| Featured Functions |
Benefits of Multicast
The benefits of using IP multicast are that it:
yUses the most efficient, sensible method to deliver the same information to many receivers with only one transmission.
yReduces the load on the source (for example, a server) since it will not need to produce several copies of the same data.
yMakes efficient use of network bandwidth and scales well as the number of multicast group members increases.
yWorks with other IP protocols and services, such as Quality of Service (QoS).
Multicast transmission makes more sense and is more efficient than unicast transmission for some applications. For example, multicasts are often used for
Multicast Filtering
Multicast filtering ensures that only
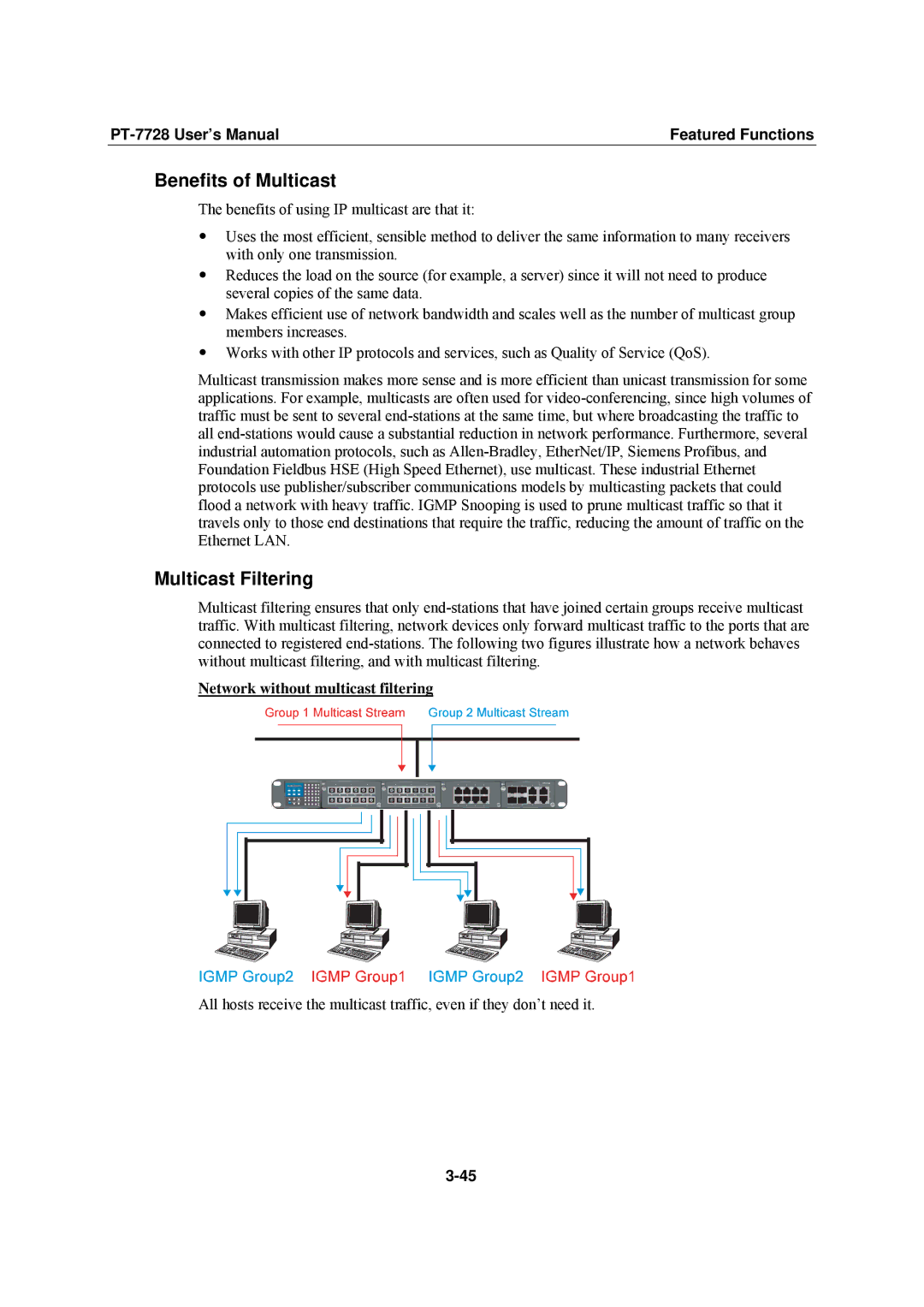
Network without multicast filtering
M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 |
All hosts receive the multicast traffic, even if they don’t need it.