Ignite-UX Administration Guide
Abstract
Revision History
Acknowledgements
B2355-90849 HP-UX 11.00, 11i v1, 11i v1.6, 11i
Contents
Simple network creating a server for anonymous clients
Complex networks challenges and solutions
Managing I/O for installation and recovery
Complex networks multi-capable servers
Booting and installing HP-UX on clients using the server 110
Security
Creating your own boot and installation media 180
Customizing your installation 161
Automating installations 174
Golden images 151
Recovery 191
Support and other resources 224
LIF volume contents 239
Documentation feedback 227 Troubleshooting 228
Configuring Dhcp services 236
Terminal keyboard shortcuts 255
HP secure development lifecycle
Ignite-UX features
Ignite-UX overview
Automated installations
One-step installation
Custom installations
Create custom installation media
Getting the Ignite-UX software
Ignite-UX bundles available in the Ignite-UX product
Ignite-UX commands and manpages
Ignite-UX command manpages
Introduction to the Ignite-UX GUI
Ignite-UX GUI
File menu
View menu
Options menu
Actions menu
How Ignite works
Client status dialog box
Installation versus recovery
Ignite-UX install environment
Boot sources
Network booting and IP addresses
Itanium-Based Systems
Phases of operation
PA-RISC Systems
Startup
Phase
Ignite-UX server requirements
Hardware requirements
Other considerations
Firmware
Supported peripherals
Disks and other I/O
Disk arrays
Boot and install client from media
Making configuration decisions for Ignite servers
Simple network solutions
Instlboottab
Alternate boot with network server installation
Complex networks
Diagnosing network boot issues
Use DVD media to boot a system for network installation
For a detailed discussion, see
HP-UX diagnosing and debugging
Investigate instlbootd errors in /var/adm/syslog/syslog.log
Instlboots allow
Simple network debugging
RDP diagnosing and debugging
Launch Ignite-UX
Configuring the Ignite-UX server for PA-RISC clients
Simple network creating a server for registered clients
Ignite
Launch the server setup wizard
Ignite-UX GUI welcome dialog box
Server setup wizard
Configure booting IP addresses
Register the PA-RISC clients with the server
Go to the software setup section
Configuring the Ignite-UX server for Itanium-based clients
Skip Dhcp setup
Register the Itanium-based clients with the server
Setting up software from OE depots
More server setup options
Configuring server options
Ignite-UX server configuration tabs
Configuring session options
Add Dhcp addresses dialog box
Session options tab
SD software
Setting up additional software on the server
Example Create a configuration for compiler software
Non-SD software
Simple network creating a server for registered clients
Itanium-based clients use Dhcp to boot anonymously
Using the server setup wizard
Editing the instlboottab file
Simple network creating a server for anonymous clients
Ignite-UX server and boot helper setup for Dhcp
