FrameSaver DSL
Copyright 2002 Paradyne Corporation All rights reserved
Contents
Configuration Procedures
Configuration Options
Configuring the FrameSaver DSL Router
Security and Logins
Access Levels Command Modes Changing Access Levels
December
Troubleshooting
Viewing LMI Captured Packets from the User Interface
Menu Hierarchy
Setting Up Network Health for FrameSaver Device
Snmp MIBs, Traps, and Rmon Alarm Defaults
Connectors, Cables, and Pin Assignments
Router CLI Commands, Codes, and Designations
Router Command Line Summaries and Shortcuts
Technical Specifications Equipment List
Index
Document Organization
About This Guide
Purpose and Intended Audience
Technical Manuals → Technical Glossary
Product-Related Documents
Document Number Document Title
NetScout Documentation
Concord Communications Documentation
Conventions Used
Convention Interpretation
X.x
Xxxxxxxxxxxx
About FrameSaver DSL Devices
System Overview
Router-Specific Features
FrameSaver DSL Features
CSU/DSU-Specific Features
About FrameSaver DSL Devices
Diagnostic Feature Set
Model # Product PVCs
Diagnostic Feature Set
Advanced SLM Feature Set
Advanced SLM Feature Set
Network Configuration Examples
Access Network
Remote Site
Customer Premises HQ Site
Access
Central Office Customer Premises
OpenLane Features
OpenLane SLM System
About FrameSaver DSL Devices December
User and Command Line Interfaces Basic Operation
If your login was Then
Logging On
Procedure
Ending a Session
Main Menu
Select
Screen Work Areas
Screen Format Description
Press
Navigating Menu-Driven User Interface Screens
Keyboard Keys
For the screen Select Function Press Enter to
Function Keys
Selecting from a Menu
Device Name MyDeviceName
Switching Between Screen Areas
Selecting a Field for Input
Navigating the Router’s CLI
CLI Keyboard Keys
9700-A2-GB20-20
Configuration Procedures
Basic Configuration From the User Interface
Configuration Edit/Display Menu
Configuration Option Areas
Configuration Option Area Description
Accessing and Displaying Configuration Options
Main Menu Configuration
Configuration PVC Connections
Changing Configuration Options
Saving Configuration Options
Configuration Procedures
Configuration Options
Configuration Options
Easy Install Screen
Using the Easy Install Feature
Main Menu Easy Install
Easy Install Configuration Options 1
Easy Install Configuration Options 2
Network 1 DSL Line Rate Mode
Create a Dedicated Network Management Link
Ethernet Management Options Screen
Easy Install Configuration Options 3
Network 1 DSL Line Rate
384
784
Port-1 Port Type 9788 CSU/DSU
Easy Install Configuration Options 4
Network 1 Channel
Entering System Information and Setting the System Clock
Changing the Operating Mode
Main Menu Control Change Operating Mode
Main Menu Control System Information
Configuration Option Tables
Main Menu Configuration System Frame Relay and LMI
Configuring the Overall System
Configuring Frame Relay and LMI for the CSU/DSU
LMI Clearing Event N3
LMI Error Event N2
CSU/DSU Frame Relay and LMI Options 2
LMI Status Enquiry N1
LMI Heartbeat T1 Possible Settings 5, 10, 15, 20, 25
CSU/DSU Frame Relay and LMI Options 3
Field Setting After RfcCodePoints Selected
Configuring Class of Service Definitions
Main Menu Configuration System Class of Service Definitions
Class of Service Definitions
Class of Svc Name
Measure Latency & Availability
Code Points Assigned
Code Point Definitions
Code Point Definitions
Code Pnt
Name
Configuring Service Level Verification Options
Main Menu Configuration System Service Level Verification
