Wireless G Router
User Manual
8820np00425 F5D7234np4
Wireless G Router
Table of Contents
4 Connecting and Configuring your Router
6 Using the Web-Based Advanced User Interface
Advantages of a Wireless Network
Introduction
Benefits of a Home Network
2. Avoid Obstacles and Interference
Introduction
Important Factors for Placement and Setup
1. Wireless Router Placement
3. Cordless Phones
4. Choose the “Quietest” Channel for your Wireless Network
5. Secure Connections, VPNs, and AOL
Web-Based Advanced User Interface
Integrated 10/100 4-Port Switch
Works with Both PCs and Mac Computers
Patent-Pending Network Status Display
Integrated 802.11g Wireless Access Point
Product Overview
Built-In Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP
Setup Assistant Software
System Requirements
Package Contents
Setup Assistant Software System Requirements
Knowing your Router
A. Internet Status
Knowing your Router
C. Router/Power Status
D. Wired-Computer Status
E. Wireless-Computer Status
F. Wireless Security
G. Wi-Fi Protected Setup WPS button
b. Restoring the Factory Defaults
J. Power Jack
K. Reset Button
a. Resetting the Router
Modem Requirements
Connecting and Configuring your Router
Verify the contents of your box. You should have the following
Setup Assistant
Connecting and Configuring your Router
Setup CD
Plug the Router’s power supply into the Router and a power outlet
Select Country
Confirmation Screen
Progress
Screen
2.2 Verifying Hardware Connections
2.1 Checking Settings
2.3 Naming your Wireless Network
2.5 Configuring the Router
Congratulations
2.6 Checking Internet Connection
2.7 Optional Assistance Connecting Other Computers
Troubleshooting
Step 3 Set Up Wireless Security - Run the Security Assistant Software
3.1 Picking the Security Type
Progress Screen
3.3 Transferring the Key
3.2 Creating a Network Key
3.4 Verifying the Connection
If all your wireless computers are able to connect to the Router, click “Next”. If you are having trouble, select “I had problem with at least one computer” and click “Next”. Then, follow on-screen instructions
Alternate Setup Method
Alternate Setup Method
Logging out of the Router
Logging into the Router
Using the Web-Based Advanced User Interface
2. Home Button
3. Internet Status Indicator
4. Login/Logout Button
1. Quick-Navigation Links
10. Version Info
7. LAN Settings
8. Features
9. Internet WAN Settings
Setting your Connection Type
Change WAN MAC Address
ISP Gateway Address
IP Address
Provided by your ISP. Enter your IP address here
Subnet Mask
Your connection type is PPPoE if
Setting your ISP Connection Type to PPPoE
4. MTU
2. Password
3. Service Name
1. User Name
up properly.2
5. Get IP by DHCP
Provided by your ISP. Enter your PPTP gateway/service IP address here
c. Default Gateway
1. User ID
Setting Custom Domain Name Server DNS Settings
Configuring your WAN Media Access Controller MAC Address
Cloning your MAC Address