Understanding PXE booting of Itanium-based systems
Working with Dhcp
Page
Dhcpclassid=IgniteDHCPDeviceGroup
Since the install kernel and install file system must be
Isolating Ignite-UX from noncontrollable Dhcp servers
Class-id=PXEClientArch00002IgniteDHCPDeviceGroup
Page
How to use this chapter
Complex networks challenges and solutions
Complex network challenges
Multiple subnets
Remote systems
Avoiding complex network issues
Multiple boot servers
Multi-capable server for each subnet
Using virtual LANs properly for Ignite-UX
An Ignite-UX server for each subnet
Extend the local subnet
Complex network solutions
Automating HP-UX OS version selection
Limit network response by system class
Directed boot
Limit network boot response by network interface address
Server selection
Control network boot via response timing
Install remote clients through a network router
Getting the client the correct networking information
Multiple NICs attach the Ignite server to multiple subnets
Having the client contact the correct server
Ignite-UX bootp boot helper
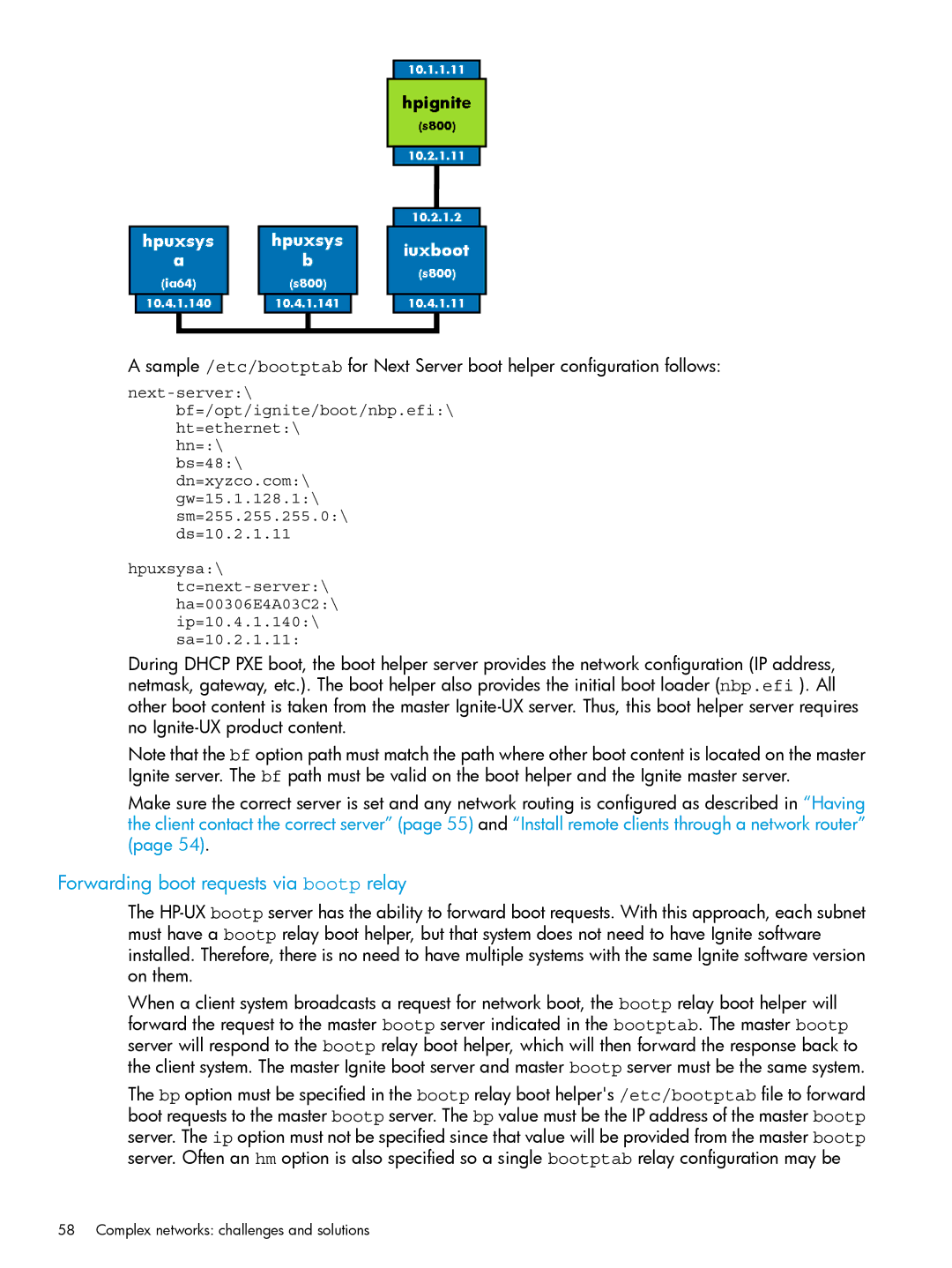
HP-UX Dhcp PXE Next server boot helper for integrity systems
Configuring a Next server boot helper for Integrity systems
Forwarding boot requests via bootp relay
Ha=000000000000\ Hm=000000000000\ Bp=10.2.1.11
Non-HP-UX Next server boot helper
Multi-capable subnet boot server
Non-HP-UX bootp boot helper
Configuring an RDP server to delay PXE response
Configuring an RDP server for specific MAC addresses
Complex networks multi-capable servers
Configuring an RDP server to initiate HP-UX installation
Setting up RDP MenuOptions via Windows commands
Setting up RDP MenuOptions via interactive UI
Complex networks multi-capable servers
Configuring an RDP server to initiate HP-UX installation
Using an RDP MenuOption for HP-UX
Client MAC Addr 00 30 6E 4C AA A5
Page
SuSE
RedHat installation from an HP-UX server
FTP Http
SuSE installation from an HP-UX server
Configuring an HP-UX server to support Windows installation
Then you must specify the location of Linux install content
Agile view concepts
Managing I/O for installation and recovery
Introducing multipathing
Agile view I/O addressing logic looks like Figure
Agile multiple path I/O stack addressing model
System installation configuration
Practical considerations
Ignite-UX client installation configuration tabs
Disk Selection Root Disk Dialog Box With Physical Locations
More Info dialog box
Support for 2 TB boot disk
Disk selection add/remove disks dialog box
Important characteristics of the agile view
Identifying devices for other tasks
UNpath Per YH/W evi
Legacy DSFs and device matching
Recovery and the agile view
Persistent DSFs and device matching
O Configuration variables
Controlling the I/O configuration process
Persistent DSF-to-device matching methods by protocol
Agile view questions and answers
O Configuration value types
Agile view questions and answers
Security
