3-5. Documents requiring use of document carrier
1)Documents smaller than B6 (128mm x 182mm).
2)Documents thinner than the thickness of 0.06mm.
3)Documents containing creases, folds, or curls, especially those whose surface is curled (maximum allowable curl is 5mm).
4)Documents containing tears.
5)
6)Documents containing an easily separable writing material (e.g., those written with a lead pencil).
7)Transparent documents.
8)Folded or glued documents.
Document in document carrier should be inserted manually into the feeder.
4. Document release
4-1. General
When the release lever is pulled by hand in the direction of arrow, the latch is released and the upper document guide moves on its axis in the derection of the arrow. The feed rollers, the separation rubber plate, and the pinch rollers become free to make it possible to remove the docu- ment.
4-2. Cross section view
Operation panel unit
Scanner frame unit
PWB case unit
Lower cabinet
Fig. 5
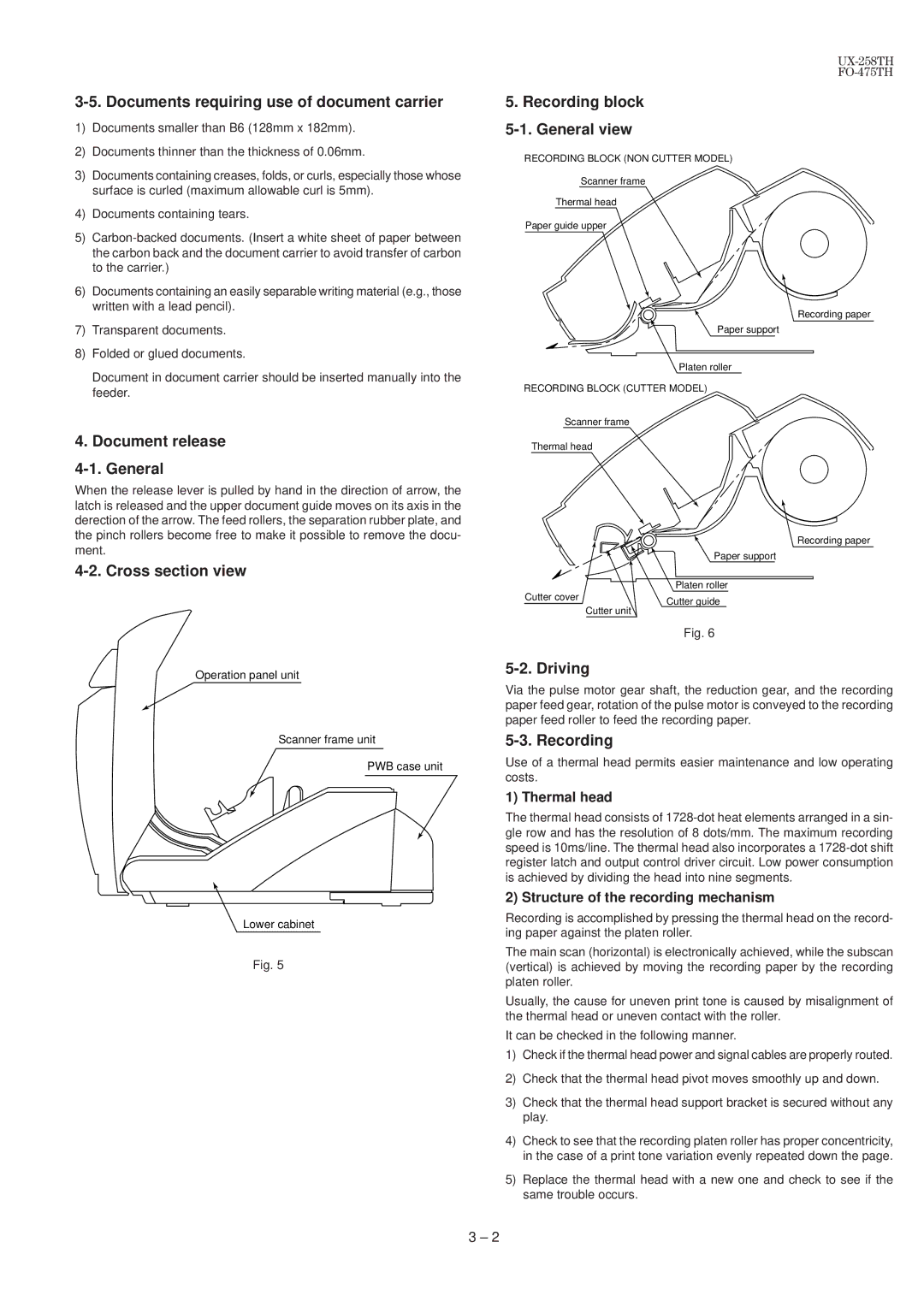
5.Recording block 5-1. General view
RECORDING BLOCK (NON CUTTER MODEL)
Scanner frame
Thermal head
Paper guide upper
Recording paper
Paper support
Platen roller
RECORDING BLOCK (CUTTER MODEL)
Scanner frame
Thermal head
Recording paper
Paper support
| Platen roller |
Cutter cover | Cutter guide |
| |
| Cutter unit |
Fig. 6
5-2. Driving
Via the pulse motor gear shaft, the reduction gear, and the recording paper feed gear, rotation of the pulse motor is conveyed to the recording paper feed roller to feed the recording paper.
5-3. Recording
Use of a thermal head permits easier maintenance and low operating costs.
1) Thermal head
The thermal head consists of
2) Structure of the recording mechanism
Recording is accomplished by pressing the thermal head on the record- ing paper against the platen roller.
The main scan (horizontal) is electronically achieved, while the subscan (vertical) is achieved by moving the recording paper by the recording platen roller.
Usually, the cause for uneven print tone is caused by misalignment of the thermal head or uneven contact with the roller.
It can be checked in the following manner.
1)Check if the thermal head power and signal cables are properly routed.
2)Check that the thermal head pivot moves smoothly up and down.
3)Check that the thermal head support bracket is secured without any play.
4)Check to see that the recording platen roller has proper concentricity, in the case of a print tone variation evenly repeated down the page.
5)Replace the thermal head with a new one and check to see if the same trouble occurs.
3 – 2