Entering a Specific MAC Address
You will see the Router’s home page in your browser window
Using the Web-Based Advanced User Interface
Using the Web-Based Advanced User Interface
Changing LAN Settings
Viewing the LAN Settings
5. Lease Time
1. IP Address
2. Subnet Mask
3. DHCP Server
Viewing the DHCP Client List Page
Configuring the Wireless Network Settings
Changing the Wireless Network Name SSID
SSID Broadcast Feature
Note This advanced feature should be employed by advanced users only
Using the Wireless Mode Switch
11b Only Mode
When to Use 11b Only Mode
Mixed 11b+11g Mode
11g Only Mode
Changing the Wireless Channel
Protected Mode Switch
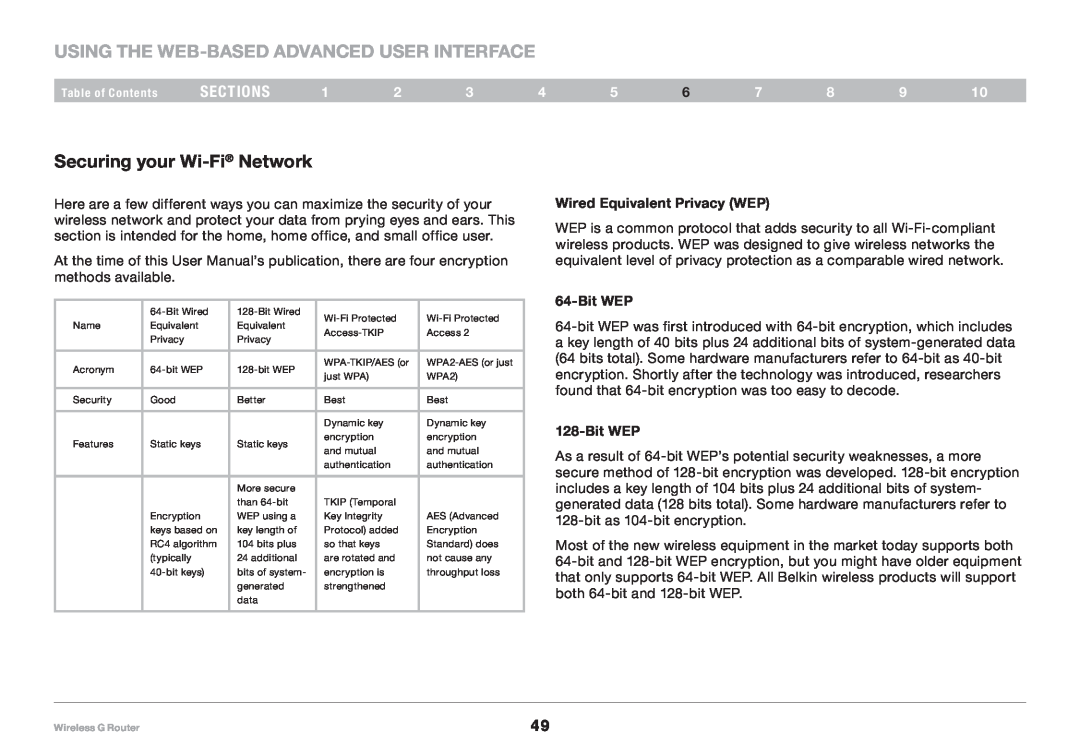
Wired Equivalent Privacy WEP
64-Bit WEP
128-Bit WEP
C3 03 0F AF 0F 4B B2 C3 D4 4B C3 D4 E7 = 128-bit WEP key
Wi-Fi Protected Access WPA
Encryption Keys
AF 0F 4B C3 D4 = 64-bit WEP key
C3 03 0F AF 0F 4B B2 C3 D4 4B C3 D4 E7 = 128-bit key
Using a Hexadecimal Key
Sharing the Same Network Keys
AF 0F 4B C3 D4 = 64-bit key
WEP Setup 64-Bit WEP Encryption
128-Bit WEP Encryption
Using Wi-Fi Protected Setup
Changing the Wireless Security Settings
WPA Setup
Guest Access Optional
Setting WPA/WPA2
Setting up Windows XP Wireless Network Utility to use WPA-PSK
7. Type in your encryption key in the “Network key” box
Using the Access Point Mode
Configuring the Firewall
Entering Settings into the Virtual Server
Configuring Internal Forwarding Settings
Setting Client IP Filters
7 8 9
Setting MAC Address Filtering
Enabling the Demilitarized Zone DMZ
Setting up the Router’s Dynamic DNS Update Client
Using Dynamic DNS
WAN Ping Blocking
Utilities Tab
Restarting the Router
Restoring Factory Default Settings
Saving a Current Configuration
Restoring a Previous Configuration
Updating the Firmware
Updating the Router’s Firmware
Searching for a New Version of Firmware
Changing System Settings
Changing the Login Time-Out Setting
Setting or Changing the Administrator Password
Enabling Remote Management
Setting the Time and Time Zone
Enabling/Disabling UPnP
Enabling/Disabling Auto Firmware Update
Your network adapters are now configured for use with the Router
Manually Configuring Network Settings
Manually Configuring Network Adapters in Windows 98SE or Me
Manually Configuring Network Settings
Manually Configuring Network Adapters in Mac OS up to
Select “Network” from the “System Preferences” menu
Manually Configuring Network Adapters in Mac OS
Click on the “System
Preferences” icon
6. If not already selected, select “Using DHCP” next to “Configure”
Internet Explorer 4.0 or Higher
Recommended Web Browser Settings
Netscape Navigator 4.0 or Higher
Recommended Web Browser Settings
Troubleshooting
Problem
Solution
Troubleshooting
Problem
Troubleshooting
Problem
Solution
Problem
Does the name of your wireless network appear in the results?
Problem
Limiting the Wireless Transmit Rate
How do I extend the range of my wireless network?
