2.11.4.2. Basic
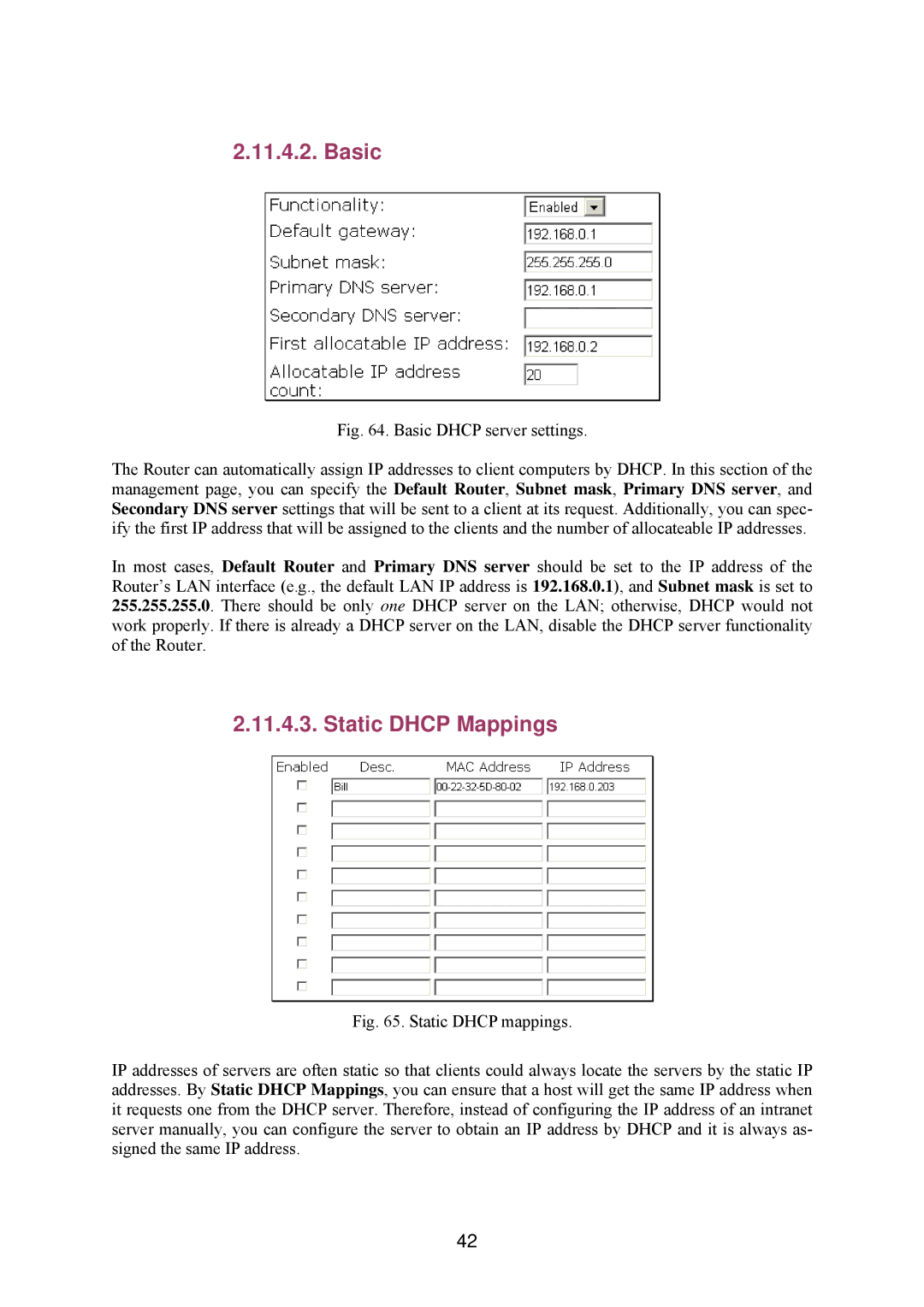
Fig. 64. Basic DHCP server settings.
The Router can automatically assign IP addresses to client computers by DHCP. In this section of the management page, you can specify the Default Router, Subnet mask, Primary DNS server, and Secondary DNS server settings that will be sent to a client at its request. Additionally, you can spec- ify the first IP address that will be assigned to the clients and the number of allocateable IP addresses.
In most cases, Default Router and Primary DNS server should be set to the IP address of the Router’s LAN interface (e.g., the default LAN IP address is 192.168.0.1), and Subnet mask is set to 255.255.255.0. There should be only one DHCP server on the LAN; otherwise, DHCP would not work properly. If there is already a DHCP server on the LAN, disable the DHCP server functionality of the Router.
2.11.4.3. Static DHCP Mappings
Fig. 65. Static DHCP mappings.
IP addresses of servers are often static so that clients could always locate the servers by the static IP addresses. By Static DHCP Mappings, you can ensure that a host will get the same IP address when it requests one from the DHCP server. Therefore, instead of configuring the IP address of an intranet server manually, you can configure the server to obtain an IP address by DHCP and it is always as- signed the same IP address.
42