Toolkit User Configuration
All the user configuration variables are kept in a single file hahttp.conf in shell script format. The variable names and their sample values are listed in Table 26 (page 106):
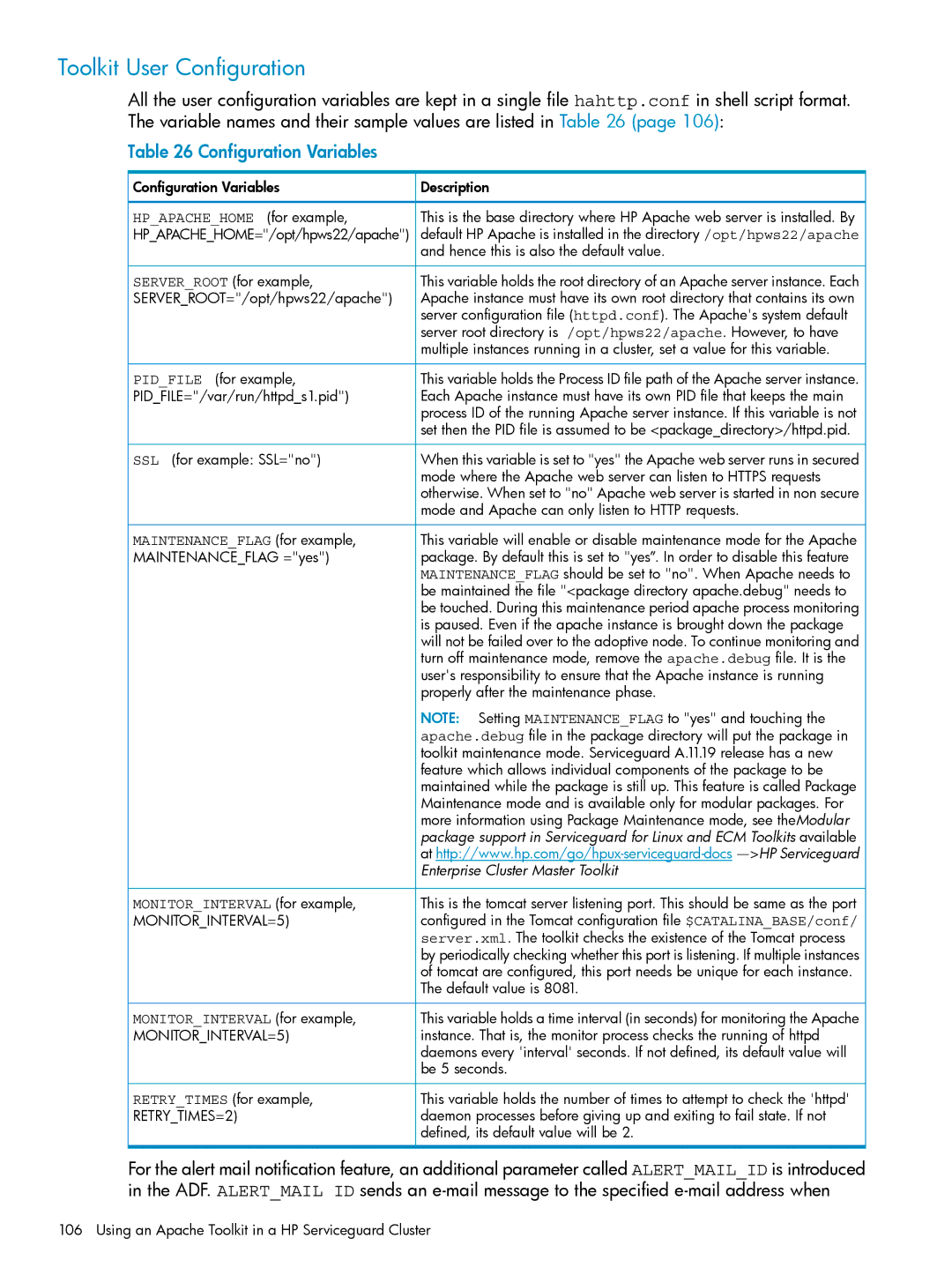
Table 26 Configuration Variables
Configuration Variables | Description |
HP_APACHE_HOME (for example, | This is the base directory where HP Apache web server is installed. By |
HP_APACHE_HOME="/opt/hpws22/apache") | default HP Apache is installed in the directory /opt/hpws22/apache |
| and hence this is also the default value. |
SERVER_ROOT (for example, | This variable holds the root directory of an Apache server instance. Each |
SERVER_ROOT="/opt/hpws22/apache") | Apache instance must have its own root directory that contains its own |
| server configuration file (httpd.conf). The Apache's system default |
| server root directory is /opt/hpws22/apache. However, to have |
| multiple instances running in a cluster, set a value for this variable. |
PID_FILE (for example, | This variable holds the Process ID file path of the Apache server instance. |
PID_FILE="/var/run/httpd_s1.pid") | Each Apache instance must have its own PID file that keeps the main |
| process ID of the running Apache server instance. If this variable is not |
| set then the PID file is assumed to be <package_directory>/httpd.pid. |
SSL (for example: SSL="no") | When this variable is set to "yes" the Apache web server runs in secured |
| mode where the Apache web server can listen to HTTPS requests |
| otherwise. When set to "no" Apache web server is started in non secure |
| mode and Apache can only listen to HTTP requests. |
MAINTENANCE_FLAG (for example, | This variable will enable or disable maintenance mode for the Apache |
MAINTENANCE_FLAG ="yes") | package. By default this is set to "yes”. In order to disable this feature |
| MAINTENANCE_FLAG should be set to "no". When Apache needs to |
| be maintained the file "<package directory apache.debug" needs to |
| be touched. During this maintenance period apache process monitoring |
| is paused. Even if the apache instance is brought down the package |
| will not be failed over to the adoptive node. To continue monitoring and |
| turn off maintenance mode, remove the apache.debug file. It is the |
| user's responsibility to ensure that the Apache instance is running |
| properly after the maintenance phase. |
| NOTE: Setting MAINTENANCE_FLAG to "yes" and touching the |
| apache.debug file in the package directory will put the package in |
| toolkit maintenance mode. Serviceguard A.11.19 release has a new |
| feature which allows individual components of the package to be |
| maintained while the package is still up. This feature is called Package |
| Maintenance mode and is available only for modular packages. For |
| more information using Package Maintenance mode, see theModular |
| package support in Serviceguard for Linux and ECM Toolkits available |
| at |
| Enterprise Cluster Master Toolkit |
MONITOR_INTERVAL (for example, | This is the tomcat server listening port. This should be same as the port |
MONITOR_INTERVAL=5) | configured in the Tomcat configuration file $CATALINA_BASE/conf/ |
| server.xml. The toolkit checks the existence of the Tomcat process |
| by periodically checking whether this port is listening. If multiple instances |
| of tomcat are configured, this port needs be unique for each instance. |
| The default value is 8081. |
MONITOR_INTERVAL (for example, | This variable holds a time interval (in seconds) for monitoring the Apache |
MONITOR_INTERVAL=5) | instance. That is, the monitor process checks the running of httpd |
| daemons every 'interval' seconds. If not defined, its default value will |
| be 5 seconds. |
RETRY_TIMES (for example, | This variable holds the number of times to attempt to check the 'httpd' |
RETRY_TIMES=2) | daemon processes before giving up and exiting to fail state. If not |
| defined, its default value will be 2. |
For the alert mail notification feature, an additional parameter called ALERT_MAIL_ID is introduced in the ADF. ALERT_MAIL ID sends an