Page
Disclaimer
Trademark Information
Your Feedback
FCC Notice
Declaration of Conformity
Compex, Inc
Technical Support Information
About This Document
How to Use this Document
Firmware
Conventions
Chapter Hardware Installation
Chapter Further Configuration
Appendix Troubleshooting 118
Features and Benefits
Hardware Installation Product Overview
Introduction
Hardware Installation
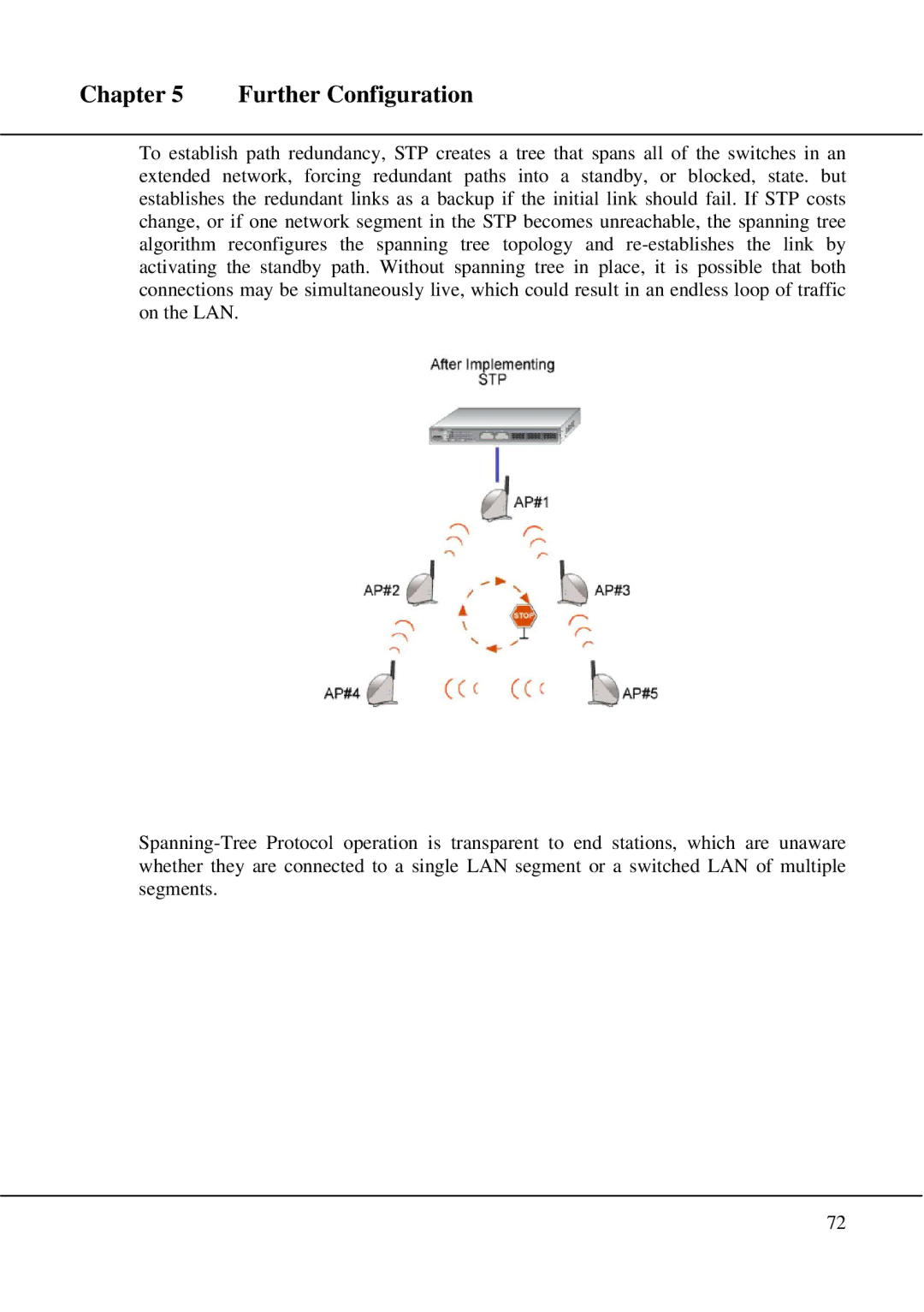
STP
When to use which mode
Access Point Mode
Access Point Client Mode
Static IP address
Gateway Mode
Dynamic IP address
Singapore Adsl Ethernet 512K
PPP over Ethernet PPPoE
Australia BPA Cable
Wireless Routing Client Mode
Wireless Bridge Link Mode
Wireless Ethernet Adapter Mode
Setup Requirements
Hardware Installation
Access to the Web interface with uConfig
Access to Web-based Interface
Through our Utility uConfig
Access to Web-based Interface
Access to Web-based Interface
Direct access to web-based interface via Internet Explorer
Access to Web-based Interface
Access to Web-based Interface
Access to Web-based Interface
Management Port Setup
Common Configuration
Management Port Wlan Basic Setup Wlan Security STP Setup
Setting up your LAN
Description
Parameters
Common Configuration
View Active Dhcp Leases
To view the active Dhcp leases
Go to the Advanced Dhcp Server
Reserve Specific IP addresses
Common Configuration
Delete Dhcp Server Reservation
Basic
Wlan Setup
Security
Advanced
Basic Setup Wireless Mode
To configure the Basic setup of the wireless mode
Common Configuration
Common Configuration
Advanced Setup Wireless Mode
To configure the Advanced setup of the wireless mode
Wlan Advanced Setup
AP/Gateway mode only
Common Configuration
Scan For Site Survey
Scan for Site Survey
Ssid
Show Link Information
Show Link Information
Link Information section
Link Information table illustrates the following data
Features Mode
Wireless Extended Features
Access Control The Wireless Pseudo Vlan
Wireless Pseudo Vlan Per Node
Wireless Pseudo Vlan Per Node
Wireless Pseudo Vlan Per Group
Wireless Pseudo Vlan Per Group
Common Configuration
Delete client from a group
Tag Vlan
Wireless Pseudo Vlan Tag Vlan
Common Configuration
Delete client from a Tag Vlan
Star Configuration WDS
Wireless Setup The Wireless Distributed System WDS
Chain Configuration WDS
WDS Configuration Setup
At the Edit WDS Link page which shows
Click on the Back button to return to the WDS Status
Common Configuration
WMM Parameters
WMM Parameters
WMM Parameters for advanced users
Long Distance Parameters
Long Distance Parameters available in all modes
CTS Timeout
ACK Timeout
Outdoor
Distance
Security Mode is set to
Selecting Security Mode
Wlan Security
Security Mode -WEP
How to set up WEP Available in ALL modes
When using 64-bit encryption
When using 128-bit encryption
How to set up WPA-PSK
Further Configuration
Security Mode -WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA-PSK-AUTO
At the Wlan Security Setup
Further Configuration
Radius Server, if any
Security Mode -802.1x/RADIUS
Security Mode WPA-EAP, WPA2-EAP, WPA-EAP-AUTO
How to set up WPA EAP
Further Configuration
STP Setup
Further Configuration
Further Configuration
Bandwidth STP Cost
Scenario #1 No STP, No Pseudo Vlan
Scenario #2 With STP, No Pseudo Vlan
Scenario #3 With STP and Pseudo Vlan
Forwarding Delay
Enabling STP Setup