Service Level Verification Options 1
SLV Sample Interval secs
Service Level Verification Options 2
SLV Type Available Settings Standard, COS 1-COS
Dlci Down on SLV Timeout
SLV Delivery Ratio
Service Level Verification Options 3
Test Duration min
Configuring General System Options
Main Menu Configuration System General
Configuring Network Interfaces
Configuring the Network Physical Interface
Main Menu Configuration Network Physical
Operating Rate Possible Settings AutoRate, 64, 128
DSL Line Rate Kbps
Line Rate Mode Possible Settings Hunt, AutoRate, Fixed
Network Physical Interface Options
Line Rate Mode
776, 784, 1544
2056
Region
Configuring Frame Relay for the Network Interface
Configuring Dlci Records for the Network Interface
Main Menu Configuration Network Frame Relay
Main Menu Configuration Network Dlci Records
Configuring Circuit Records for the Network Interface 9783
Main Menu Configuration Network Circuit Records
11. Circuit Records Options 1
Dlci Number
11. Circuit Records Options 2
CIR bps
9783 0 9788 0
Committed Burst Size Bc Bits
11. Circuit Records Options 3
Excess Burst Size Be Bits
9783 9788
Outbound Management Priority
Configuring ATM for the Network Interface 9783
Main Menu Configuration Network ATM
Cell Delineation Error Event Threshold
Cell Payload Scrambling
Configuring the User Data or Virtual Router Port
Configuring the CSU/DSU’s Data Port Physical Interface
Main Menu Configuration Data Ports Physical
13. CSU/DSU Data Port Physical Interface Options 1
13. CSU/DSU Data Port Physical Interface Options 2
Transmit Clock Source
Monitor RTS Control
Monitor DTR
Configuring Frame Relay on the CSU/DSU’s Data Port
Main Menu Configuration Data Ports Frame Relay
14. CSU/DSU Frame Relay Options 1
LMI
14. CSU/DSU Frame Relay Options 2
Configuring Dlci Records
Main Menu Configuration Network Dlci Records Data Ports
Frame relay interface. Dlci
Reserved. Entry of an
15. Dlci Records 2
9720 0 9783 0 9788 0
Dlci Priority
15. Dlci Records 3
9720
16. PVC Connections 1
Configuring PVC Connections
Main Menu Configuration PVC Connections
16. PVC Connections 2
Destination Link
Destination Dlci
Destination Edlci
17. IP Path List
Configuring the IP Path List
Main Menu Configuration IP Path List Static
Management Link
Setting Up Management and Communication
Configuring Node IP Information
18. Node IP Options 1
Management MTU Size
TS Access Management Link
18. Node IP Options 2
Configuring Management PVCs
Components associated with the deleted PVC?
19. Management PVC Options 1
Payload Managed
Primary Dlci
19. Management PVC Options 2
Set DE
19. Management PVC Options 3
Primary Edlci
Primary VPI,VCI Number
VPI 0 VCI 32
19. Management PVC Options 4
Encapsulation
Configuring General Snmp Management
Name 1 Access
20. General Snmp Management Options 1
Snmp Management
Name 2 Access
20. General Snmp Management Options 2
Configuring Telnet and/or FTP Sessions
Telnet Login Required
21. Telnet and FTP Session Options 1
Telnet Session
Inactivity Timeout
21. Telnet and FTP Session Options 2
Disconnect Time Minutes
FTP Session
FTP Login Required
21. Telnet and FTP Session Options 3
FTP Max Transfer Rate Kbps
9720 1 9783 1 9788 1
Configuring Snmp NMS Security
22. Snmp NMS Security Options 1
NMS IP Validation
Number of Managers
Access Type
22. Snmp NMS Security Options 2
Configuring Snmp Traps
23. Snmp Traps Options 1
Snmp Traps
Number of Trap Managers
23. Snmp Traps Options 2
Enterprise Specific Traps
Link Traps Possible Settings Disable, Up, Down, Both
