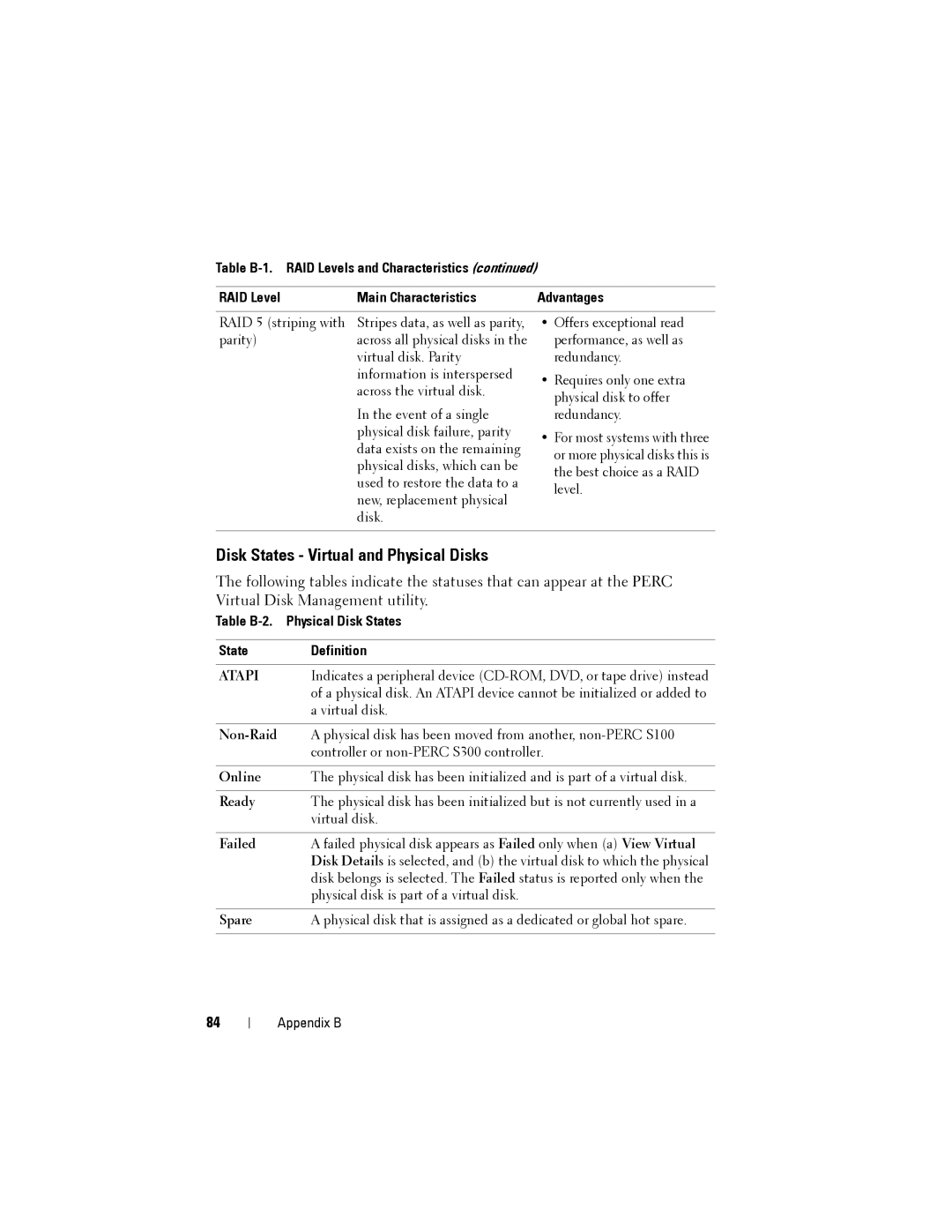
Table
RAID Level | Main Characteristics | Advantages |
RAID 5 (striping with | Stripes data, as well as parity, |
parity) | across all physical disks in the |
| virtual disk. Parity |
| information is interspersed |
| across the virtual disk. |
| In the event of a single |
| physical disk failure, parity |
| data exists on the remaining |
| physical disks, which can be |
| used to restore the data to a |
| new, replacement physical |
| disk. |
•Offers exceptional read performance, as well as redundancy.
•Requires only one extra physical disk to offer redundancy.
•For most systems with three or more physical disks this is the best choice as a RAID level.
Disk States - Virtual and Physical Disks
The following tables indicate the statuses that can appear at the PERC Virtual Disk Management utility.
Table B-2. Physical Disk States
State | Definition |
|
|
ATAPI | Indicates a peripheral device |
| of a physical disk. An ATAPI device cannot be initialized or added to |
| a virtual disk. |
|
|
| A physical disk has been moved from another, |
| controller or |
|
|
Online | The physical disk has been initialized and is part of a virtual disk. |
|
|
Ready | The physical disk has been initialized but is not currently used in a |
| virtual disk. |
|
|
Failed | A failed physical disk appears as Failed only when (a) View Virtual |
| Disk Details is selected, and (b) the virtual disk to which the physical |
| disk belongs is selected. The Failed status is reported only when the |
| physical disk is part of a virtual disk. |
|
|
Spare | A physical disk that is assigned as a dedicated or global hot spare. |
|
|
84