| Featured Functions |
STP Reconfiguration
Once the network topology has stabilized, each bridge listens for "Hello" BPDUs that are transmitted from the Root Bridge at regular intervals. If a bridge does not receive a "Hello" BPDU after a certain interval (the Max Age time), the bridge assumes that the Root Bridge, or a link between itself and the Root Bridge, has gone down. This will trigger the bridge to reconfigure the network to account for the change. If you have configured an SNMP trap destination, the first bridge to detect a topology change in your network sends out an SNMP trap.
Differences between RSTP and STP
RSTP is similar to STP, but includes additional information in the BPDUs that allow each bridge to confirm that it has taken action to prevent loops from forming when it decides to enable a link to a neighboring bridge. Adjacent bridges connected via
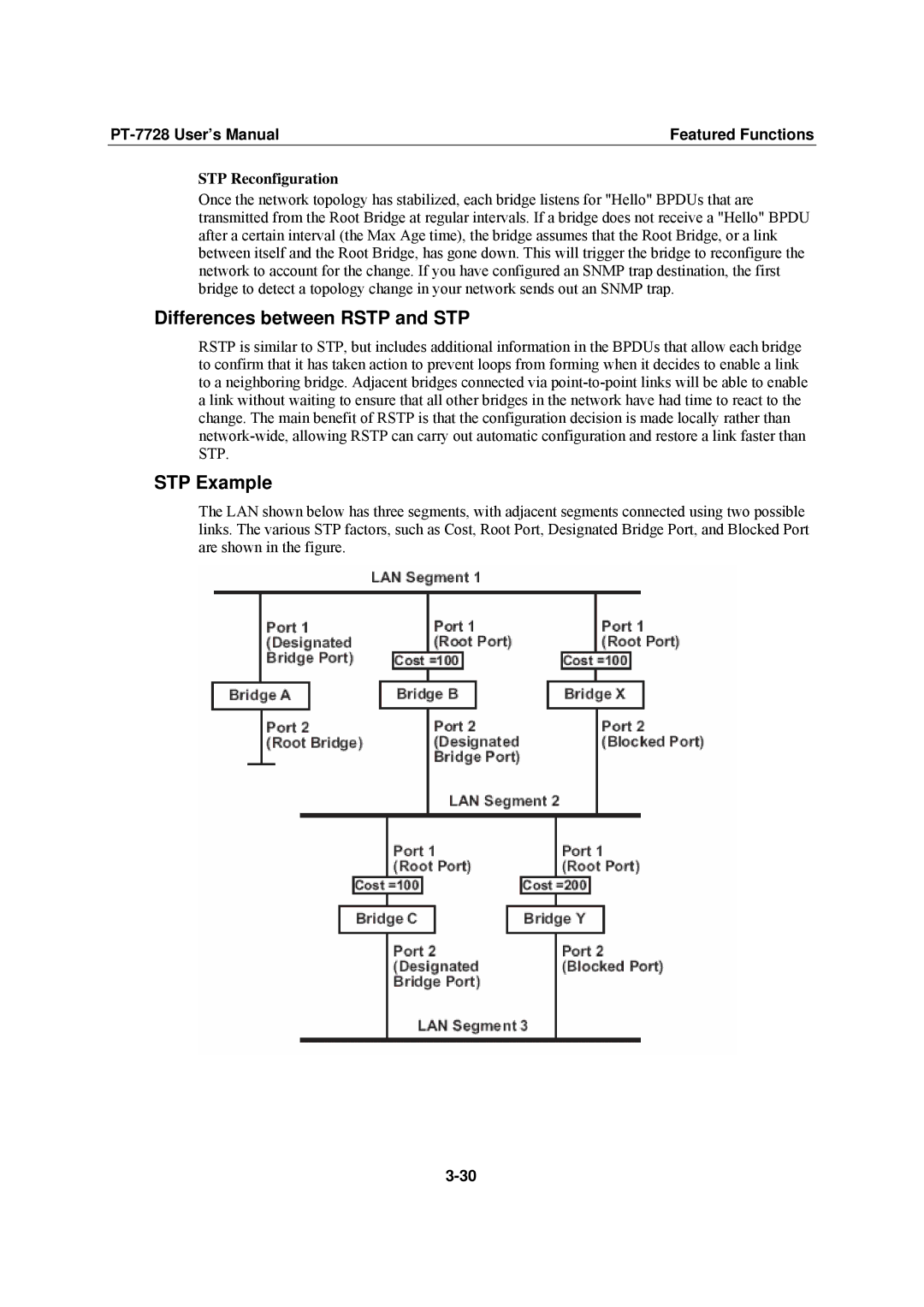
STP Example
The LAN shown below has three segments, with adjacent segments connected using two possible links. The various STP factors, such as Cost, Root Port, Designated Bridge Port, and Blocked Port are shown in the figure.