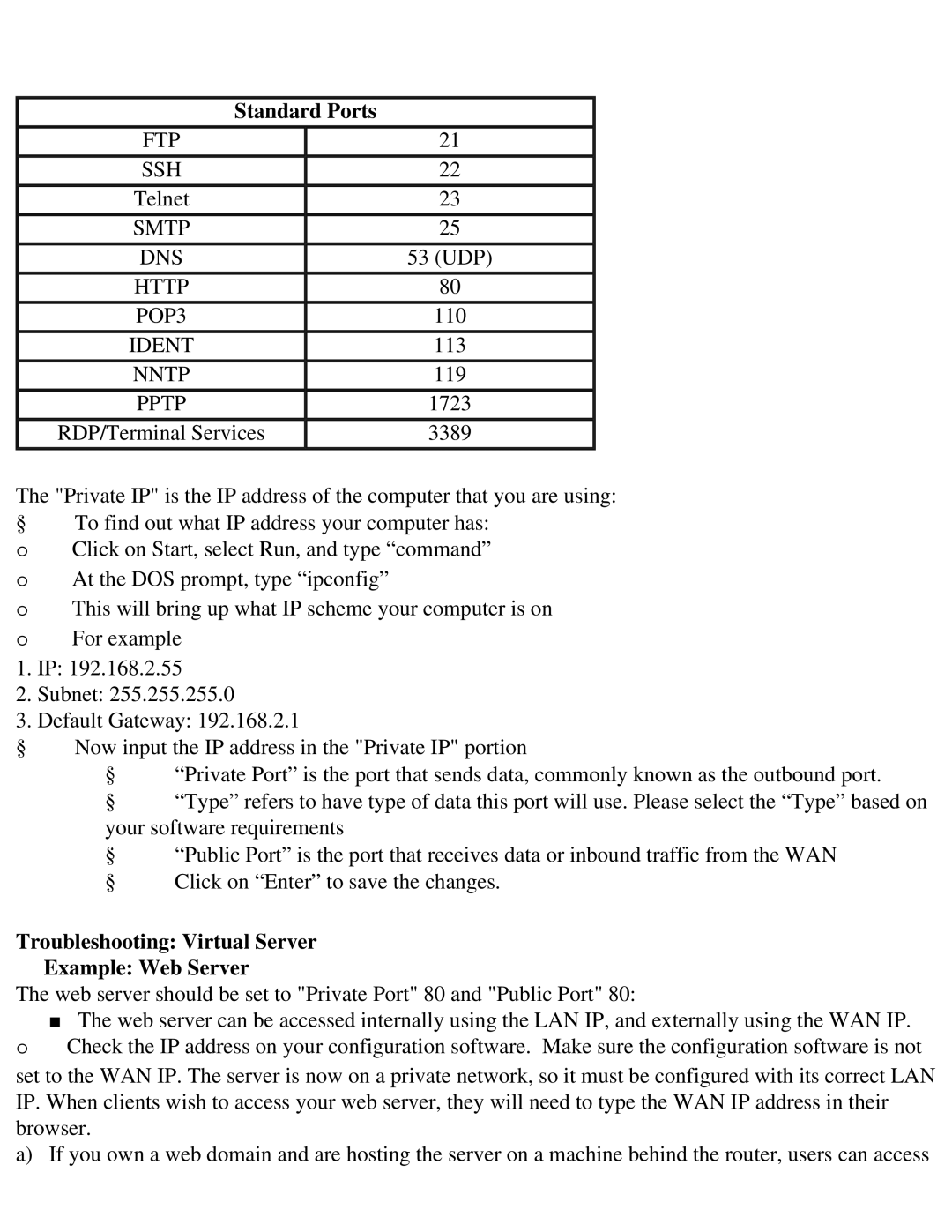
Standard Ports |
|
FTP | 21 |
SSH | 22 |
Telnet | 23 |
SMTP | 25 |
DNS | 53 (UDP) |
HTTP | 80 |
POP3 | 110 |
IDENT | 113 |
NNTP | 119 |
PPTP | 1723 |
RDP/Terminal Services | 3389 |
The "Private IP" is the IP address of the computer that you are using:
§To find out what IP address your computer has: o Click on Start, select Run, and type “command” o At the DOS prompt, type “ipconfig”
o This will bring up what IP scheme your computer is on o For example
1.IP: 192.168.2.55
2.Subnet: 255.255.255.0
3.Default Gateway: 192.168.2.1
§Now input the IP address in the "Private IP" portion
§“Private Port” is the port that sends data, commonly known as the outbound port.
§“Type” refers to have type of data this port will use. Please select the “Type” based on your software requirements
§“Public Port” is the port that receives data or inbound traffic from the WAN
§Click on “Enter” to save the changes.
Troubleshooting: Virtual Server
Example: Web Server
The web server should be set to "Private Port" 80 and "Public Port" 80:
■The web server can be accessed internally using the LAN IP, and externally using the WAN IP. o Check the IP address on your configuration software. Make sure the configuration software is not
set to the WAN IP. The server is now on a private network, so it must be configured with its correct LAN IP. When clients wish to access your web server, they will need to type the WAN IP address in their browser.
a) If you own a web domain and are hosting the server on a machine behind the router, users can access