When you disable a port, the application might not update some of the statistics counters associated with it.
An alarm calculates the difference in counter values over a set time interval and remembers the high and low values. When the value of a counter exceeds a preset threshold, the alarm reports this occurrence.
You can assign alarms with Transcend Enterprise Manager or any other SNMP network management application to monitor any counter, gauge, timetick, or integer. Consult the documentation for your management application for details on setting up alarms.
Setting Alarm Thresholds
Thresholds determine when an alarm reports that a counter has exceeded a certain value. You can set alarm thresholds through the network manually, and choose any value for them that is appropriate for your application. The network management software monitors the counters and thresholds continually during normal operations to provide data for later calibration.
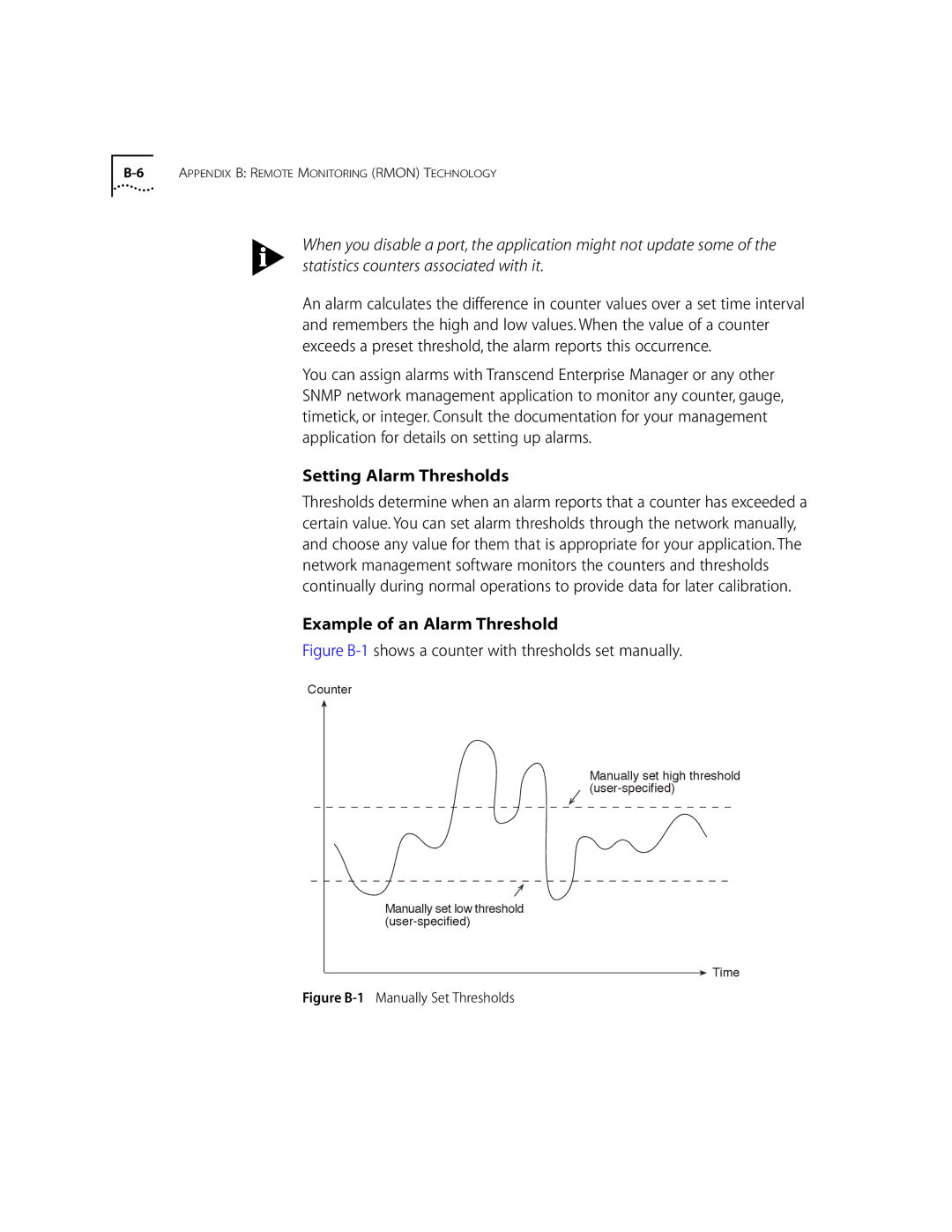
Example of an Alarm Threshold
Figure B-1 shows a counter with thresholds set manually.
Counter
Manually set high threshold
Manually set low threshold
![]() Time
Time