ProCurve Switches
Page
IPv6 Configuration Guide
Publication Number
Contents
Information Sources for Tunneling IPv6 Over IPv4
IPv6 Addressing
IPv6 Addressing Configuration
Operating Notes
Contents Introduction
Vii
Contents IPv6 Management Security
IP Preserve for IPv6
Secure Copy and Secure FTP for IPv6
Terminology
Page
About Your Switch Manual Set
Printed Publications
Electronic Publications
Page
Example
IPv6 Command Index
Mands covered in this guide
Index begins on the next
Xii
Copy
Command Min. Level IPv6 Management
Xiii
Xiv
Getting Started
Command Syntax Statements
Introduction
Conventions
Screen Simulations
Command Prompts
Configuration and Operation Examples
Keys
13.01, and includes an IPv6 command index on
Refer to the switch publications listed in this section
Sources for More Information
PIM SM and DM IP routing
Vrrp
Getting Documentation From the Web
Online Help
Menu Interface
Command Line Interface
Web Browser Interface
To Set Up and Install the Switch in Your Network
Introduction to IPv6
Introduction to IPv6
Migrating to IPv6
Individual IPv4 and IPv6 devices ignore each others traffic
IPv6 Propagation
Dual-Stack Operation
Over IPv4 tunneling
Connecting to Devices Supporting IPv6 Over IPv4
Tunneling
Information Sources for Tunneling IPv6 Over IPv4
Use Model
Adding IPv6 Capability
Supported IPv6 Operation in Release K.13.01
Slaac Stateless Automatic Address Configuration
Configuration and Management
Management Features
IPv6 Addressing
DHCPv6 Stateful Address Configuration
Static Address Configuration
Default IPv6 Gateway
Neighbor Discovery ND in IPv6
TFTPv6 Transfers
IPv6 Management Features
IPv6 Time Configuration
Telnet6
IP Preserve
Configurable IPv6 Security
SSHv2 on IPv6
Multicast Listener Discovery MLD
IP Authorized Managers
Ping6
Diagnostic and Troubleshooting
Icmp Rate-Limiting
Traceroute6
Domain Name System DNS Resolution
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery ND Controls
Event Log
IPv6 Scalability
Loopback Address
Debug/Syslog Enhancements
Path MTU Pmtu Discovery
IPv6 Addressing
Loopback Address Unspecified Address
Address Notation
IPv6 Address Structure and Format
Address Format
2001db8a921560fffe7aadc0 2001db8260021201b4
Network Prefix
Interface Device Identifier
IPv6 Addressing Options
IPv6 Address Sources
General IPv6 Address Types
Related Information
Stateless Address Autoconfiguration Slaac
IPv6 Address Sources
Applications
Stateful DHCPv6 Address Configuration
DHCPv6 addressing must be enabled per-VLAN on the switch
Router
Static Address Configuration
Refer to Configuring a Static IPv6 Address on a Vlan on
Address Types and Scope
Address Types
Address Scope
Unicast Address Prefixes
Fe80000000000000021560fffe7aadc0/64 Fe8021560fffe7aasc0/64
IPv6 Addressing
Autoconfiguring Link-Local Unicast Addresses
Link-Local Unicast Address
Fe80/64 plus a 64-bit device identifier
Configures the Vlan to send DHCPv6 requests
Extended Unique Identifier EUI
Generate a link-local address
RFC 2373 IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture
Statically Configuring Link-Local Addresses
Interface
Unique local addresses
Stateless Autoconfiguration of a Global Unicast Address
Global Unicast Address
Link-local unicast fe8021560fffe7aadc0/64
