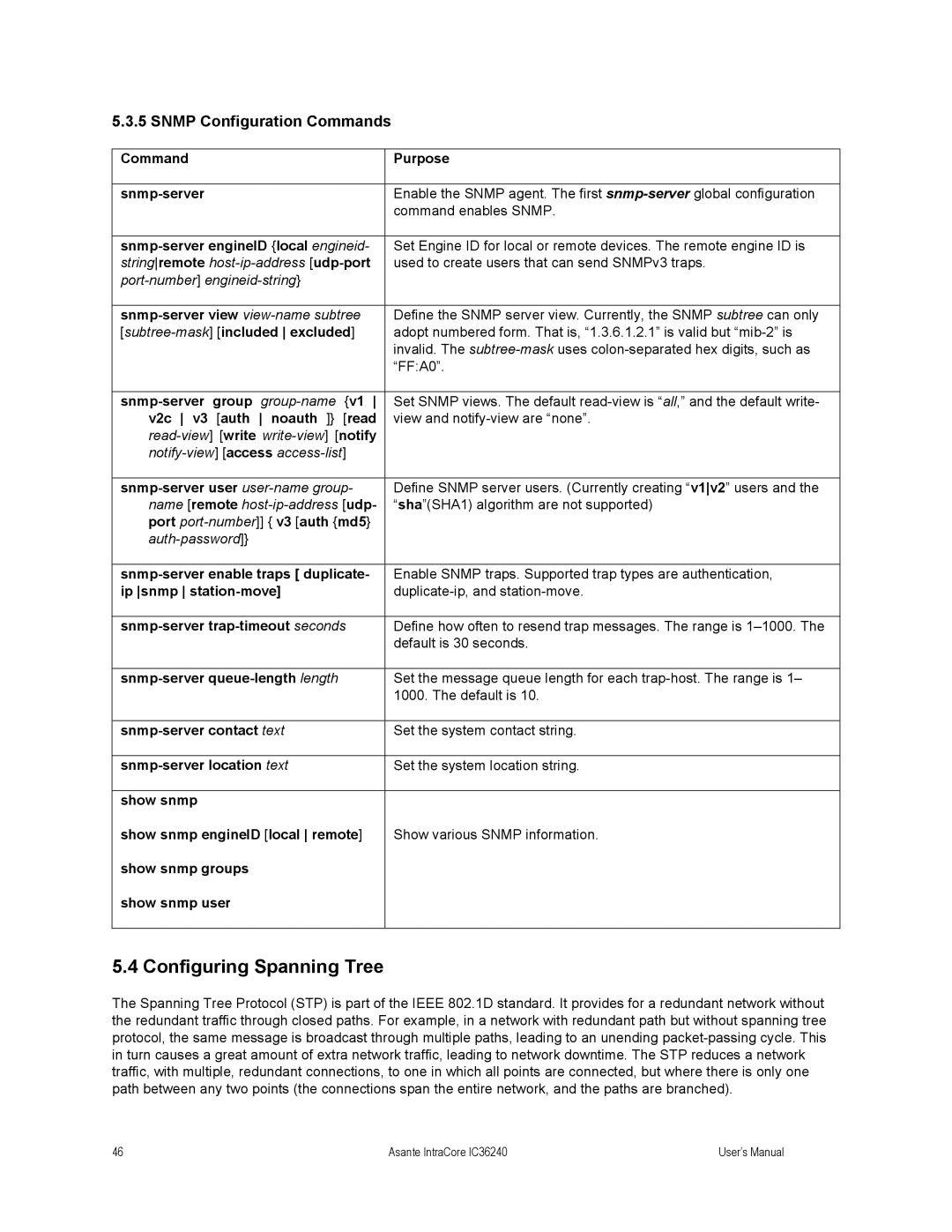
5.3.5 SNMP Configuration Commands
Command | Purpose |
|
|
Enable the SNMP agent. The first | |
| command enables SNMP. |
|
|
| Set Engine ID for local or remote devices. The remote engine ID is |
stringremote | used to create users that can send SNMPv3 traps. |
| |
|
|
Define the SNMP server view. Currently, the SNMP subtree can only | |
| adopt numbered form. That is, “1.3.6.1.2.1” is valid but |
| invalid. The |
| “FF:A0”. |
|
|
Set SNMP views. The default | |
v2c v3 [auth noauth ]} [read | view and |
| |
| |
|
|
| Define SNMP server users. (Currently creating “v1v2” users and the |
name [remote | “sha”(SHA1) algorithm are not supported) |
port |
|
| |
|
|
Enable SNMP traps. Supported trap types are authentication, | |
ip snmp | |
|
|
Define how often to resend trap messages. The range is | |
| default is 30 seconds. |
|
|
Set the message queue length for each | |
| 1000. The default is 10. |
|
|
Set the system contact string. | |
|
|
Set the system location string. | |
|
|
show snmp |
|
show snmp engineID [local remote] | Show various SNMP information. |
show snmp groups |
|
show snmp user |
|
|
|
5.4 Configuring Spanning Tree
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is part of the IEEE 802.1D standard. It provides for a redundant network without the redundant traffic through closed paths. For example, in a network with redundant path but without spanning tree protocol, the same message is broadcast through multiple paths, leading to an unending
46 | Asante IntraCore IC36240 | User’s Manual |