Possible Settings Network, Ports, All, None
23. Snmp Traps Options 3
Link Traps Interfaces
23. Snmp Traps Options 4
Rmon Traps
Latency Traps
IP SLV Availability Traps
Status
Configuring Ethernet Management
24. Ethernet→Management→Options 1
24. Ethernet Management Options 2
Proxy ARP
Configuring the Communication Port
25. Communication→ Port→Options 1
Port Use
Character Length
Login Required
25. Communication Port Options 2
Stop Bits
Ignore Control Leads
25. Communication Port Options 3
25. Communication Port Options 4
RIP
Configuring the COM Port to Support an External Modem
Main Menu Configuration Management and Communication
External Modem Com Port→
26. External Modem COM Port Options
Configuration Options December
Configuring the FrameSaver DSL Router
NAT and Napt Configuration Example
Ethernet
FrameSaver DSL Router Overview
DSL Network Interface
Proxy ARP
Address Resolution Protocol
IP Routing
Interface Configuration
Applications Supported by NAT
Network Address Translation
IP Options Processing
NAT Configuration Example
NAT Mapping Public IP Addresses Private IP Addresses
Save exit
Napt Mapping Public IP Address Private IP Addresses
Napt Configuration Example
Network Address Port Translation
Int ethernet 0 ip nat inside int serial 0.x ip nat outside
Access-list 1 permit 10.1.3.0
Ip nat inside source list 1 interface se 0.x overload
NAT and Napt Configuration Example
Ip nat inside source static 10.1.1.1
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Server
NAT
Dhcp Server with NAT Configuration Example
Public IP Addresses for NAT Private IP Addresses
Dhcp Server at Remote Site Configuration Example
Dhcp Relay Agent
Dhcp Relay Configuration Example
Ip dhcp server Ip route 155.1.3.254 serial
Dhcp LAN
DSL
Router Security
IP Router Filtering Bridge Filtering
IP Filtering
Land Bug Prevention
Smurf Attack Prevention
NAT DSL
Provisioning the Router Interface
Diagnostics ATM Ping D-C
Verifying the End-to-End Management Path
Configuring the Router Using Terminal Emulation
Security and Logins
Limiting Access
FTP Snmp
Controlling Asynchronous Terminal Access
Set the configuration option
External Modem Com Port
Controlling External COM Port Device Access
Controlling Telnet and FTP Access
Limiting Telnet Access
See Creating a Login for the User Interface on
Limiting FTP Access
FTP
Limiting Telnet or FTP Access Over the TS Management Link
Controlling Snmp Access
Disabling Snmp Access
Assigning Snmp Community Names and Access Levels
Limiting Snmp Access Through IP Addresses
See Configuring→General Snmp →Management in , Configuration
Largo
Controlling Router CLI Access
Access Levels Command Modes
Page
Creating a Login for the User Interface
Main Menu Control Administer Logins
Security in , Configuration Options
Field Enter
Example
Modifying a Login
Deleting a Login
Operation and Maintenance
View this field To find
Displaying Identity System Information
Main Menu Status Identity
Viewing LEDs and Control Leads
Main Menu Status Display LEDs and Control Leads
LED Descriptions
Display LEDs & Control Leads Screen for a 9783 Router
LED Descriptions 1
Label Indication Color What It Means
Control Lead Descriptions
LED Descriptions 2
Network LEDs
Port LED CSU/DSU
Control Leads Label Indication What It Means
Device Messages
Device Messages 1 What It Indicates What To Do
Seen at an FTP
Terminal
Device Messages 2 What It Indicates What To Do
Software. See Activating Software
Device Messages 3 What It Indicates What To Do
Device Messages 4 What It Indicates What To Do
See Upgrading System
