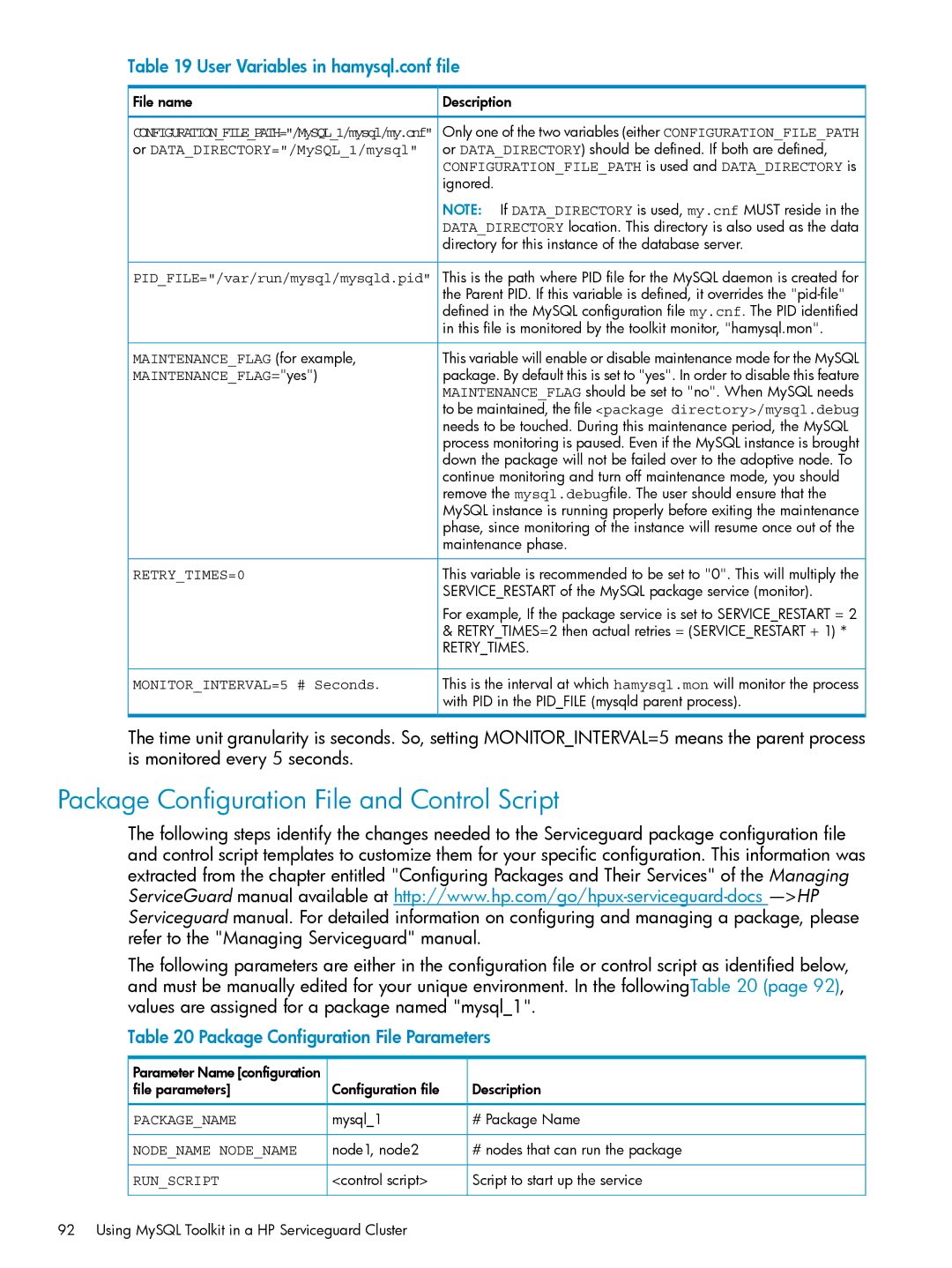
Table 19 User Variables in hamysql.conf file
File name | Description |
CONFIGURATION_FILE_PATH="/MySQL_1/mysql/my.cnf" | Only one of the two variables (either CONFIGURATION_FILE_PATH |
or DATA_DIRECTORY="/MySQL_1/mysql" | or DATA_DIRECTORY) should be defined. If both are defined, |
| CONFIGURATION_FILE_PATH is used and DATA_DIRECTORY is |
| ignored. |
| NOTE: If DATA_DIRECTORY is used, my.cnf MUST reside in the |
| DATA_DIRECTORY location. This directory is also used as the data |
| directory for this instance of the database server. |
PID_FILE="/var/run/mysql/mysqld.pid" | This is the path where PID file for the MySQL daemon is created for |
| the Parent PID. If this variable is defined, it overrides the |
| defined in the MySQL configuration file my.cnf. The PID identified |
| in this file is monitored by the toolkit monitor, "hamysql.mon". |
MAINTENANCE_FLAG (for example, | This variable will enable or disable maintenance mode for the MySQL |
MAINTENANCE_FLAG="yes") | package. By default this is set to "yes". In order to disable this feature |
| MAINTENANCE_FLAG should be set to "no". When MySQL needs |
| to be maintained, the file <package directory>/mysql.debug |
| needs to be touched. During this maintenance period, the MySQL |
| process monitoring is paused. Even if the MySQL instance is brought |
| down the package will not be failed over to the adoptive node. To |
| continue monitoring and turn off maintenance mode, you should |
| remove the mysql.debugfile. The user should ensure that the |
| MySQL instance is running properly before exiting the maintenance |
| phase, since monitoring of the instance will resume once out of the |
| maintenance phase. |
RETRY_TIMES=0 | This variable is recommended to be set to "0". This will multiply the |
| SERVICE_RESTART of the MySQL package service (monitor). |
| For example, If the package service is set to SERVICE_RESTART = 2 |
| & RETRY_TIMES=2 then actual retries = (SERVICE_RESTART + 1) * |
| RETRY_TIMES. |
MONITOR_INTERVAL=5 # Seconds. | This is the interval at which hamysql.mon will monitor the process |
| with PID in the PID_FILE (mysqld parent process). |
The time unit granularity is seconds. So, setting MONITOR_INTERVAL=5 means the parent process is monitored every 5 seconds.
Package Configuration File and Control Script
The following steps identify the changes needed to the Serviceguard package configuration file and control script templates to customize them for your specific configuration. This information was extracted from the chapter entitled "Configuring Packages and Their Services" of the Managing ServiceGuard manual available at
The following parameters are either in the configuration file or control script as identified below, and must be manually edited for your unique environment. In the followingTable 20 (page 92), values are assigned for a package named "mysql_1".
Table 20 Package Configuration File Parameters
Parameter Name [configuration |
|
|
file parameters] | Configuration file | Description |
PACKAGE_NAME | mysql_1 | # Package Name |
NODE_NAME NODE_NAME | node1, node2 | # nodes that can run the package |
RUN_SCRIPT | <control script> | Script to start up the service |