C3 03 0F AF 4B B2 C3 D4 4B C3 D4 E7 E4 = 128-bit key
For example C3030FAF4BB2C3D44BC3D4E7E4 = 128-bit key
Problem
Troubleshooting
Problem
Solution
sections
Troubleshooting
Problem
Solution
sections
Enabling WPA-PSK no server
Wireless Comparison Chart
Technical Support
Federal Communications Commission Notice
FCC Statement
F5D7234-4
Caution Exposure to Radio Frequency Radiation
Canada-Industry Canada IC
Information
Modifications
Europe-European Union Notice
What is not covered by this warranty?
What this warranty covers
What will we do to correct problems?
Product Warranty
How state law relates to the warranty
Manual del usuario
Enrutador Wireless G
6 Cómo usar la Interfaz de usuario avanzada basada en Internet
7 Cómo ajustar manualmente las configuraciones de la red
8 Configuraciones recomendadas para el navegador de la Web81
4 Conexión y configuración de su enrutador
Compartir una impresora con toda la familia
Factores importantes para la ubicación y configuración
1. Ubicación del enrutador inalámbrico
2. Evite los obstáculos y la interferencia
4. Elija el canal “más silencioso” para su red inalámbrica
3. Teléfonos inalámbricos
5. Conexiones seguras, VPNs y AOL
Compartido de NAT de direcciones IP
Funciona con computadoras PC y Mac
Pantalla de estatus de red con patente pendiente
Interfaz de usuario avanzada basada en Internet
Punto de acceso inalámbrico 802.11g integrado
Protocolo de configuración del host dinámico integrado DHCP
Soporte para el protocolo de paso VPN
Programa de Asistente de Instalación
Contenido del paquete
Requisitos del sistema
Requisitos para el sistema del programa de asistente de instalación
D. Estatus de la computadora alambrada
A. Estatus de Internet
B. Estatus de módem
C. Estatus del enrutador/encendido
G. Botón de Wi-Fi Protected Setup WPS
E. Estatus de la computadora inalámbrica
F. Seguridad inalámbrica
J. Entrada de corriente
b. Restauración de las configuraciones de fábrica
H. Conexión al módem - Amarillo
I. Conexiones a las computadoras - Gris
Verifique el contenido de su caja. Debe contener lo siguiente
Requisitos del módem
Asistente de instalación
1 Verifique que su línea de DSL o cable esté nchufada a su enrutador
sections
Seleccione el país
Pantalla de progreso
Pantalla de confirmación
2.2 Verificación de las conexiones del hardware
2.1 Verificación de las configuraciones
2.4 Solicitud de información de cuenta de Internet si fuera necesario
2.3 Nombramiento de su red inalámbrica
2.5 Cómo configurar su enrutador
Felicidades
2.6 Verificación de la conexión de Internet
2.7 Opcional Asistencia para conectar otras computadoras
Resolución de problemas
sections
3.1 Selección del tipo de seguridad
Pantalla de progreso
3.3 Transferencia de la clave
3.2 Cómo crear una clave de red
3.4 Cómo verificar la conexión
Si todas sus computadoras inalámbricas se pueden conectar al enrutador, pulse en Next Siguiente. Si está teniendo problemas, seleccione I had problem with at least one computer Tuve problemas con al menos una computadora y luego pulse Next Siguiente. Siga las instrucciones que se presentan en la pantalla
Ver la configuración y el estado actual del enrutador
DHCP
Salida del sistema del enrutador
Entrada al sistema del enrutador
Cómo usar la Interfaz de usuario avanzada basada en Internet
3. Indicador del estatus del Internet
4. Botón Login/Logout Entrada/Salida del sistema
1. Enlaces de navegación rápida
2. Botón Home Página principal
10. Version Info Información de versión
7. LAN Settings Configuraciones LAN
9. Internet WAN Settings Configuraciones WAN de Internet
8. Características
Cómo configurar su tipo de conexión
Cambio de la dirección MAC de WAN
1 2. Subnet Mask Máscara de subred
1. IP Address Dirección IP
El tipo de conexión que tiene es Poe si
5. Maximum Idle Time Tiempo máximo de inactividad
2. Password Contraseña
3. Service Name Nombre de servicio
1. User Name Nombre de usuario
sections
3. PPTP Gateway Puerta de enlace PPTP
1. User ID Identificación de usuario
5. Get IP by DHCP Obtener el IP por medio de DHCP
a. IP Address Dirección IP
Cómo configurar su tipo de conexión si es un usuario de BigPond/OptusNet de Telstra