Device Messages 5 What It Indicates What To Do
COM Port usage field
MaximumDHCPClients
Router CLI Messages
CLI Messages 1 What It Indicates
CLI Messages 2 What It Indicates
Start-ip-address or end-ip-address
CLI Messages 3 What It Indicates
Either pool or interface, and overload are
CLI Messages 4 What It Indicates
CLI Messages 5 What It Indicates
Status Information
Status Menu
Last Reset
System and Test Status Messages
Self-Test Results Messages
Main Menu Status System and Test Status
Health and Status Messages
Health and Status Messages 1 What It Indicates
Health and Status Messages 2 What It Indicates
Atmlink
PathIP Address Down
InterfaceDLCInnnn
IP Path Connection Status
Test Status Messages
Test Status Messages What It Indicates
Main Menu Status IP Path Connection Status
IP Path Connection Status Screen Example
IP Path Connection Status
FR Link Net1-FR1, Port-1 Frame relay link
This is the IP address
PVC Connection Status
PVC Connection Status Screen Example
PVC Connection Status Screen 1
Field Display What It Indicates
PVC Connection Status Screen 2
Edlci
Network Interface Status Screen Example
Network Interface Status
Main Menu Status Network Interface Status
IP Routing Table Management Traffic
IP Routing Table Screen Example
11. IP Routing Table Values Field What It Indicates
TTL
Performance Statistics Menu
Performance Statistics
Main Menu Status Performance Statistics
Service Level Verification Performance Statistics
13, SLV Performance Statistics for IP Enabled Dlci
Inbound Dropped
Dlci connection
Service Definitions in , Configuration Options
COS ID
Dlci Performance Statistics
Main Menu Status Performance Statistics Dlci
14. Dlci Performance Statistics 1 Field What It Indicates
CIR&EIR
Additional Performance Statistics for IP Enabled Dlci
14. Dlci Performance Statistics 2 Field What It Indicates
Frame Relay Errors
Frame Relay Performance Statistics
16. Frame Relay Performance Statistics 1 What It Indicates
Frame Relay Link
Frame Relay LMI CSU/DSUs only
Frame Relay Hdlc Errors
16. Frame Relay Performance Statistics 2 What It Indicates
OAM Operations, Administration, and Maintenance
ATM Performance Statistics 9783
17. ATM Performance Statistics What It Indicates
AAL5 ATM Adaption Layer
VCC Performance Statistics 9783
Main Menu Status Performance Statistics VCC
18. VCC Performance Statistics 1 What It Indicates
VCC Virtual Channel Connection
Shdsl Line Performance Statistics
18. VCC Performance Statistics 2 What It Indicates
Main Menu Status Performance Statistics XDSL Line
19. Shdsl Line Performance Statistics What It Indicates
20. Ethernet Performance Statistics What It Indicates
Ethernet Performance Statistics
Main Menu Status Performance Statistics Ethernet
Clearing Performance Statistics
Function key Main Menu
Frame Relay
→ →Ethernet
Trap Event Log
Trap Event Log Screen Example
FTP File Transfers
Command Definition
Initiating an FTP Session
Upgrading System Software
If the message displayed is Then
Main Menu Control Select Software Release
Determining Whether a Download Is Completed
Activating Software
Main Menu Control LMI Packet Capture Utility
Transferring Collected Data
If retrieving Then
Troubleshooting
Problem Indicators
Indicators See
Device Messages in , Operation and Maintenance
Main Menu Status Display LEDs and Control LEDs
Resetting the Unit By Cycling the Power
Resetting the Unit and Restoring Communication
Resetting the Unit from the Control Menu
Restoring Communication with an Improperly Configured Unit
If selecting Following occurs
