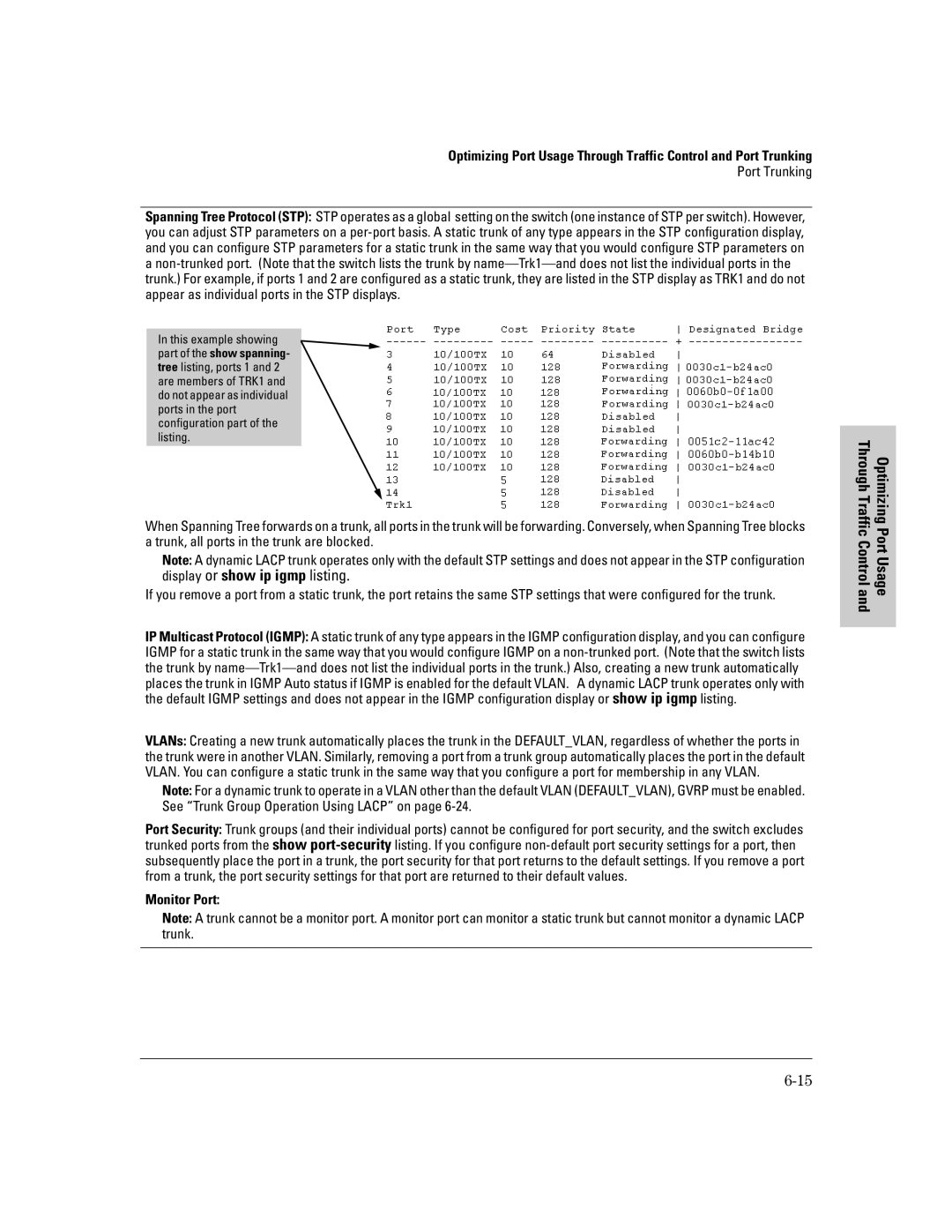
Port Trunking
Viewing port status Configuring ports 10/100TX
Viewing Port Status and Configuring Port Parameters
Port Status and ConfigurationFeatures
Status or Description Parameter
Status and Parameters for Each Port Type
Status or Description
Using the Menu To Configure Ports
Menu Viewing Port Status and Configuring Port Parameters
Trunking on
From the Main Menu, Select
Show interfaces Below Show interface config Interface
CLI Viewing Port Status and Configuring Port Parameters
Port Status and Configuration Commands
Example of a Show Interface Command Listing
Viewing Port Status and Configuring Port Parameters
Click on Port Configuration
Web Viewing Port Status and Configuring Port Parameters
Web browser interface Click on the Configuration tab
Port Trunking
Viewing port trunks Configuring a static trunk None Group
Port Trunking
Mbps Links
T e U t i o n C P N o t e
Switch 2512 and 2524 Port Trunk Features and Operation
HP2512config# Int e
Trunk Configuration Methods
Lacp passive
Trunk Types Used in Static and Dynamic Trunk Groups
See Trunk Group Operation Using Lacp on
Trunk Configuration Protocols
See Trunk Operation Using the FEC Option on
Protocol Trunking Options
General Operating Rules for Port Trunks
Monitor Port
Switch Configuration Port/Trunk Settings
CLI To Configure Ports on
Example of the Configuration for a Two-Port Trunk Group
Show trunks Below Show lacp Trunk Interface lacp
Using the CLI To View Port Trunks
Trunk Status and Configuration Commands
Example of a Show Trunk Listing Without Specifying Ports
Using the CLI To Configure a Static or Dynamic Trunk Group
Trunk Type Trunk Group Membership
You can configure trunk group types as follows
Trk1 Static Dyn1 Dynamic
Yes Trunk
HP2512config# interface 5-6 lacp active
HP2512config# interface 1 lacp passive
HP2512config# no interface 1 lacp
Web Viewing Existing Port Trunk Groups
Click on Port Status
Trunk group
Trunk Group Operation Using Lacp
Lacp trunk status include
Lacp Trunk Types
Particular switch, execute the following command in the CLI
Default Port Operation
HP2512 show lacp
Lacp Port Status Data
Lacp Notes and Restrictions
Disabled The port cannot carry traffic
Trunk Operation Using the FEC Option
Trunk Group Operation Using the Trunk Option
Outbound Traffic Distribution Across Trunked Links
How the Switch Lists Trunk Data
Node a Node W Node B Node C Node Y Node D Node Z
11. Example of Port-Trunked Network
Through Traffic Control Optimizing Port Usage
CLI Port Security Command Options and Operation
Chapter Contents
Using Passwords, Port
Overview
Level Actions Permitted
Using Password Security
Password Features Default Menu
Menu Setting Manager and Operator passwords
Continue Deletion of password protection? No
To set a new password
Password Commands Used in This Section
CLI Setting Manager and Operator Passwords
Password below
Syntax password manager operator no password
Click on the Security tab
Web Configuring User Names and Passwords
Click on Device Passwords
Configuring Port Security Disabled
Configuring and Monitoring Port Security
Basic Operation
Cast traffic
Blocking Unauthorized Traffic
Configuring and Monitoring Port Security
Trunk Group Exclusion
Planning Port Security
Configuring and Monitoring Port Security
Port Security Commands Used in This Section
CLI Port Security Command Options and Operation
Commands
Acquires and maintains authorized addresses
Ethernet port-list
Port Security Parameters
Clear-intrusion-flag
Address-limit integer
Mac-address mac-addr
Using the CLI To Display Port Security Settings
CLI Displaying Current Port Security Settings
CLI Configuring Port Security
Using Passwords, Port Security, and Authorized IP
