CrosscuttingResawing
Crosscutting is the process of cutting across the grain of wood. For plywood and other processed wood, crosscutting simply means cutting across the width of the material.
To make a 90˚ crosscut:
1.Mark the workpiece on the edge where you want to begin the cut.
2.Adjust the blade guide assembly to the cor- rect height and make sure the miter gauge is set to 0° (or other angle for angled cuts).
3.Move the fence out of the way. Place the workpiece evenly against the miter gauge, then line up the mark with the blade.
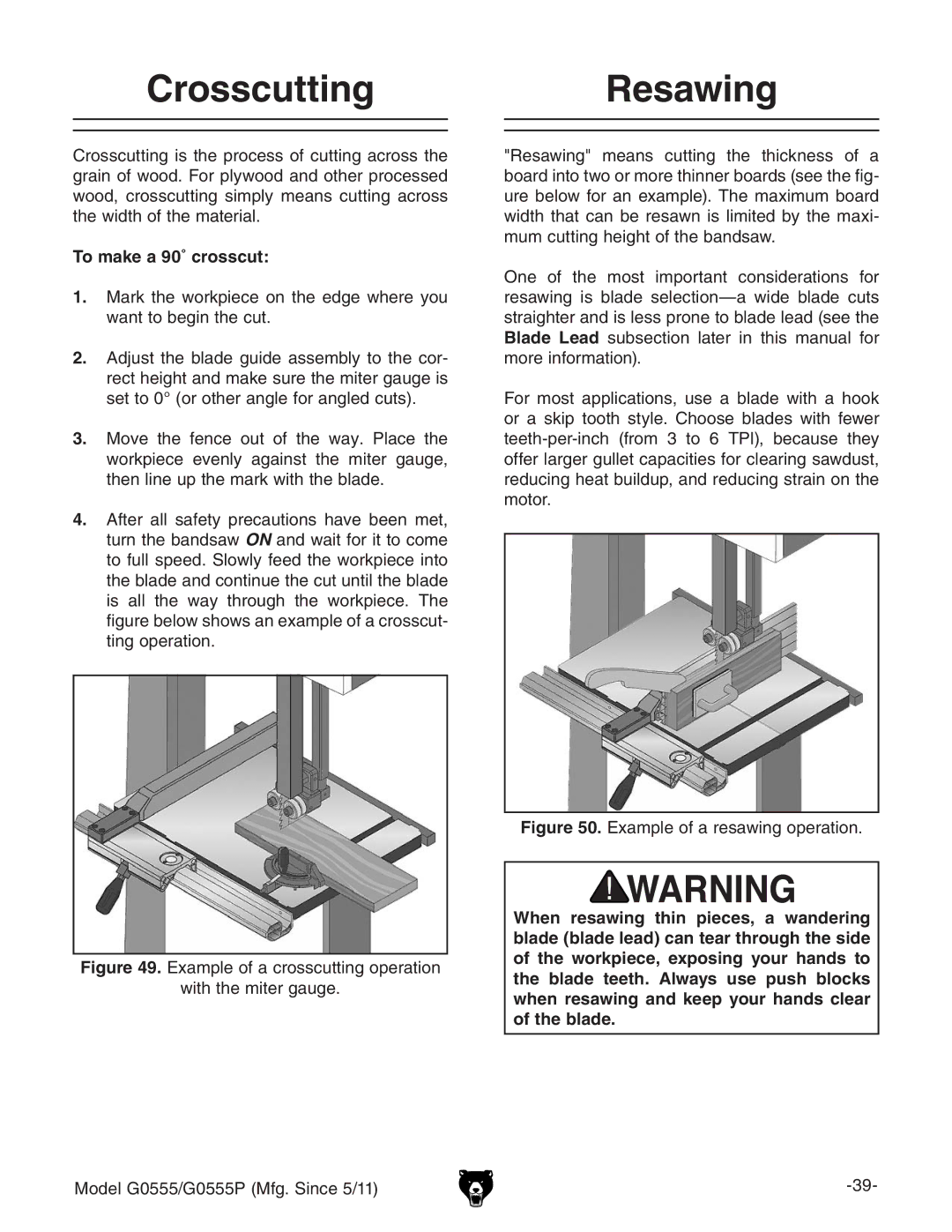
4.After all safety precautions have been met, turn the bandsaw ON and wait for it to come to full speed. Slowly feed the workpiece into the blade and continue the cut until the blade is all the way through the workpiece. The figure below shows an example of a crosscut- ting operation.
Figure 49. Example of a crosscutting operation
with the miter gauge.
Model G0555/G0555P (Mfg. Since 5/11)
"Resawing" means cutting the thickness of a board into two or more thinner boards (see the fig- ure below for an example). The maximum board width that can be resawn is limited by the maxi- mum cutting height of the bandsaw.
One of the most important considerations for resawing is blade selection—a wide blade cuts straighter and is less prone to blade lead (see the Blade Lead subsection later in this manual for more information).
For most applications, use a blade with a hook or a skip tooth style. Choose blades with fewer teeth-per-inch (from 3 to 6 TPI), because they offer larger gullet capacities for clearing sawdust, reducing heat buildup, and reducing strain on the motor.
Figure 50. Example of a resawing operation.
When resawing thin pieces, a wandering blade (blade lead) can tear through the side of the workpiece, exposing your hands to the blade teeth. Always use push blocks when resawing and keep your hands clear of the blade.