Ignite-UX server ports
Port usage initiate LAN boot for Itanium-based clients
Winstallfs
Sequence
Boot
Kernel
Port usage makenetrecovery initiated from the client
Makenetrecovery Initiated from Client
Port usage makenetrecovery initiated from the server
Makesysimage Initiated from Client
Enabling Ignite-UX server requirements
Remove or comment-out the following line
Enabling Ignite-UX client requirements
Run Bastille
Overview
Configuring Ignite to replace Tftp with NFS
Procedure
Ignite Product Files Moved in Version C.7.9 and Later
Use vi to add hploadfileusenfs=true to the file
Now use instladm to update the install file system
Set up NFS exports and check custom configuration files
Would need to be modified to be
Disable Tftp on the Ignite-UX server optional
For 64-bit PA-RISC clients the files on the server are
Preparing the client for installation
Where release is the release identifier
For Itanium-based clients the files on the server are
Making boot decisions when using the client console
Boot using the network
Boot using media
Using bootsys on the client console
Support?
Booting PA-RISC clients from the console
Boot ADMINhelp boot
Booting Itanium-based clients using the network
Enter the data type of this boot option
Select Add a Boot Option
Enter a brief description for this boot option
Press Y to save the new boot option
Direct boot profiles for Itanium-based systems
LAN1
Syntax
Dbprofile command
Options and operands
Examples
Lanboot command
Lanboot select -od optionaldata -dn name
Shell dbprofile or
Installing HP-UX from the client console
Shell lanboot or
User interface and media options
Network Configuration with no Dhcp
Examples
Add this configuration clause to Wviinstallfs
Setting 100 Full Duplex
Setting Mixed interface types
Edit the file
Methods of installing client systems
Booting and installing HP-UX on clients using the server
Installation using bootsys
Touch /.bootsysblock
Starting Ignite-UX
Installation using the Ignite-UX GUI
Prepare the client for installation
Adding clients
Booting a client
Select boot release
Boot confirmation dialog box
Boot process terminal window
New client displayed in GUI
Configuring the installation
New installation
Initializing the installation
Client installation configuration interface
Functions available from all tabs
Basic tab
No environments note
Booting and installing HP-UX on clients using the server
File system default choices
All Legacy HW Paths Dialog Box
Root Swap MB... button
Languages dialog box
Additional Configuration Controls Dialog Box
Additional Configuration Controls Dialog Box Software tab
Software tab for HP-UX 11i v1 and 11i
Software cannot be unselected
Marked ? column status can be
Change Depot Location note
Interactive swinstall notes
Job? x/s/c
System tab
#nslookup test
255.255.248.0 or 0xfffff800 255.255.255.0 or 0xffffff00
Set Time Zone dialog box
Set Root Password dialog box
Network Services tabs
Set DNS Search Domains Dialog Box