HP2512config# port-security 1 mac-address 0c0090-456456
U t i o n T e
Click on Port Security
Web Displaying and Configuring Port Security Features
How the Intrusion Log Operates
Reading Intrusion Alerts and Resetting Alert Flags
Example of Multiple Intrusion Log Entries for the Same Port
Keeping the Intrusion Log Current by Resetting Alert Flags
Status and Counters Port Status
Type I Intrusion log to display the Intrusion Log
Configuring and Monitoring Port Security
Clear Intrusion flags on all ports
List Intrusion Log content
List Intrusion Alert status
Event Log lists port security intrusions as
Using the Event Log To Find Intrusion Alerts
Operating Notes for Port Security
Configuring and Monitoring Port Security
Authorized IP Manager Features
Using IP Authorized Managers
Defining Authorized Management Stations
Access Levels
Using IP Authorized Managers
Masks on
Overview of IP Mask Operation
From the console Main Menu, select
Menu Viewing and Configuring IP Authorized Managers
Switch Configuration IP Authorized Managers
Listing the Switch’s Current Authorized IP Managers
CLI Viewing and Configuring Authorized IP Managers
Authorized IP Managers Commands Used in This Section
IP Mask
HP2512config# ip authorized-managers
Configuring IP Authorized Managers for the Switch
Configuring One Station Per Authorized Manager IP Entry
Web Configuring IP Authorized Managers
Building IP Masks
Address of the authorized manager you want to delete
Manager IP
Analysis of IP Mask for Single-Station Entries
Authorized 227 125
Analysis of IP Mask for Multiple-Station Entries
Port IP
Additional Examples for Authorizing Multiple Stations
Operating and Troubleshooting Notes
Results
Authorized
Security, and Authorized IP Using Passwords, Port
Monitoring and Managing the Switch
Configuring for Network Management Applications
Monitoring Configuring for Network Management Applications
Managing Switch
Snmp Management Features
Snmp Management Features
Switch Configuration Snmp Community Names
Configuring for Snmp Access to Switch
Configuring for Snmp Access to the Switch
HP Entity MIB entity.mib
To Restricted
Write access for the public community to Restricted
Snmp Community Features
Snmp Communities
To View, Edit, or Add Snmp Communities
Snmp Add or Edit Screen
Snmp Communities Screen Default Values
Community Name Commands Used in This Section
CLI Viewing and Configuring Community Names
Listing Current Community Names and Values
Community community-str
HP2512# show snmp-server public
Configuring Identity Information
Configuring Community Names and Values
Trap Features
Trap Receivers and Authentication Traps
Regardless of the trap receiver configuration
Opotions are used with the snmp-server host command
Using the CLI To List Current Snmp Trap Receivers
CLI Configuring and Displaying Trap Receivers
Trap Receiver Commands Used in This Section
Syntax show snmp-server
Using the CLI To Enable Authentication Traps
Using the CLI To Enable Authentication Traps
Configuring Trap Receivers
Extended Rmon
Advanced Management Rmon and HP Extended Rmon Support
Monitoring
Advanced Management Rmon and HP Extended Rmon Support
Features
Using the CLI To View Stack Status and Configure Stacking
Configuring Advanced Features
Configuring Advanced Features
105
103
108
109
Overview
Configure stacking
Stacking Features Default Menu
HP ProCurve Stack Management
Reduce the number of IP addresses needed in your network
Which Devices Support Stacking?
HP ProCurve Switch 8000M
HP ProCurve Switch 4000M
Stacking Definitions
Components of HP ProCurve Stack Management
General Stacking Operation
Network Backbone
Operating Rules for Stacking
General Rules
Specific Rules
Stack Name N/A
IP Addr Optional
