Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
THEORY OF OPERATION
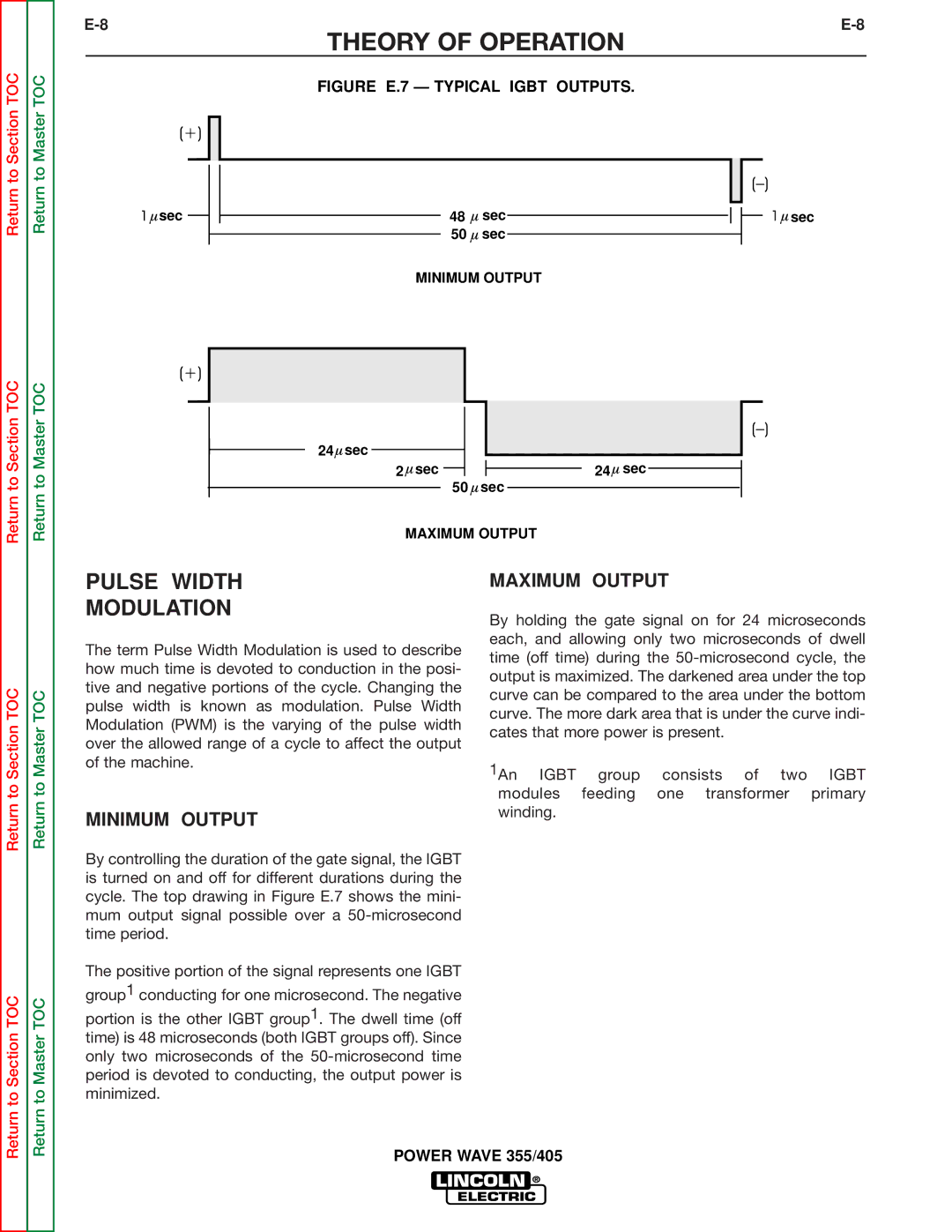
FIGURE E.7 — TYPICAL IGBT OUTPUTS.
|
|
|
|
|
|
sec |
|
|
| 48 | sec |
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 50 | sec |
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
MINIMUM OUTPUT
sec
Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
24 sec
2 sec |
|
|
| 24 sec |
|
|
50sec
MAXIMUM OUTPUT
Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
PULSE WIDTH
MODULATION
The term Pulse Width Modulation is used to describe how much time is devoted to conduction in the posi- tive and negative portions of the cycle. Changing the pulse width is known as modulation. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is the varying of the pulse width over the allowed range of a cycle to affect the output of the machine.
MINIMUM OUTPUT
MAXIMUM OUTPUT
By holding the gate signal on for 24 microseconds each, and allowing only two microseconds of dwell time (off time) during the
1An IGBT group consists of two IGBT modules feeding one transformer primary winding.
Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
By controlling the duration of the gate signal, the IGBT is turned on and off for different durations during the cycle. The top drawing in Figure E.7 shows the mini- mum output signal possible over a
The positive portion of the signal represents one IGBT group1 conducting for one microsecond. The negative
portion is the other IGBT group1. The dwell time (off time) is 48 microseconds (both IGBT groups off). Since only two microseconds of the