MECHANICAL INSTALLATION — HOTWELL COOLING
Hot Well Installation
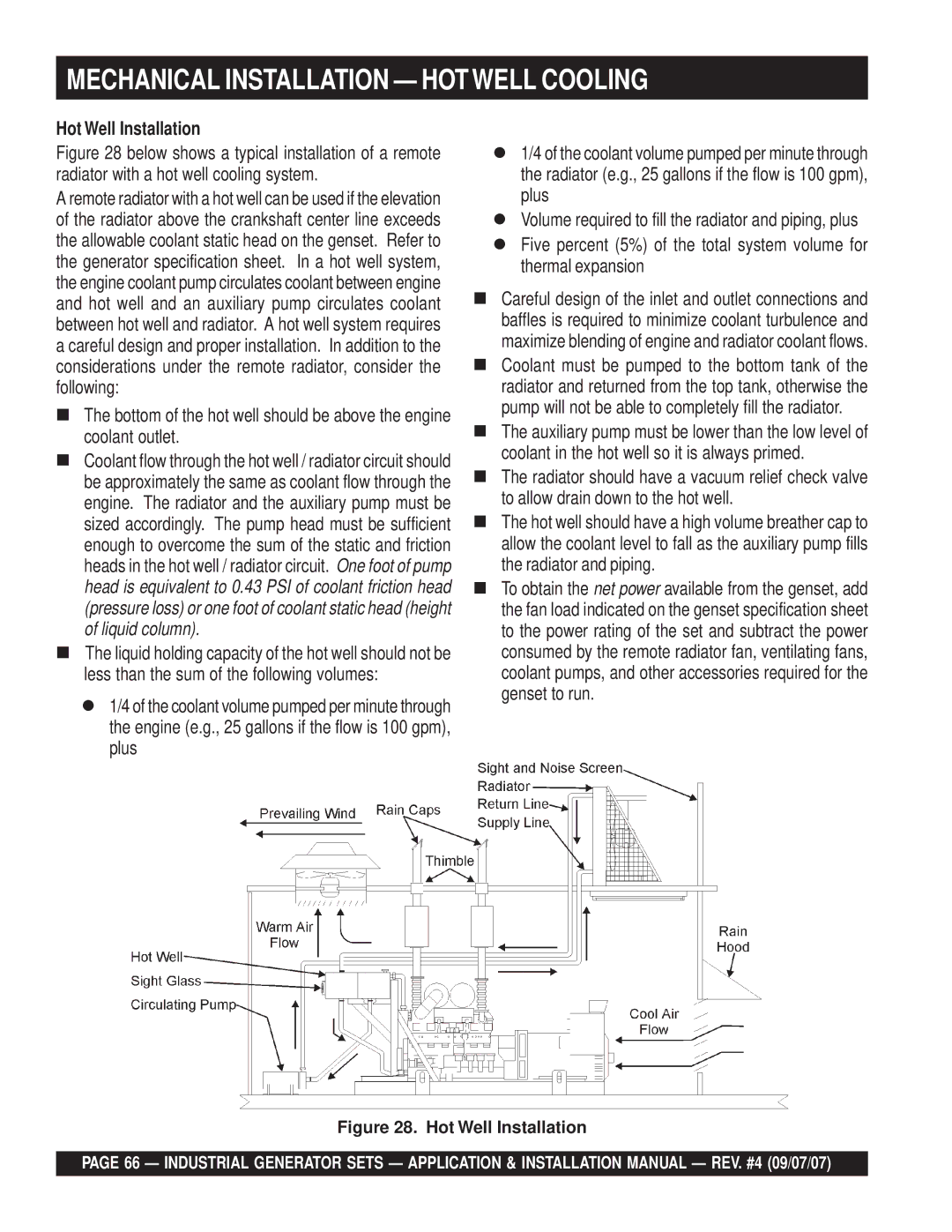
Figure 28 below shows a typical installation of a remote radiator with a hot well cooling system.
A remote radiator with a hot well can be used if the elevation of the radiator above the crankshaft center line exceeds the allowable coolant static head on the genset. Refer to the generator specification sheet. In a hot well system, the engine coolant pump circulates coolant between engine and hot well and an auxiliary pump circulates coolant between hot well and radiator. A hot well system requires a careful design and proper installation. In addition to the considerations under the remote radiator, consider the following:
The bottom of the hot well should be above the engine coolant outlet.
Coolant flow through the hot well / radiator circuit should be approximately the same as coolant flow through the engine. The radiator and the auxiliary pump must be sized accordingly. The pump head must be sufficient enough to overcome the sum of the static and friction heads in the hot well / radiator circuit. One foot of pump head is equivalent to 0.43 PSI of coolant friction head (pressure loss) or one foot of coolant static head (height of liquid column).
The liquid holding capacity of the hot well should not be less than the sum of the following volumes:
z1/4 of the coolant volume pumped per minute through the engine (e.g., 25 gallons if the flow is 100 gpm), plus
z1/4 of the coolant volume pumped per minute through the radiator (e.g., 25 gallons if the flow is 100 gpm), plus
zVolume required to fill the radiator and piping, plus
zFive percent (5%) of the total system volume for thermal expansion
Careful design of the inlet and outlet connections and baffles is required to minimize coolant turbulence and maximize blending of engine and radiator coolant flows.
Coolant must be pumped to the bottom tank of the radiator and returned from the top tank, otherwise the pump will not be able to completely fill the radiator.
The auxiliary pump must be lower than the low level of coolant in the hot well so it is always primed.
The radiator should have a vacuum relief check valve to allow drain down to the hot well.
The hot well should have a high volume breather cap to allow the coolant level to fall as the auxiliary pump fills the radiator and piping.
To obtain the net power available from the genset, add the fan load indicated on the genset specification sheet to the power rating of the set and subtract the power consumed by the remote radiator fan, ventilating fans, coolant pumps, and other accessories required for the genset to run.
Figure 28. Hot Well Installation
PAGE 66 — INDUSTRIAL GENERATOR SETS — APPLICATION & INSTALLATION MANUAL — REV. #4 (09/07/07)