Appendix B: Troubleshooting
Check the following first:
zMake sure that the power of the Router is on and the Ethernet cables are connected firmly to the
zMake sure that the LED ALV of the Router is blinking to indicate the Router is working.
zMake sure the types of the Ethernet cables are correct. Recall that there are two
zMake sure that the DSL, cable, V.90, or ISDN modem connected with the Router is powered on.
B-1: TCP/IP Settings Problems
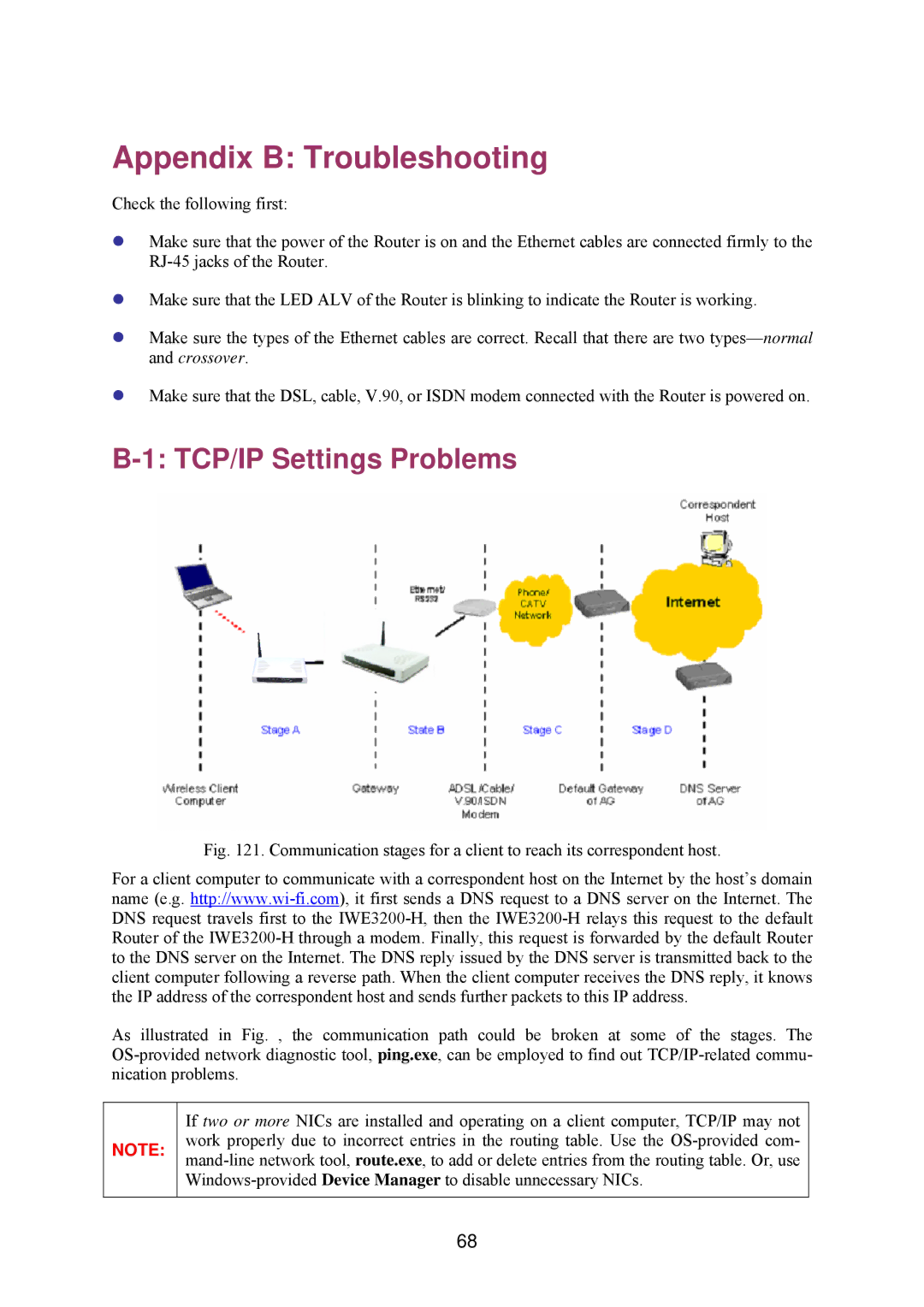
Fig. 121. Communication stages for a client to reach its correspondent host.
For a client computer to communicate with a correspondent host on the Internet by the host’s domain name (e.g.
As illustrated in Fig. , the communication path could be broken at some of the stages. The OS-provided network diagnostic tool, ping.exe, can be employed to find out TCP/IP-related commu- nication problems.
NOTE:
If two or more NICs are installed and operating on a client computer, TCP/IP may not work properly due to incorrect entries in the routing table. Use the OS-provided com- mand-line network tool, route.exe, to add or delete entries from the routing table. Or, use Windows-provided Device Manager to disable unnecessary NICs.
68