Main Menu Control LMI Packet Capture Utility
Troubleshooting Management Link Feature
LMI Packet Capture Utility Feature
Viewing LMI Captured Packets from the User Interface
LMI Trace Log Example
Telnet Example
Telnet
Control Telnet
Alarms
Alarm Conditions 1 What It Indicates What To Do
Alarm Conditions 2 What It Indicates What To Do
CSU/DSU only minor Alarm
Only minor alarm
IPAddress
PathIP Address
Alarm Conditions 3 What It Indicates What To Do
Down minor alarm
Troubleshooting Tables
Viewing the Trap Event Log
Device Problems
Device Problems Symptom Possible Cause Solutions
ATM Problems
ATM Problems Symptom Possible Cause Solutions
Frame Relay PVC Problems
Frame Relay PVC Problems Symptom Possible Cause Solutions
Router Test Menu Example
Tests Available
CSU/DSU Test Menu Example
Test Timeout Feature
Starting and Stopping a Test
Aborting All Tests
PVC Tests
PVC Tests Screen Example
PVC Loopback
Send Pattern
Main Menu Test Network PVC Tests
Main Menu Test Data Port PVC Tests
To run a connectivity test on a link
When 5 frames out of 25 are missing or out of sequence
Monitor Pattern
Network ATM Loopback
Network ATM Loopback Tests Screen Example
For
Main Menu Test Data Port Physical Tests
Data Port Physical Tests
DTE Loopback
IP Ping Test
On page 8-29 to ping Snmp trap managers Ping Screen Example
Source IP Address
Ping Options 1
Target IP Address
Inter-Ping Delay
Response Timeout
Ping Options 2
Packet Size
Ping Responses Field Possible Values Description
IP Ping Test Procedure
Main Menu Test IP Ping
Central →site NMS, then select Start
Lamp Test
Main Menu Test Lamp Test
Setting Up OpenLane for FrameSaver Device
Setting Up the OpenLane SLM System
OpenLane Support of FrameSaver Devices
Setting Up FrameSaver Support
Ordering Advanced SLM Feature Set Activations
To Find Your License Key Number
Activation Certificate
Administering and Managing Advanced SLM Activations
Entering an Activation Certificate
Checking Activation Certificate Status
Scheduling Activations
Checking the Status of Scheduled Activations
Canceling Scheduled Activations
Accessing and Printing the Certificate Summary Report
Setting Up OpenLane for FrameSaver Device December
Setting Up Network Health for FrameSaver Device
Installation and Setup of Network Health
Discovering FrameSaver Elements
Configuring the Discovered Elements
Grouping Elements for Reports
About At-a-Glance Reports
About Service Level Reports
Generating Reports for a Group
Printed Reports
Reports Applicable to FrameSaver Devices
About Trend Reports
10-8
10-9
FrameSaver SLV Plus At-a-Glance Report
10-10
Menu Hierarchy
Menus
FrameSaver DSL CSU/DSUs Menu Structure
Administer Logins
Change Operating Mode
Reset Device
System
FrameSaver DSL Routers Menu Structure
VCC
Virtual Router Ports
Menu Hierarchy December
Snmp MIBs, Traps, and Rmon Alarm Defaults
Support Online Technical Support
MIB Support
Downloading MIBs and Snmp Traps
FrameSaver Unit’s sysObjectID system
System Group mib-2
FrameSaver Unit’s sysDescr system
Interfaces Group mib-2
Paradyne Indexes to the Interface Table ifTable
Physical Layer
Frame Relay Logical Layer
NetScout Probe Indexes to the Interface Table ifTable
Rmon Logical Layer
Interface number
Dlci number ALL
Standards Compliance for Snmp Traps
Examples
Trap authenticationFailure
Trap warmStart
Table B-3. warmStart Trap What It Indicates Possible Cause
Variable-Binding
Trap linkUp and linkDown
Table B-5. linkUp and linkDown Traps What It Indicates
Physical Sublayer
Strings
‘$ifString $alarmString down.’