Static Configuration of a Global Unicast Address
Following address assignments on Vlan
Global unicast2001026021221560fffe7aadc0/64
Prefixes in Routable IPv6 Addresses
Unique Local Unicast IPv6 Address
Anycast Addresses
DNS UDP
Multicast Application to IPv6 Addressing
Overview of the Multicast Operation in IPv6
IPv6 Multicast Address Format
Multicast Group Identification
Solicited-Node Multicast Address Format
Bit Use
Loopback Address
Unspecified Address
IPv6 Address Deprecation
Preferred and Valid Address Lifetimes
T e s
Do not expire
Link-Local Address
Router Advertisements
Router Solicitations Default IPv6 Router Router Redirection
CLI
General Configuration Steps
Configuring IPv6 Addressing
Default Disabled
Implements unicast address autoconfiguration as follows
Operating Notes
Enabling DHCPv6
Default Disabled
Configuring a Static IPv6 Address on a
Vlan
Statically Configuring a Link-Local Unicast Address
Syntax no ipv6 address fe80 device-identifier link-local
Statically Configuring a Global Unicast Address
Device-id Enters a user-defined device identity
Statically Configuring An Anycast Address
Default None
Ipv6 enable
Disabling IPv6 on a Vlan
Neighbor Discovery ND
Duplicate Address Detection DAD
DAD Operation
Configuring DAD
No form of the command restores the default setting
Operating Notes
View the Current IPv6 Addressing Configuration
Address Origin
Example of Show IPv6 Command Output
IPv6 Addressing Configuration
Syntax show run
Address autoconfig
Router Access and Default Router Selection
Router Advertisements
Router Solicitations
Default IPv6 Router
Router Redirection
Nected
View IPv6 Gateway, Route, and Router Neighbors
Viewing Gateway and IPv6 Route Information
Viewing IPv6 Router Information
Router Address The IPv6 address of the router interface
Example of Show IPv6 Routers Output
Valid Lifetime
Address Lifetimes
Preferred Lifetime
Sources of IPv6 Address Lifetimes
Link-Local Permanent
IPv6 Addressing Configuration
IPv6 Management Features
Viewing and Clearing the IPv6 Neighbors Cache
Viewing the Neighbor Cache
Example of Neighbor Cache Without Specifying a Vlan
Clearing the Neighbor Cache
Syntax clear ipv6 neighbors
Telnet6 Operation
Outbound Telnet6 to Another Device
Viewing the Current Telnet Activity on a Switch
Example of Show Telnet Output with Three Sessions Active
Enabling or Disabling Inbound Telnet6 Access
Viewing the Current Inbound Telnet6 Configuration
Configuring Enabling or Disabling the Sntp Mode
Sntp and Timep
Configuring an IPv6 Address for an Sntp Server
Router on a Vlan configured on the switch
Vlan must be configured on the switch. For example
Fe8021560fffe7aadc0 on Vlan 10, configured on the switch
2001db821560fffe798980
Configuring Enabling or Disabling the Timep Mode
Vlan configured on the switch
Configured on the switch. For example fe8011215%vlan10
ProCurveconfig# ip timep manual
Tftp File Transfers Over IPv6
Tftp File Transfers over IPv6
For more information, see Using Auto-TFTP for IPv6 on
Enabling Tftp for IPv6
Menu interface Download OS screen become unavailable
Using Tftp to Copy Files over IPv6
Syntax copy source tftp ipv6-addr filename pc unix
Using Auto-TFTP for IPv6
Snmp Features Supported
Snmp Management for IPv6
SNMPv1 and V2c
Snmp Configuration Commands Supported