NIS tab
Network Interfaces Dialog Box
Select an Interface card from the selection list
Adding or changing a file system configuration
Configuring the installation
Volume requirements for LVM and VxVM
To change, add, or remove a disk from the client
Advanced Disk Parameters dialog box
Highlight a disk in the selection list to select it
Advanced File System Parameters dialog box
Volume
Has these characteristics
No gap is enabled between physical extents within a mirror
Root volume /, the boot volume /stand, dump volumes
Advanced tab
For more information, see manageindex1M
Repeat an installation
Executing the installation
Repeat Install dialog box
Installation Confirmation dialog box
Client Status... dialog box
Installation log file
Viewing and printing a manifest
Printmanifest
Advantages of golden images
Golden images
Creating a golden image
Installing the HP-UX operating system
Installing critical patches onto the operating system
Customizing the system
Installing optional software
Install the patch non-interactively
Creating the golden archive
On the golden system, run
Localedescription
Here are the HP-UX 11i v1 swsource and swsel examples
Creating and using golden images using GUI and CLI
Creating golden image using GUI
Xhost +Ignite-UXserverhostname
Opt/ignite/bin/ignite
Examples on using makegoldenimage script
Creation of a golden image using CLI
Enabling the client
Installing the golden image on the client
Using configuration files
Customizing your installation
Classes of configuration files
Configuration File Use and Locations
These install kernels and install file systems are located
Var/opt/ignite/config.local
Opt/ignite/data/Relrelease/config
Var/opt/ignite/data/Relrelease
Combining configuration files using Index entries
Var/opt/ignite/clients/client/config
Configuration choices dialog box
Example configuration files
Defining Disks
Combining Disks to Form a Single Volume Group
Defining Networking Parameters
Defining an Installation Depot
Customizations based on the client hardware
# ia64 hp workstation zx2000
Customizations based on user selection
# ia64
# 9000/785
Avoid archiving patch files
Xpatchsavefiles=falsetrue
Using post-installation scripts
Debugging configuration files
For more information, see instldbg1M
Adding a post-installation script
How the installation functions
Example
Where t is for postconfigscript selection settings
Starting a non-interactive installation with bootsys
Automating installations
Using a saved configuration
Setting defaults with instladm
Specifying defaults in the config.local file
Using the per-client configuration file
Final systemname=system11 Final ipaddrlan0=10.2.75.193
Setting installation parameters dynamically
Scheduling installations
Press Ctrl-D
Example
Checking modified files for errors
Instladm -T -f file
Building PA-RISC boot and installation tape
Creating your own boot and installation media
Why use custom boot and installation media?