MIB
ATM Logical Link Sublayer
Trap enterprise-Specific
Xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx , COS nn
Nnnn ’
‘Path xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx Up
Trap RMON-Specific
Rmon Alarm and Event Defaults
Event Defaults
EventIndex EventDescription EventType
Rising Event Operation
Network Physical Interface Alarm Defaults
Frame Relay Link Alarm Defaults
OID
Dlci Alarm Defaults
OID
CIR
6.1.2.1.2.10.32.2.1
OID Cross-References
6.1.2.1.2.2.1
6.1.4.1.1795.2.24.2.6.9.4.1.1
Dlci CIR
Dlci EIR
6.1.4.1.1795.2.24.2.6.9.4
6.1.4.1.1795.2.24.2.6.9.4.4.2
6.1.4.1.1795.2.24.2.6.9.4.5.2.1
6.1.4.1.1795.2.24.2.6.9.4.7.1
6.1.4.1.1795.2.24.2.6.9.4.10.3.1
6.1.2.1.10.32.2.1
6.1.4.1.1795.2.24.2.6.9.4
Router CLI Commands, Codes, Designations
CLI Commands
Convention Translation
Interfaces, and Basic Operation, for additional information
Router CLI Commands, Codes, and Designations
Pager Command
Access Control Commands
Table C-1. Pager Command
Table C-2. Access Control Commands
Configuration Commands
Table C-3. Configuration Commands
Configure terminal factory
Save
Command Mode config, config-if, config-subif
Interface Commands
Table C-4. Interface Commands 1
Table C-4. Interface Commands 2
Encapsulation encapsulation-type encapsulation-protocol
No frame-relay interface-dlci dlci-num
Table C-4. Interface Commands 3
No ip unnumbered null
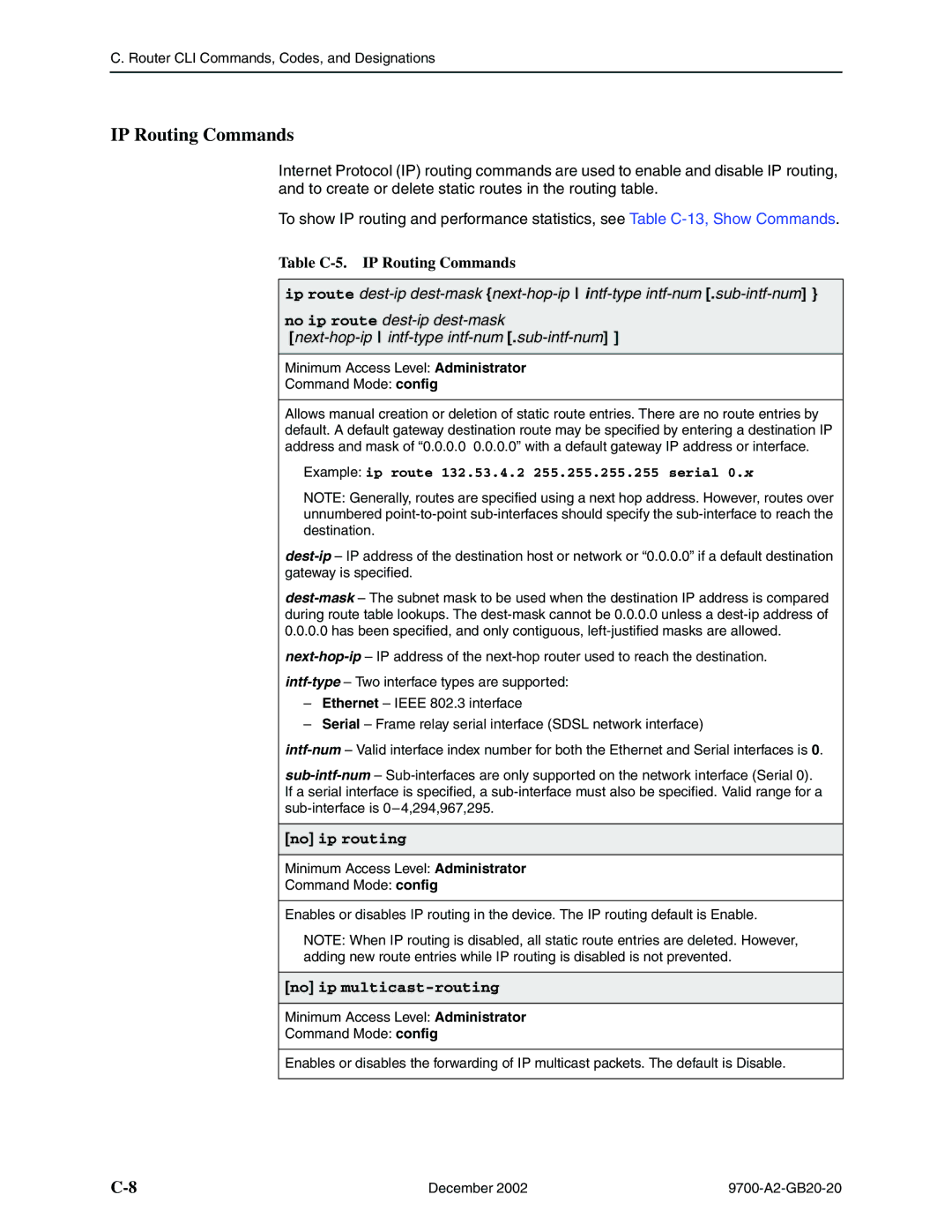
IP Routing Commands
Table C-5. IP Routing Commands
No ip routing
No ip multicast-routing
Bridge Commands
Table C-6. Bridge Commands 1
No bridge-group bridge-group
Table C-6. Bridge Commands 2
Command Mode config-if, config-subif
ARP Commands
Table C-7. ARP Commands
Arp timeout time No arp timeout time
Clear arp-cache
No ip nat inside outside
NAT Commands
Table C-8. NAT Commands 1
Table C-8. NAT Commands 2
Ip nat pool pool-name start-ip-addr end-ip-addr
Netmask netmask prefix-length / prefix-length
No ip nat pool pool-namestart-ip-addr end-ip-addr
From previous
