GR-DVL9600
It is recommended that you
Dear Customer
This unit is produced to comply with Standard IEC Publ
EN3
Remote Control Unit RM-V711U Video Cable DC Cord
AC Power Adapter
Cleaning Cloth
Charger AA-V68EA Min DVM-30
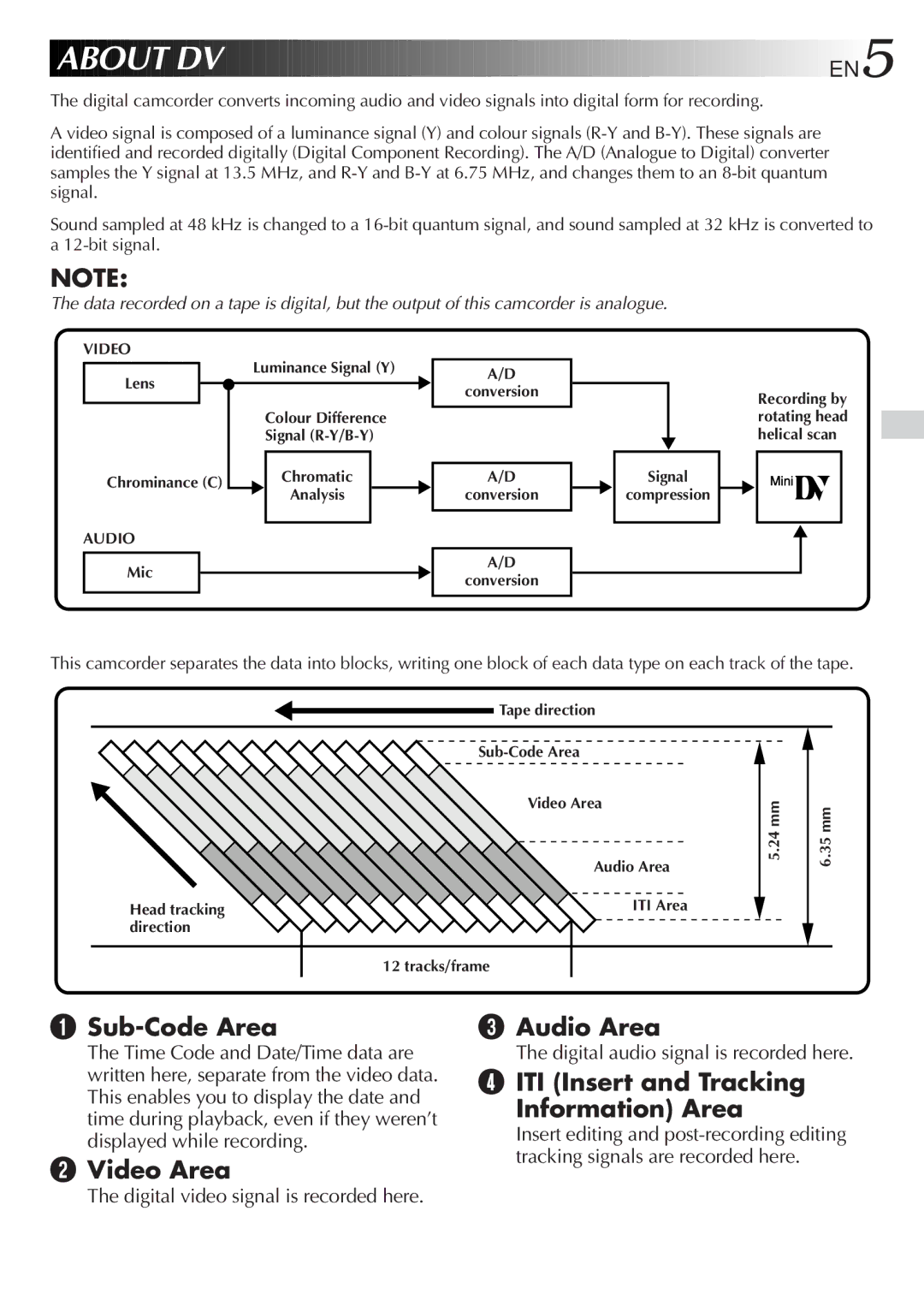
Signal Compression
Luminance Signal Y Lens Colour Difference Signal R-Y/B-Y
About DV
Analysis Mic Conversion
Charging the Battery Pack
Power
Using AC Power
Using the Battery Pack
Tilt Viewfinder Upward Attach Battery Pack
To Detach The Battery Pack
Getting Started
Date/Time Settings
Battery
Open Cassette Cover
Loading/Unloading a Cassette
INSERT/REMOVE Tape
Close Cassette Cover
SET Recording Mode
Recording Mode Setting
10 EN
Set depending on your preference
Viewfinder Adjustment
Grip Adjustment
Tripod Mounting
12 EN
Shoulder Strap Attachment
Operation Mode
Recording Basic Recording
14 EN
Load a Cassette
Start Shooting
Press IND. ON/OFF Button
LCD Monitor/Viewfinder Indications
Stop Recording
Before the following steps, perform pg
16 EN
Shooting While Watching The LCD Monitor
Brightness Control
Journalistic Shooting
Interface Shooting
Basic Recording
18 EN
Zoom
Zoom Out
After playing back the recorded tape, when you shoot again
When blank portion is recorded on a tape
Proper recording
Shooting
Displaying The Date And Time During Recording
Recording Advanced Features
20 EN
END 5S Mode
Engage 5S Mode
Set the Power Switch to the , , or OFF position
Dissolves during 5 second recording mode
Start Progressive Mode Recording
Progressive Mode Recording
22 EN
To End Progressive Video Recording
Regular shooting of moving images
Description of Progressive Scan CCD
Frame Scan a Scan B
Scan C
24 EN
Advanced Features
Recording
Pro Snapshot
Progressive Mode
Motor Drive Mode
Pin-Up mode √ Multi-Analyser
To Remove The Shutter Sound
26 EN
If the Power Switch is set to
Snapshot Flash Auto Flash
Engage RECORD-STANDBY
Press the Select Dial
Flash Brightness Adjustment
Access Flash Adjustment
28 EN
Using Menu For Detailed Adjustment
Recording Menu Explanations
Factory-preset
System Menu Explanations
30 EN
Date/Time Menu Explanations
Effect Selection
Fade/Wipe Effects
FADE/WIPE Selection
Select Effect
Picture Wipe or Dissolve Selection
32 EN
Before the following steps, perform steps 1 through 4 on pg
If you select Picture Wipe/Dissolve during recording
Menu
Fader And Wipe Menu
Disable Mode
Select Mode
Manual Mode Item Menu AE/EFFECT Menu
34 EN
Classic Film
Shutter
Twilight
Sepia
36 EN
Focusing
Auto Focus
Patterns that are regularly repeated
END Adjustment of Focus
Access Manual Focus
Manual Focus
To nearer subject
Access Exposure Control
Access Manual Mode Item Menu
38 EN
Exposure Control
Center SUBJECT, Lock Iris
Iris Lock
Iris
To Return To Automatic Iris Control
