Agilent Technologies
Innovating the HPWay
Multifunction Synthesizer
Copyright@ HEWLETT-PACKARD Company
Regulatory Information
Safety Considerations
Safety Considerationsfor this Instrument
Product Markings
Contents
Service cont’d Section
Reu.200CT88
Replaceable Parts List
Introductionto this Section
Reference Designationsand Abbreviations Used in this Manual
Replaceable Parts List Updating Manual Updates
How to Order
Access
Nable 6-1.Reference Designations
Abbreviations 1
ALC
Abbreviations 2
Replaceable Parts
Rev.01JUL91
Description
Number Code
Fible 6-3.Replaceable Parts
HPPart Description Number Mfr- Mfr. Part Number Code
CAPACITOR-FXD22PF +-5% Poovdc CER 0+-30 Not Assigned
Reference HP Part Description
Designation Number
Reference HP Part Description Designation Number
Mfr
Me 6-3. Replaceable Parts
Rev.1 7MAY88
Reference HP Part Designation Number
DIODE-SWITCHING 80V 200MA 2NS DO45
Not Assigned Connector Spin M Post Type
CONNECTOR-RFSMC M PC 5 W H M
CONNECTOR-RF SMC M PC W H M
Reference
Mfr
Cable 6-3.Replaceable Parts
HP Part Description
RESISTOR-TRMR 1K 10% C TOP-ADJ 17-TRN
RESISTOR-TRMR20K 10% C TOP-ADJ 17-TRN
Mfr. Part Number
0698-3430
Rev.17MAY88
Description Mfr
Transistor Array 16-PIN Plstc DIP
IC OP AMP Prcn 8-DIP-C PKG
IC Instm Ampl CUR 10-DIP-P PKG
IC OP AMP LOW-BIAS-H-IMPD 8-DIP4 PKG
Nble 6-3. Replaceable Parts
HPPart Description
A10
L e 6-3. Replaceable Parts
Miscellaneous Parts
Ble 6-3.Replaceable Parts
HPPart
Reference HPPart Description Mfr
Designation Number Code
Deck Assy
Rnftsund Plstem DOME-HD .125DIA
RIVET-BUND PL-STEM DOME-HD .125DIA
RIVET-BUND Plstem Domehd .125DIA
PANEL, Front AY
Not Separaretlyreplaceable
Keypad Punched
Shield Display
Reference HPPart Designation Number
QW. Description
Qty.Description
Designation Code
Lbble 6-3. Replaceable Parts
Mfrm Mfr. Part Number Code
Order by Description
IZZ-9
Main Deck Assembly Top, 2923A and above
Model 8904A
Main Deck Assembly Bottom
Main Deck Assembly Bottom, Option 006 2948A and above
Reu.30NOV89
Front Panel Assembly, 2923A and above
Rent Panel Assembly, Option 006 2948A and above Reu.30NOV89
Rear Panel Assembly
Rear Panel Assembly, Option 005 2948A and above Rev.30N0
Covers, Labels, and ROMs
Rev.ZSSEP88
Output Cables 1
Output Cables, Option 005 29484 and above 2 Rev.30N0V89
Table of Contents
Option Conversions
Rev.15DEC89