Overview of Configuring and Bringing Up a Stack
No Manager password Or fewer stack members at the moment
Stacking Configuration Guide
General Steps for Creating a Stack
Use of System Name to Help Identify Individual Switches
Configuring Advanced Features
Default Stacking Menu
Default Stack Configuration Screen
Using the Menu To Manage a Candidate Switch
Parameter Default Setting Other Settings Stack State
Candidate Configuration Options in the Menu Interface
Candidate Commander, Member, or Disabled
Seconds Range 1 to 300 seconds
Using the Commander To Manage The Stack
To add a Member, start at the Main Menu and select
Using the Commander’s Menu To Manually Add a Candidate to a
You will then see the Stack Management screen
Stacking Stack Management
10. Example of Candidate List in Stack Management Screen
Stacking Status All
Stacking
Member MAC Addresses
You will then see the Stacking Status All screen
Member listed
Commander
14. Example of Selecting a Member for Removal from the Stack
Stacking Stack Access
You will then see the Stack Access screen
Stacking Status All Features
From the Main Menu of the switch you want to move, select
Press Return
Stacking
Screen Name Commander Member Candidate
Stack Configuration
Monitoring Stack Status
Stack Status Environments
Stacking Stacking Status All
You will then see the Commander’s Stacking Status screen
Stacking Stacking Status This Switch
You will then see the Member’s Stacking Status screen
19. Example of the Commander’s Stacking Status Screen
You will then see the Candidate’s Stacking Status screen
Configuring Advanced
Interface
CLI Commands for Configuring Stacking on a Switch
Manager password
CLI Command Operation No stack member
Used In Commander Only
Commander’s CLI
Viewing the Status of Candidates the Commander Has Detected
Using the CLI To View Stack Status
Viewing the Status of the Commander and Current Members
Features Configuring Advanced
Using the CLI To Configure a Commander Switch
26. Example of the Commander’s Show Stack Screen with Only
Commander Discovered
Adding to a Stack or Moving Switches Between Stacks
28. Example of How To Determine Available Switch Numbers SNs
Using the Commander’s CLI To Manually Add a Candidate to
HP2512config# no stack auto-join
HP2512config# stack member 2 mac-address 0060b0-dfla00
HP 2512config# stack auto-join
Candidate
31. Example of Pushing a Candidate Into a Stack
Using the Destination Commander CLI To Pull a Member from
32. Example of Stack Listing with Two Stacks in the Subnet
HP2524config# stack member 1 mac-address 0060b0-df1a00
Access to the Commander
Using the CLI To Remove a Member from a Stack
Member
Or the Member
Using the Member’s CLI To Remove the Member from a Stack
HP2512config# no stack member 3 mac-address 0030c1-7fc700
HP2512config# telnet
North Seaconfig# no stack join 0030c1-7fec40
Commander Switch
Snmp Management Station Access to Members Via the Commander
Member Switch
Snmp Community Operation in a Stack
Snmpget MIB variable 10.31.29.100 blue@sw2
Using the CLI To Disable or Re-Enable Stacking
Transmission Interval
38. Example of the Web Browser Interface for a Commander
Web Viewing and Configuring Stacking
Message Condition Action or Remedy
Status Messages
Stacking screens and listings display these status messages
Disabled See Gvrp on VLANs
Vlan Features Default Menu
Port-Based Virtual LANs Static VLANs
Address would normally belong to the same Vlan
39. Example of Routing Between VLANs via an External Router
40. Example of Overlapping VLANs Using the Same Server
Which Vlan Is Primary?
Overview of Using VLANs
Vlan Support and the Default Vlan
Per-Port Static Vlan Configuration Options
Untagged
Tagged
Auto
Forbid
General Steps for Using VLANs
