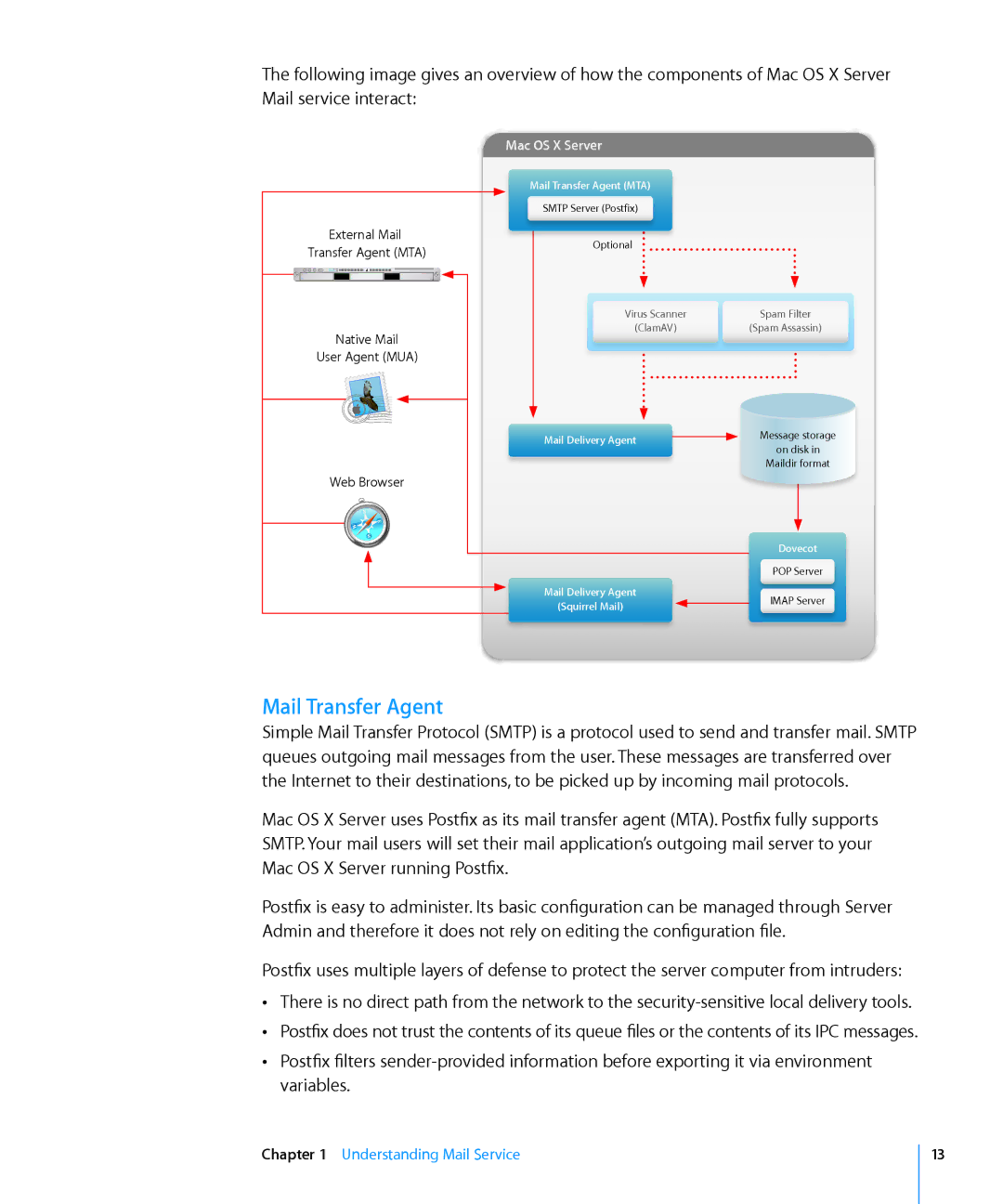
The following image gives an overview of how the components of Mac OS X Server Mail service interact:
Mac OS X Server
Mail Transfer Agent (MTA)
SMTP Server (Postfix)
External Mail
Transfer Agent (MTA)
Native Mail
User Agent (MUA)
Web Browser
Optional
Virus Scanner | Spam Filter |
(ClamAV) | (Spam Assassin) |
Mail Delivery Agent |
| Message storage |
| ||
| on disk in | |
|
| |
|
| Maildir format |
| Dovecot | |
| POP Server | |
Mail Delivery Agent | IMAP Server | |
(Squirrel Mail) | ||
|
Mail Transfer Agent
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is a protocol used to send and transfer mail. SMTP queues outgoing mail messages from the user. These messages are transferred over the Internet to their destinations, to be picked up by incoming mail protocols.
Mac OS X Server uses Postfix as its mail transfer agent (MTA). Postfix fully supports SMTP. Your mail users will set their mail application’s outgoing mail server to your Mac OS X Server running Postfix.
Postfix is easy to administer. Its basic configuration can be managed through Server Admin and therefore it does not rely on editing the configuration file.
Postfix uses multiple layers of defense to protect the server computer from intruders:
ÂÂ There is no direct path from the network to the
ÂÂ Postfix does not trust the contents of its queue files or the contents of its IPC messages.
ÂÂ Postfix filters
Chapter 1 Understanding Mail Service
13