Number 2942A and below
Instrument Modifications
Titled Hardware Modifications
Revision 22987A with HP 08904-8701 0 as A2U12
Modification Procedure
FRONT-TO-REAR-PANELOUTPUT Conversion Description
Parts Required
Tools Required
Fl Channel Config
Operation Verification
REAR-TO-FRONT-PANELOUTPUT Conversion
Description
Rev.15DEC89 Rear-to-Front-Panel Output Conversion
Fl Channel Config
Ront Panel Output Hardware
Output Cable Routing ALL Options
Firmware Updates A2U12 and A2U13
Rev.01JUL91 Firmware UpdatesBardware Modifications
Different function
Modification for Possible Ground Wire Shock Hazard
Serial Prefix 2737A and below
Parts Location Shown with Power Supply Removed
Firmware Updates/Hardware Modifications
Ground Wire Wrapping
Firmware Updates/Hardware Modifications
Parts List
Modification for Output Overvoltage Protection Improvement
HPPartNumber ~~ Qty Description
Fixed Resistor, 261 or
Modification for Potential Power Supply Short
Cabinet Parts Color Change
1. Modificationfor Front Panel Assembly
Reu.15DEC89 Firmware UpdatesIHardwareModifications
Removing the Front Panel
Installingthe Front Panel
Dont-Panel Assembly, 2923A and above
A3 or A10 Output Assembly Phase Synchronization Option
Section Service
Safety Considerations
Before Applying Power
HOW the Section is Organized
Iwarning
Service TOOLS, HELPS, and Information
Schematic Symbology and Schematic Diagram Notes
Schematic Diagram Notes 1
Pin of socket
Schematic Diagram Notes 2
Schematic Diagram Notes 3
Llzble 8-1.Schematic Diagram Notes 4
Digital Symbology Reference Information
Schematic Diagram Notes 5
Combinational Logic Symbols and Functions
Digital Symbology Reference Information
Schematic Diagram Notes 6
Schematic Diagram Notes 7
Only with D-type flip-flops Gate and Dependency-Binary
Llable 8-1.Schematic Diagram Notes 8of
Miscellaneous
Service
Schematic Diagram Notes 9
Schematic Diagram Notes 10
Active Levels
Schematic Diagram Notes 11
Enable
Principles of Operation Overall
What the Multifunction Synthesizer Can Do
How Waveforms Are Generated
Channel a
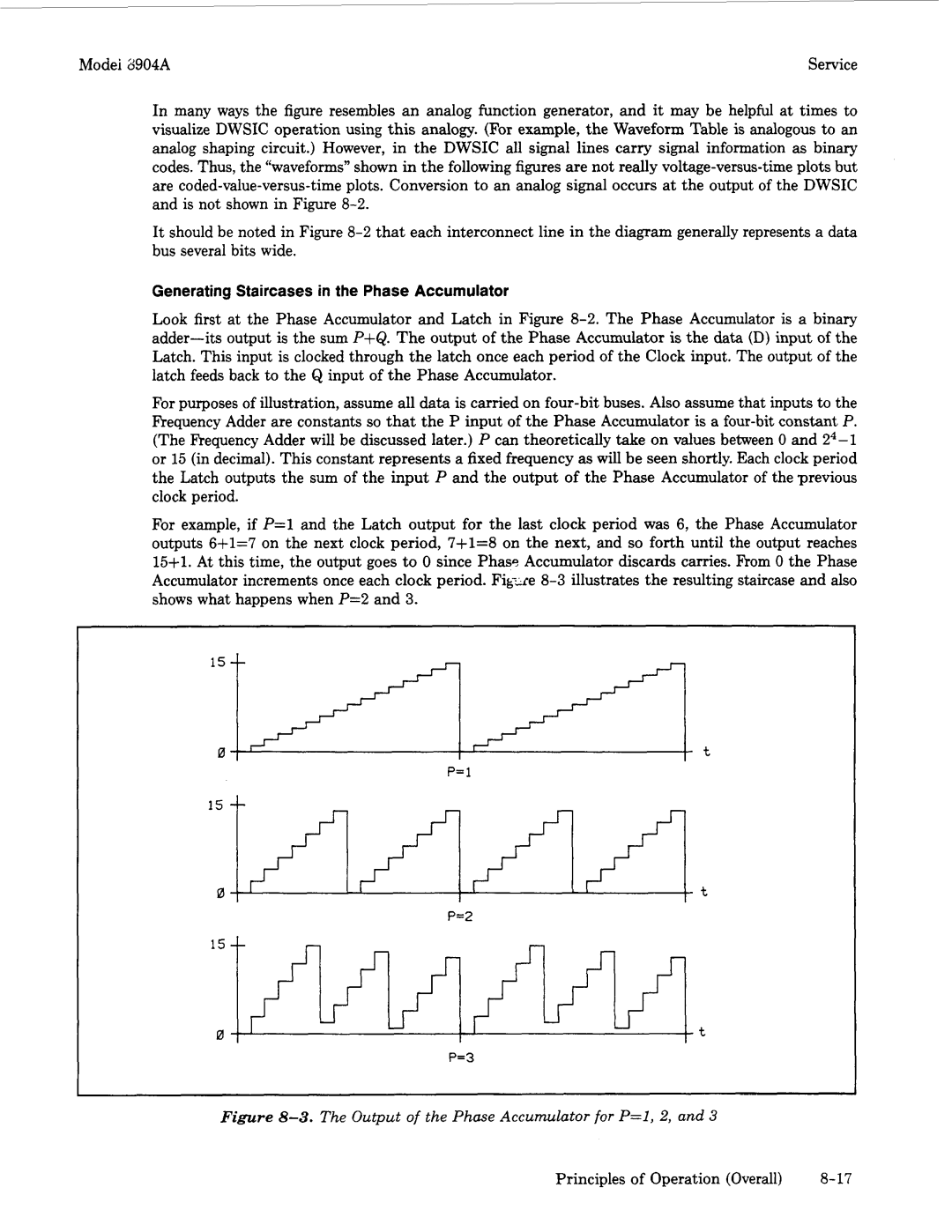
Generating Staircases in the Phase Accumulator
Output of the Phase Adder for P=O, 1,
Further Digital Waveform Processing with Options
Phase @PHASE Freouency
Pulse
Freouency SUM Pulse Level
Analog Waveform Processing
Interrelationshipof the Circuit Assemblies