Cómo ingresar una dirección MAC específica
Cómo copiar su dirección MAC
Con su navegador de Internet usted puede tener acceso a la interfaz avanzada de usuario basada en Internet del enrutador. En su navegador, ingrese “192.168.2.1” no escriba nada más como “http//” o “www” y luego oprima la tecla Intro
Para ver las configuraciones LAN
Cambio de las configuraciones LAN
5. Lease Time Tiempo de reserva
2. Subnet Mask Máscara de subred
3. DHCP Server Servidor DHCP
4. IP Pool Grupo de direcciones IP
Cómo ver la página de la lista de clientes DHCP
Ajuste de las configuraciones de la red inalámbrica
Cómo cambiar el nombre de la red inalámbrica SSID
Cómo usar el conmutador de modalidad inalámbrica
Función de difusión del SSID
Cuándo usar la modalidad 11b Only
Modalidad 11b+11g
Modalidad 11g-Only Únicamente 802.11 g
Modalidad 11b Only Únicamente 11b
Cómo cambiar el canal inalámbrico
Conmutador de modalidad protegida
Privacidad equivalente a la cableada WEP
WEP de 64 bits
WEP de 128 bits
C3 03 0F AF 0F 4B B2 C3 D4 4B C3 D4 E7 = Clave WEP de 128 bits
Claves de Encriptación
Para compartir las mismas claves de red
Cómo utilizar una clave hexadecimal
AF 0F 4B C3 D4 = Clave de 64 bits
Configuración WEP Encriptación WEP de 64 bits
Encriptación WEP de 128 bits
Uso de la Wi-Fi Protected Setup WPS
Cómo cambiar las configuraciones de seguridad inalámbrica
Configuración WPA
Acceso para huésped opcional
Cómo configurar WPA/WPA2
Cómo configurar la WPA para tarjetas inalámbricas de computadora de escritorio y de laptop que NO son fabricadas por Belkin
8. Pulse en “OK” Aceptar para aplicar los valores
Cómo usar la modalidad de punto de acceso
Cómo configurar el firewall
Cómo introducir las configuraciones en el servidor virtual
Cómo configurar las propiedades de reenvío interno
Cómo configurar filtros IP de cliente
Para configurar el Filtrado de direcciones MAC
Cómo habilitar la zona desmilitarizada DMZ
Uso de DNS dinámico
Bloqueo de WAN ping
Ficha Utilities Utilidades
Cómo reiniciar el enrutador
Cómo restablecer las configuraciones de fábrica
Para salvar una configuración existente
Para restablecer una configuración previa
Cómo actualizar el firmware
Cómo actualizar el firmware de su enrutador
Para buscar por una nueva versión de firmware
Cambio de configuraciones del sistema
Cómo cambiar la contraseña del administrador
Cómo habilitar la administración remota
Cómo configurar la hora y la zona horaria
Cómo habilitar/deshabilitar la actualización automática del firmware
Activación/Desactivación del UPnP
5. Si Use the following IP address Utilizar la siguiente dirección IP
Cómo configurar manualmente los adaptadores de red en Windows 98SE o Me
Cómo configurar manualmente los adaptadores de la red en Mac OS hasta
Cómo configurar manualmente los adaptadores de la red en Mac OS
5. Si Manually Manualmente esta seleccionado
Internet Explorer 4.0 ó superior
Netscape Navigator 4.0 o superior
Solución
Problema
El Asistente de instalación no puede encontrar mi enrutador
sections
Troubleshooting
Problema
Problema
sections
¿El nombre de su red inalámbrica aparece en los resultados?
sections
Cómo limitar la velocidad de transmisión inalámbrica
¿Cómo extiendo el rango de mi red inalámbrica?
C3 03 0F AF 4B B2 C3 D4 4B C3 D4 E7 E4 = clave de 128 bits
4. Bajo Data Encryption Encriptación de datos, seleccione WEP
sections
Troubleshooting
Problema
Problema
Solución
Troubleshooting
Problema
sections
Solución
Para habilitar la WPA-PSK sin servidor
3. Bajo la ficha Wireless Networks Redes inalámbricas, pulse
Tabla de comparación de tecnologías inalámbricas
Asistencia técnica
NOTA IMPORTANTE Declaración de exposición a la radiación de la FCC
Declaración de la FCC
Precaución Exposición a la radiación de la radiofrecuencia
Declaración de la Federal Communications Commission
Europa - Aviso de la Unión Europea
Modificaciones
Canadá- Industry Canada IC
NOTA IMPORTANTE Declaración de exposición a la radiación de la IC
¿Qué es lo que no está cubierto con esta garantía?
¿Qué haremos para corregir problemas? Garantía del producto
Qué cubre esta garantía
Cuál es el periodo de cobertura
Cómo se relaciona la ley estatal a la garantía
Belkin Tech Support