Possible tape contents
Possible PA-RISC installation tape layouts
Logical interchange format
Archives and depots
#nfssource=
Sdserver = IPaddress Sddepotdir = /var/tmp/depot
PA-RISC installation tape creation example
Assumptions
Change the sourcetype attribute from NET to MT
Verify your changes
Example PA-RISC installation tape creation
Instladm -d -F /var/tmp/lifvol /var/tmp/cfg
Instladm -d -f /var/tmp/lifvol
Assumptions
Creating a boot CD/DVD or an installation DVD
Boot and archive-based CD/DVDs
File and ISO image size considerations
# makemediainstall -?
Boot CD/DVD examples
Installation archive-based DVD examples
# makeopticaldiscrecovery -?
Put a PA-RISC HP-UX 11i v2 golden archive on a DVD
Error messages
Create a recovery DVD
No DVD available
No DVD special files
HP-UX 11i v2 Depot-based installation DVDs
Depot-based DVDs
Missing -cargument on HP-UX 11i v2 USB DVD drive
Copy the EFI partition into the first DVD pseudo-root
For more information, see instladm1M and instladm4
Create the first DVD
Run mkisofs to create the first DVD image pathtodvd1image
Run mkisofs to create the second DVD image pathtodvd2image
HP-UX 11i v3 Depot-based installation DVDs
Create the second DVD
Burn the DVD images and test them
System recovery
Recovery
Overview
Use maketaperecovery to
System recovery tools
Recovery tool comparison
Use makenetrecovery to
Recovery image contents
Recovery image configuration policies
Var/opt/ignite/clients/client/recovery/2005-03-17,1119
Recovery image creation process
Create files and directories for the recovery image
Var/opt/ignite/recovery/archives/client directory
Var/opt/ignite/clients/client/recovery directory
Run the recovery interface
Var/opt/ignite/clients/client/recovery/defaults
Prepare the configuration file
Recovery image creation status
Examining recovery image contents
Opt/ignite/lbin/listexpander -f archivecontent
Verifying recovery image results
Init hpignoreswimpact=1
Recovery
Recovery tape creation examples
Creating and using recovery tapes
Opt/ignite/recovery/mnressentials
Maketaperecovery -x incentire=vg00
Tape recovery for PA-RISC systems
Recovering a minimal operating system
Maketaperecovery -A -s myserver -a /dev/rmt/0m
Tape recovery for Itanium-based systems
Determining the tape drive’s EFI path
EFI menu with timer
Select Boot Configuration from the Boot Menu
Boot configuration
Add boot entry
List of selectable boot devices
Enter load options
Tape recovery for Integrity Blade systems
Boot Manager menu with the new option
Determine tape drive EFI path using Command Line Interface
Creating and using network recovery images
Shell tapeboot select Fibre-Channel
Adding clients for recovery
Network recovery server dependency
Networking features
Var/opt/ignite/recovery/datetime/recovery.log
Xhost +Ignite-UXserverhostname
Makenetrecovery -s myserver
Examples of network recovery image creation
Recovering using the network for PA-RISC clients
Makenetrecovery -s myserver -x incentire=vg00
Recovering using the network for Itanium-based clients
Retaining recovery images
Hpux
# rm latest # ln -s RecoveryArchive.sav latest
Var/opt/ignite/clients/client/recovery/config.local
Making recovery configuration file additions
Using the recovery config.local file
Var/opt/ignite/recovery/config.local
Selecting file systems during recovery
Opt/ignite/data/RelB.11.11/config
CD/DVD
Using the makesysimage method
Cloning a system using makenetrecovery
Run # shareall -F nfs
System recovery questions and answers
Question
Check /etc/inetd.conf
# rm oldhostname
Contacting HP
Support and other resources
Related information
Websites
Following conventions are used in this document
Typographic conventions
Typographic Conventions
Documentation feedback
Ignite-UX server problems
Troubleshooting
Errors and warnings
Installing systems with Ignite-UX
Too much file space needed
Problem installing clients on multiple subnets
Debugging SD during cold-installation
Ignite-UX requests more file system space than expected
Booting errors on PA-RISC systems
Corrupted /opt/ignite/boot/bootlif file
Received n bytes in s seconds
Problems pointing to client over network
Applications hang after igniting
Tftp quit
Bootsys Command Seems to Work in Reverse
Server not listed
Installing from media
Installing from golden images
Insufficient Response to PXE Boot Request
Common network booting errors
File size miscalculated
Creation of archive
File Size miscalculated on HP Integrity virtual machines
Configuring Dhcp services
Overview of Dhcp services
Dhcp usage examples
Using bootptab as an alternative to Dhcp
Background information on Dhcp design
LIF volume contents
For more information, see Using configuration files
For more information, see Classes of configuration files
Description of the files in the LIF volume
Using Integrated Lights Out Virtual Media with Ignite-UX
243
Using Integrated Lights Out Virtual Media with Ignite-UX
245
Using Integrated Lights Out Virtual Media with Ignite-UX
247
Using vMedia with DVD installation media and ISO images
Expert recovery preparation
Expert recovery
Expert recovery procedure
Expert recovery
Expert recovery procedure
Expert recovery
Expert recovery procedure
# mknod /ROOT/dev/console c 0
Advanced keyboard navigation
Terminal keyboard shortcuts
Basic keyboard shortcuts
HP terminals
Vt100 terminals
Function keys
Advanced keyboard actions
Glossary
See Link Level Address LLA
Checknetrecovery1M
Maketaperecovery. See copyboottape1M
Iinstall
See instlcombine1M
Makebundles1M
Maketapenetrecovery
See Software Distributor
Vinstall
Setting hplanadminargs, 108 boot source
Index
Index
DVD
Index
LVM
PXE
Port usage on makenetrecovery, 89 port usage with bootsys
Page
Server display Xntp configuring, 136 screen Xntpd daemon