Reu.15DEC89 Principles of Operation Overall
Synthesizer
PASSY- t
A2 Digital Assembly
General
A3 Output Assembly Service Sheets 1 through General
Digital-to-Analog Converter Service Sheet
Track-and-Hold Circuit Service Sheet
Simplified Diagram of the Sampler Drive
10.Simplified Diagram of the Sampler Amplifier
Low-Pass Filters Service Sheet
Audio Amplifier Service Sheet
Sine X/X CompensationService Sheet
12, and 24 dB Attenuators Service Sheet
Floating Amplifier Driver and On/Off Switch Service Sheet
Floating Output Amplifier Service Sheet
Overvoltage Protectionand Output Circuits Service Sheet
Troubleshooting General
Rev.15DEC89 Troubleshooting General
A2 Digital Assembly to A3 or A10 Output Assembly Interface
Procedure
Equipment
1. How to Access A3 in Instruments Equipped with Option
Troubleshooting Digital/Output Interface
Serial Prefix
Fl Channel Config
Period
Fl Channel Config
Pin Frequency Hz
Function A3 Key Sequence A10 Key Sequence
A3/A10 Connection
IC Pin Level
F3 Memory Map Access
Clocks A10
Pin
J1 and J5
Miscellaneous Control
A2 Digital Assembly to A1 Keyboard Assembly Interface
Fl Keyboard Check
AMPTD, Wave Form
Pin Key Pressed Response lTL
F3 Memory Map Access
Key Sequence Annunciator Status IC on A2 Pin Level lTL
A2 Digital Assembly to A5 Display Assembly Interface
Description
A3 or A10 Output Assembly
Phase Synchronizationoption
Troubleshooting Phase Synchronization
HP 8904A Opts
After keying in 8 7, the display should be
IFirmware Revision 18387A Serial No
IFirmware Revision 18387A Serial No
HP 8904A Opts 02/01
After keying in 4 8, the display should be
Begin again at step
HOW to Replace the Memory Backup Battery
Troubleshooting Memory Backup Battery 48.1
Tools and Supplies
Parts
Troubleshooting Memory Backup Battery
Rev.15DEC89 Troubleshooting Memory Backup Battery
48.3
Page
N a
12.4. Line Voltage Wiring Harness
A3 Component Coordinates 1
R300
Ipower Supply Conditioners
L0nA Current Source
A3 Component Coordinates 2
Comp
On the A3 schematic
Ss2
Rev.28MAR89
I813IldIll3 JJOlfl3 dWHS
31901 N3AILlO ONV
15.Service Sheet Information Component Locator
Changes
Rev.28MAR89 54.1
Aooitions I T I a L Instrument Settings
Ampto Instrument Settings Measure
Coup OUT
K2A
+ a
Component Coordinates 1
Ss4
56.1
Ss4
A6 Schematic and Component locator
Ss5
Output Assembly
0 A3/A10