Priority
Hello Time
MAC Filtering
Snmp Setup
Enabling Snmp
Enabling MAC Filtering
UConfig Set up
Setting up uConfig
Click on WAN Setup from the Configuration menu
Configuring WAN Setup
Changing WAN Type
At the Dynamic IP WAN Setup
Changing WAN Type Dynamic IP Configuration
Dynamic IP
At the Static IP WAN Setup
Changing WAN Type Static IP Configuration
Static IP
At the PPPoE WAN Setup
Changing WAN Type PPPoE Configuration
PPPoE
PPPoE Parameter Description
Chapter Further Configuration
At the Singapore Adsl WAN Setup
Changing WAN Type Singapore Adsl Configuration
Singapore Adsl
At the Australia BPA WAN Setup
At the Pptp WAN Setup
Changing WAN Type Pptp Configuration
Pptp
Enabling NAT
Setting up DMZ
To set up a De-Militarised Zone host
Disable DMZ
To set up port forwarding
Address field
Set up Port Forwarding For Known Server
Delete a table entry
Set up Port Forwarding For Custom Server
Application Port Number
Routing
Static Routing
Static Routing
Specify the Destination IP
Delete Static Routing
Dynamic Routing
By default, Dynamic Routing is disabled
Dynamic Routing
TCP Port
Source IP Address
Time frame
IP Filtering
Click on IP Filtering from the Configuration menu
At the Destination Port drop down list, select either
Further Configuration
Delete IP Filtering
Filtering Configuration table will then be refreshed
Remote Management
Remote Management feature
Port and the Telnet Port
Load balancing
Enabling Parallel Broadband Only available in Gateway mode
Fail-Over Redundancy
Enable Parallel Broadband
To enable Parallel Broadband
Click on Parallel Broadband from the Configuration menu
System Utilities
Using the System Tools Menu
System Tools menu
System Identity
Wlan Station List
Wlan Station List
Click on Wlan Station List from the System Tools menu
Set System’s Clock
Set System’s Clock
Click on Set System’s Clock from the System Tools menu
Time Zone for the system
Firmware Upgrade
Firmware Upgrade
Click on Firmware Upgrade from the System Tools menu
Upgrade Firmware path and file name field
Backup Your Settings
Save Your Settings
Restore Your Settings
Reset Your Settings to Factory Default
Reboot Your device
Reboot System
Click on Reboot System from the System Tools menu
Changing your Password
Change Password
Logout
Get Technical Support
Using the Help menu Get Technical Support
Click on Get Technical Support from the Help menu
About System
AI Solutions to Common Problems
Appendix I Troubleshooting
For Netscape 4.7 or later versions
Am not able to access the Web interface of the access point
My laptop is not able to access the AP
Want to set the access point to its factory default settings
Appendix I Troubleshooting
Diag LED
Operation State
AIII.1 Configure dynamic IP Address in Windows 98SE/ME
Appendix III TCP/IP Configuration
124
Appendix III TCP/IP Configuration
Appendix III TCP/IP Configuration
AIII.2 Configure dynamic IP Address in Windows XP/2000
Appendix III TCP/IP Configuration
AIII.3 Configure static IP Address in Windows 98SE/ME
AIII.4 Configure static IP Address in Windows XP/2000
Appendix Panel Views and Descriptions
Features Status and Indications
Appendix IV Panel Views and Descriptions
WPA1/2-PSK / WPA1/2-EAP
Appendix Technical Specifications
Snmp
CE R&TTE
Appendix V Technical Specifications
Manual Number 0428-V1.4C Version May Cxxxvi