To Change Vlan Support Settings
Menu Configuring Vlan Parameters
Switch Configuration Vlan Menu Vlan Support
You will then see the following screen
To the Vlan Menu screen
Space bar to select from the existing options
Gvrp on
802.1Q Vlan ID Name
Switch Configuration Vlan Menu Vlan Names
Adding or Editing Vlan Names
Adding or Changing a Vlan Port Assignment
Switch Configuration Vlan Menu Vlan Port Assignment
Untagged, or Forbid
48. Example of Vlan Port Assignment Screen
49. Example of Vlan Assignments for Specific Ports
CLI Configuring Vlan Parameters
9-67 Available if Gvrp enabled
Vlan Commands Used in this Section
Static-vlan vlan-id 9-67 Available if Gvrp enabled
No tagged port-list No untagged port-list No forbid
51. Example of Show Vlan for a Specific Static Vlan
For example, to make Vlan 22 the primary Vlan
For example, to reconfigure the switch to allow 10 VLANs
HP2512config# primary-vlan
Creating a New Static Vlan Changing the Vlan Context Level
HP2512vlan-100# vlan defaultvlan
That static Vlan
For example, to create a new static Vlan with a VID
HP2512config# static-vlan
HP2512config# no vlan 100 tagged
Web Viewing and Configuring Vlan Parameters
At the Vlan 100 context level, use
HP2512vlan-100# no tagged
Vlan Tagging Information
Click on Vlan Configuration Click on Add/Remove VLANs
54. Example of Tagged and Untagged Vlan Port Assignments
For the Red VID in switch Y
Untagged Tagged
Switch Switch Y
Port Red Vlan Green Vlan
Spanning Tree Protocol Operation with VLANs
Effect of VLANs on Other Switch Features
IP Interfaces
To summarize
Port Monitoring
Vlan MAC Addresses
Port Trunks
IP Host-Only
Vlan Restrictions
Supported
Vlan to another Vlan
Symptoms of Duplicate MAC Addresses in Vlan Environments
On a GVRP-enabled switch
View Gvrp configuration
Vlan Advertising and Joining on
General Operation
Switch C Gvrp On
Switch D Gvrp On
Switch E Gvrp On
To allow tagged packets to pass through
Per-Port Options for Handling Gvrp Unknown VLANs
Mode
Options for Handling Unknown Vlan Advertisements
Per-Port Options for Dynamic Vlan Advertising Joining
Per-Port Static Vlan Options Gvrp Configuration
Controlling Vlan Behavior on Ports with Static VLANs
Tagged or Untagged2 Auto2 Forbid2
Port-Leave From a Dynamic Vlan
Gvrp and Vlan Access Control
Dynamically joining other VLANs
To generate advertisements
Planning for Gvrp Operation
Configuring Gvrp On a Switch
Menu Viewing and Configuring Gvrp
60. The Vlan Support Screen Default Configuration
Show gvrp Below Gvrp Unknown -vlans
CLI Viewing and Configuring Gvrp
Gvrp Commands Used in This Section
HP2512config# interface 1-2 unknown-vlans block
HP2512config# gvrp
HP2512config# no gvrp
VLAN-222 VLAN-33
64. Example of Listing Showing Dynamic VLANs
Gvrp Operating Notes
Web Viewing and Configuring Gvrp
HP2512config# static
Configuring Advanced
View igmp configuration
Igmp Features Default Menu
Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast Igmp
Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast Igmp
Address Information screen
Igmp Operating Features
IGMP. Refer to IP Configuration on
Indicating whether querier functionality is enabled
CLI Configuring and Displaying Igmp
Igmp Commands Used in This Section
How Igmp Operates on
VLANs on the switch
Igmp configuration for all
Igmp configuration for a
Including per-port data
HP2512vlan-1# ip igmp
HP2512config# vlan 1 ip igmp
HP2512config# no vlan 1 ip igmp
Configuring Per-Port Igmp Packet Control. Use this command
How Igmp Operates
Web Enabling or Disabling Igmp
Role of the Switch
67. The Advantage of Using Igmp
68. Isolating IP Multicast Traffic in a Network
Number of IP Multicast Addresses Allowed
Be flooded instead of filtered by the switch