Supported in the following configuration commands
SNMPv3
Show snmp-server Command Output with IPv6 Address
Show snmpv3 targetaddress Command Output with IPv6 Address
IP Preserve for IPv6
IPv6 Management Features
IPv6 Management Features
IPv6 Management Features
IPv6 Management Security Features
IPv6 Management Security
Authorized IP Managers for IPv6
Usage Notes
IPv6 Management Security Features
Configuring Single Station Access
Configuring Authorized IP Managers for Switch Access
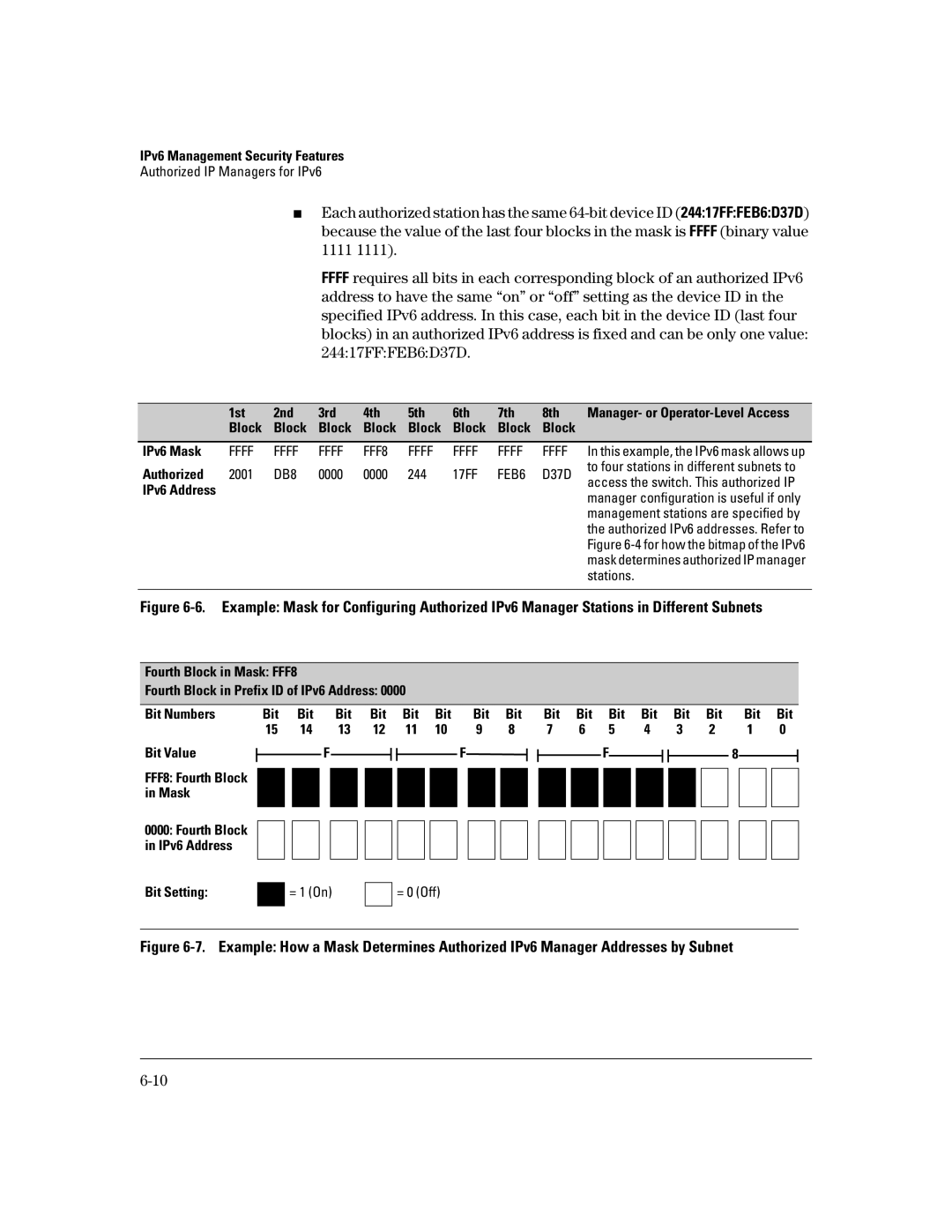
Using a Mask to Configure Authorized Management Stations
Mask and is applied in a different manner
Configuring Multiple Station Access
T e s
Hexadecimal Mask Values and Binary Equivalents
FFFFFFFFFFFFFFF8FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFC
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th 8th Block IPv6 Mask
Ffff FFF8
Binary Equivalents of Authorized Subnet IDs in Hexadecimal
Authorized to access the switch for example
Granted access
11. Default IPv6 Mask
IPv6 Management Security Features
Configuring SSH for IPv6
Secure Shell for IPv6
T e
Displaying an SSH Configuration
Inactive
Secure Copy and Secure FTP for IPv6
Mands and software utilities to use
Message
Multicast Listener Discovery MLD Snooping
Overview
Introduction to MLD Snooping
Without MLD, multicast traffic is flooded to all ports
Multicast Listener Discovery MLD Snooping
Multicast Listener Discovery MLD Snooping
Multicast Listener Discovery MLD Snooping
To disable MLD snooping on Vlan
Configuring MLD
For example, to enable MLD snooping on Vlan
Enabling or Disabling MLD Snooping on a Vlan
Configuring Per-Port MLD Traffic Filters
Vlan Name VLAN8
Configuring the Querier
Configuring Fast Leave
To enable the switch to act as querier on Vlan
To enable fast leave on ports in Vlan
Configuring Forced Fast Leave
For example, to disable fast leave on ports in Vlan
For example, to enable forced fast leave on ports in Vlan
Displaying MLD Status Configuration
Current MLD Status
Continuation of Figure
Multicast Listener Discovery MLD Snooping
Current MLD Configuration
Following information, for all MLD-enabled VLANs, is shown
Specific form of the command might look like this
Example of an MLD Configuration for a Specific Vlan
Ports Currently Joined
Vlan ID
Statistics
Shows MLD statistics for the specified Vlan vid-VLAN ID
For example, the general form of the command
Example of MLD Statistics for All VLANs Configured
Counters
Displays MLD counters for the specified Vlan vid-VLAN ID
Following information is shown
Multicast Listener Discovery MLD Snooping
IPv6 Diagnostic and Troubleshooting
Icmp Rate-Limiting
Default 10 Range 1
Ping for IPv6 Ping6
Examples of IPv6 Ping Tests
Traceroute for IPv6
Syntax traceroute6 ipv6-address hostname
Examples of IPv6 Traceroute Probes
DNS Configuration
DNS Resolver for IPv6
Domain suffix mygroup.procurve.net
Viewing the Current Configuration
Operating Notes
Configuring Debug and Event Log Messaging
Debug/Syslog for IPv6
Severity level System module
Debug Command
Ip rip database event trigger
Configuring Debug Destinations
Logging Command
Terminology
Terminology
Index
Index
DAD
Icmp
Lldp
SCP
Sntp
Vlan
Page
5992-3067

![]()
![]() F
F![]()
![]()
![]() F
F![]()
![]() 8
8