Accessment White Balance Adjust
White Balance Adjustment
40 EN
To Return To Automatic White Balance
Exit Manual White Balance Adjustment
Enter Setting
Manual White Balance Operation
To Change The Tint For Recording
High Speed Recording
42 EN
Engage High Speed Recording Standby
END Recording
Playback Basic Playback
Adjust Volume
Rewind or Fast-forward the tape
Play Back
Basic Playback
EN Playback
END Playback
Progressive Slow-Motion Playback
Find Scene of Interest
Playback
46 EN
Playback Menu
Close Menu
Recording sound Display Output sound
Playback Sound
Displaying The Time Code During Playback
48 EN
When connecting the cables, open this cover
Basic Connections
Use the provided S-Video cable and Audio/Video cable
Turn on the camcorder, the VCR and the TV
Connectinput VCR Output to TV Supply Power
Connectvcr Camcorder to TV or
50 EN
Turn on Power
Playback Advanced Connections
Connection To a Personal Computer
Connect Printer to PC if Necessary
Connection To a Video Unit Equipped With a DV Connector
Tape Dubbing
52 EN
Make Connections
Digital Dubbing
Start Playback
Press Play 4 to play back the source tape
Pull OUT Battery Holder
Installing The Battery
Insert Battery in Holder
54EN
Infrared beam transmitting window
Switch set to the camera position
Functions Buttons
56 EN
Using the Remote Control Unit
Effect
Play 4 Button
Select Menu Remote sensor
Random Assemble Editing R.A.Edit
58 EN
SET REMOTE/VCR Code
SET Remote to Operate VCR
Select Scenes
Make Connections
Select Scenes
EN Using the Remote Control Unit
SET EDIT-IN Point
SET EDIT-OUT Point
Prepare Source Tape
Automatic Editing to VCR
Stop Editing
RM-V711U Provided T W
Diagnosing VCR’S Against Camcorder Timing
62 EN
For More Accurate Editing
Access Playback Menu
Adjustment of VCR’S Against Camcorder Timing
Power Switch Playback Menu
Input Correction Data
Audio Dubbing
64 EN
Begin Dubbing
Pause During Dubbing
Find Edit OUT Point
Insert Editing
Find Edit in Point
Pause During Editing
Corrective Action
66 EN
Corrective Action
Symptom Possible Causes
68 EN
Troubleshooting
During recording, the date
EN Troubleshooting
Remove
After Use
72EN
Tally Lamp Power Lamp
# Date/Time Reset Button Reset
Red-Eye Reduction Button
Control VOL
Index
74 EN
Indications
LCD Monitor/Viewfinder Indications During Recording
Indications Function
LCD Monitor/Viewfinder Indications During Playback
76 EN
For safety, do not
To prolong service life
Avoid using the unit
To avoid hazard
To protect the unit, do not
Do not leave the unit
About moisture condensation
Serious malfunctioning
Connectors
AC Power Adapter/Charger AA-V68EA
Camcorder
General
GR-DVL9600

 ABOUT
ABOUT
 DV
DV





































































 EN5
EN5