Interaction with Multicast Traffic/Security Filters
Per Vlan in which it is used
Cast storm that can bring down the network
STP Features Default Menu
Spanning Tree Protocol STP
Switch Configuration Spanning Tree Operation
Menu Configuring STP
Actions line
69. Example of the STP Configuration Screen
Default
CLI Configuring STP
Default configuration, STP appears as shown here
STP Commands Used in This Section
10.General STP Operating Parameters
HP2512config# spanning tree
Default See -11, above
HP2512config# spanning tree maximum-age 30 hello-time
11.Per-Port STP Parameters
107
How STP Operates
Web Enabling or Disabling STP
71. Example of Redundant Paths Between Two Nodes
STP Fast Mode
HP2512config# spanning-tree ethernet 1-3,5 mode fast
To Configure Fast Mode for a Switch Port
STP Operation with 802.1Q VLANs
Ing network loops
72. Example of Using a Trunked Link with STP and VLANs
112
10-1
Switch Operation
Internet Group Management Protocol Igmp Status
Monitoring Switch Monitoring and Analyzing Switch Operation
Ing. See Diagnostic Tools on
Analyzing Operation
10-2
Status and Counters Data
Window under the Configuration tab
10-3
Interface Purpose
Status and Counters
Menu Access To Status and Counters
CLI Access
Menu Access
General System Information
10-5
10-6
Switch Management Address Information
Monitoring Switch
Status and Counters . . .3. Port Status Switch Operation
Web Access
Port Status
Menu Displaying Port Status
For all ports
Particular port or trunk Resetting counters
Viewing Port and Trunk Group Statistics
Status and Counters Port Counters
Menu Access to Port and Trunk Statistics
To access this screen from the Main Menu, select
Web Browser Access To View Port and Trunk Group Statistics
CLI Access To Port and Trunk Group Statistics
Mand provides traffic details for the port you specify
Click on Port Counters
10-11
Viewing the Switch’s MAC Address Tables
Status and Counters Address Table
Menu Access to the MAC Address Views and Searches
To page through the listing, use Next page and Prev
Enter MAC address
Listing MAC Addresses for a Specific Port
Example of Menu Indicating Located MAC Address
To Find the Port On Which the Switch Learned a Specific MAC
CLI Access for MAC Address Views and Searches
Status and Counters Spanning Tree Information
Menu Access to STP Data
Spanning Tree Protocol STP Information
10-16
CLI Access to STP Data
HP2512 show spanning-tree
10-17
Show Command Output
Vlan Information
Switch uses the CLI to display the following Vlan status
Ports
10-18
10-19
Listing the Vlan ID VID and Status for Specific Ports
Listing Individual Vlan Status
10-20
Web Browser Interface Status Information
10-21
Port Monitoring Features
Port Monitoring Features Default Menu
Switch Configuration Network Monitoring Port
Menu Configuring Port Monitoring
Monitoring and Analyzing
To monitor individual ports
To monitor all ports in a Vlan
Port Monitoring Commands Used in This Section
CLI Configuring Port Monitoring
HP2512config# no mirror-port
HP2512config# mirror-port
For example, to assign port 12 as the monitoring port
To turn off port monitoring
To enable port monitoring Click on the Configuration tab
Web Configuring Port Monitoring
Click on Monitor Port
Click on Apply Changes
11-1
Troubleshooting
Menu Entering and Navigating in the Event Log
Troubleshooting
11-3
Troubleshooting Approaches
Troubleshooting Approaches
Browser or Console Access Problems
Browser or Console Access Problems
Cannot access the web browser interface
11-5
Unusual Network Activity
General Problems
Ip Invalid ARP source IP address on IP address
11-6
11-7
IGMP-Related Problems
Stacking-Related Problems
Problems Related to Spanning-Tree Protocol STP
Timep or Gateway Problems
