|
| Featured Functions | |||
| Fixed VLAN List (Tagged) |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Setting | Description |
| Factory Default |
|
| VID range from 1 | This field will be active only when selecting the Trunk |
| None |
|
| to 4094 | port type. Set the other VLAN ID for tagged devices that |
|
| |
|
| connect to the Trunk port. Use commas to separate |
|
|
|
|
| different VIDs. |
|
|
|
| Forbidden VLAN List |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Setting | Description |
| Factory Default |
|
| VID range from 1 | This field will be active only when selecting the Trunk |
| None |
|
| to 4094 | port type. Set the VLAN IDs that will not be supported |
|
|
|
|
| by this trunk port. Use commas to separate different |
|
|
|
|
| VIDs. |
|
|
|
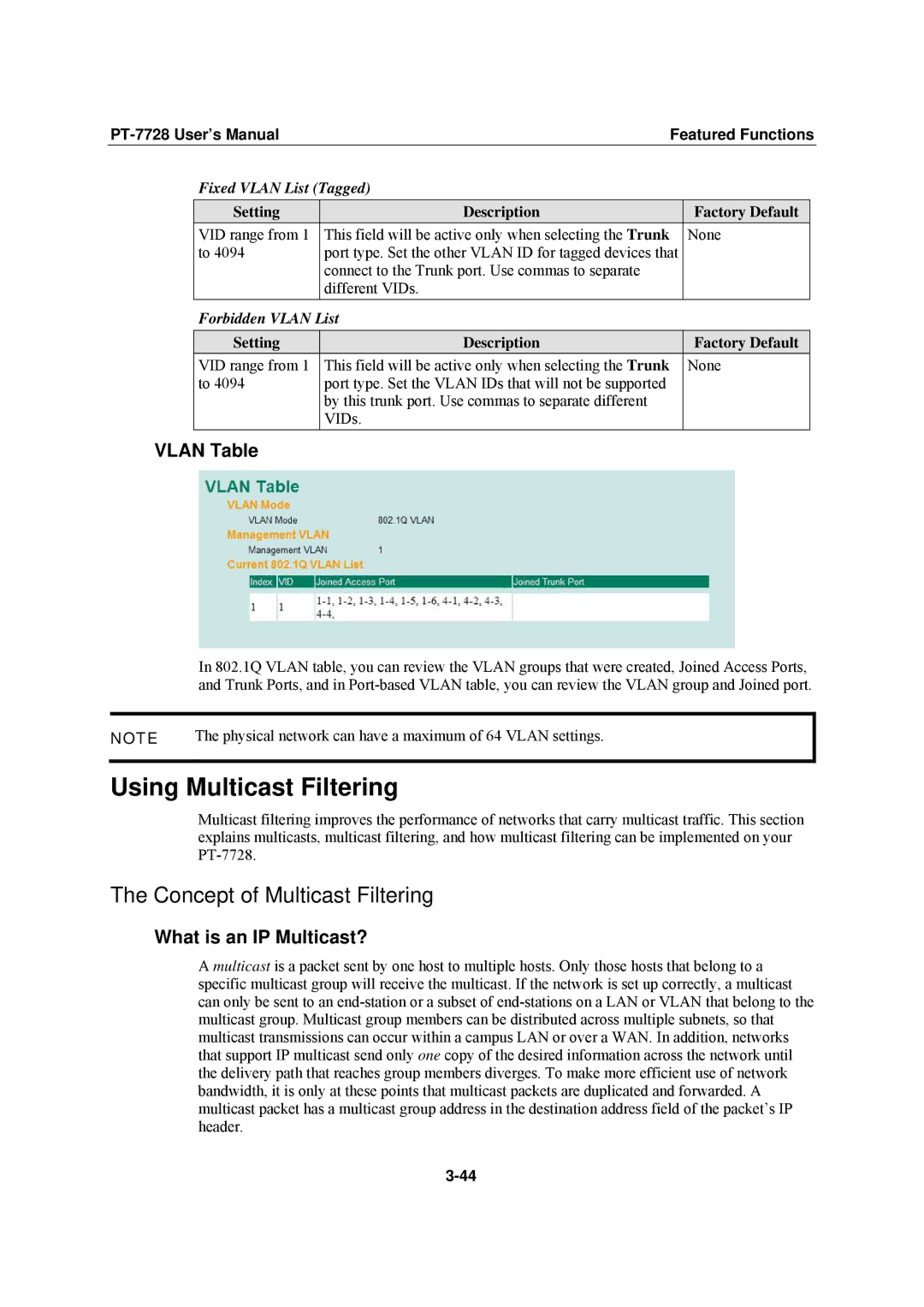
VLAN Table
In 802.1Q VLAN table, you can review the VLAN groups that were created, Joined Access Ports, and Trunk Ports, and in
NOTE | The physical network can have a maximum of 64 VLAN settings. |
Using Multicast Filtering
Multicast filtering improves the performance of networks that carry multicast traffic. This section explains multicasts, multicast filtering, and how multicast filtering can be implemented on your
The Concept of Multicast Filtering
What is an IP Multicast?
A multicast is a packet sent by one host to multiple hosts. Only those hosts that belong to a specific multicast group will receive the multicast. If the network is set up correctly, a multicast can only be sent to an