Switch Cannot Find the Timep Server or the Configured
11-9
VLAN-Related Problems
Within Same Outside Tagged Vlan
Tagged Monitor
11-10
08/05/98 105232 Ports Port 1 enabled
Using the Event Log To Identify Problem Sources
Date Time System Module
11-11
Event Log System Modules
Menu Entering and Navigating in the Event Log
From the Main Menu, select Event Log
11-12
HP2512 show logging -a system
Event Log Control Keys
Diagnostic Features
Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic Tools
Ping and Link Tests
11-15
Web Executing Ping or Link Tests
To halt a ping test before it concludes, press Ctrl C 11-16
CLI Ping or Link Tests
11-17
14.Example of Link Tests Troubleshooting
CLI Viewing the Configuration File
Displaying the Configuration File
Web Viewing the Configuration File
Click on Configuration Report
Displays the switch shutdown
Currently running on the switch
Displays the current command
Toggles the paging mode for
Clear/Reset Resetting to the Factory-Default Configuration
Restoring the Factory-Default Configuration
CLI Resetting to the Factory-Default Configuration
Appendix Contents
Downloading an Operating System OS
Model. See Transferring Switch Configurations on page A-10
Downloading an Operating System OS
Using Tftp To Download the OS File from a Server
Console Main Menu, select Download OS to display this screen
Menu Tftp Download from a Server
Validating and Writing System Software to Flash
CLI Tftp Download from a Server
Check the Firmware revision line
Menu Switch-to-Switch Download
Using the SNMP-Based Software Update Utility
Series 2500 Switch-to-Switch Download
CLI Switch-To-Switch Download
Using Xmodem to Download the OS File From a PC
Menu Xmodem Download
Syntax
HP2512 show system
CLI Xmodem Download from a PC or Unix Workstation
HP2512# show log tftp
Troubleshooting Tftp Downloads
Troubleshooting Tftp Downloads
Tftp Retrieving a Configuration from a Remote Host
Transferring Switch Configurations
Transfer Features Default Menu
Session in which the download was attempted
Tftp Copying a Configuration to a Remote Host
Syntax copy xmodem startup-config pc unix
MAC Address Management
Appendix B Contents
Determining MAC Addresses
MAC Address Viewing Methods Feature Default Menu
MAC Address Management
Determining MAC Addresses
Base switch default Vlan VID =
Menu Viewing the Switch’s MAC Addresses
Any additional VLANs configured on the switch
Configured on the Switch
HP2512# walkmib ifPhysAddress
CLI Viewing the Port and Vlan MAC Addresses
Switch Memory and Configuration
Switch Memory and Configuration
Startup-Config File
Overview of Configuration File Management
HP2512config# interface ethernet 5 disable
Any of the following actions reboots the switch
HP2512config# write memory
Overview of Configuration File Management
Using the CLI To Implement Configuration Changes
Using the CLI To Implement Configuration Changes
Syntax write memory
HP2512config# interface e 5 speed-duplex auto-10
With the factory-default startup configuration
Do you want to save current configuration y/n?
Changes on page C-9
Syntax erase startup-config
Changes
Memory in the CLI before rebooting the switch
Using Save and Cancel in the Menu Interface
Cancelled
73.The Reboot Switch Option in the Main Menu
Rebooting from the Menu Interface
Config file and the startup-config file
Using the Web Browser Interface To Implement
Configuration Changes
Daylight Savings Time on HP ProCurve Switches
2524 2400M 224M Switches 2424M
Alaska
Canada and Continental US
Middle Europe and Portugal
ProCurve Switches
Southern Hemisphere
Western Europe
Daylight Savings Time on HP ProCurve Switches
Page
Index
Index
See FEC
Garp
Lacp
See Igmp
See Vlan
See MIB
See also IP
VID
Xmodem OS download … A-7 XNS …