Table C-8. NAT Commands 3
Clear ip nat translation
Dhcp Server Commands
Table C-9. Dhcp Server Commands 1
No service dhcp
No ip dhcp pool pool-name
Table C-9. Dhcp Server Commands 2
Default-router ip-address No default-router ip-address
Domain-name domain-name No domain-name domain-name
Dns-server ip-address No dns-server ip-address
Table C-9. Dhcp Server Commands 3
Network network-num
No ip dhcp-server ip-address
Dhcp Relay Agent Commands
Table C-10. Dhcp Relay Agent Commands
Filter access-list Commands
Table C-11. Filter Commands 1
Access-list access-list-numpermit deny
No access-list access-list-numpermit deny
Table C-11. Filter Commands 2
For Extended IP Access Lists
Table C-11. Filter Commands 3
For Protocol Type Access Lists
Table C-11. Filter Commands 4
No ip access-group access-list-1-199numin out
Diagnostic Commands
Table C-12. Diagnostic Commands 1
Table C-12. Diagnostic Commands 2
Traceroute protocol dest-ipsource source-ip length bytes
Show Commands
Table C-13. Show Commands 1
Show configuration
Show arp
Table C-13. Show Commands 2
Show configuration saved unsaved
Show frame-relay map
Show interface intf-type intf-num .sub-intf-num
Table C-13. Show Commands 3
Show ip dhcp binding ip-address
Show ip nat translations
Show ip route ip-address
Show spanning-tree
Table C-13. Show Commands 4
Show ip traffic
Ethernet Type Codes
Table C-14. Ethernet Type Codes Hex 1 Description
Table C-14. Ethernet Type Codes Hex 2 Description
All 3 n = Destination unreachable
Protocol and Port Designations
Icmp Designations
All 5 n = All redirects
TCP Port Designations
UDP Port Designations
Router Command Line Summaries Shortcuts
CLI Summaries
Intf-type intf-num .sub-intf-num
Show Command Summary
Table D-1. Show Commands Function
Access Control and System Level Command Summary
Table D-2. Access Control and System Level Commands Function
CLI Command Summary
Table D-3. CLI Commands 1
Clear counters intf-type intf-num .sub-intf-num
Dns-serverip-address
Table D-3. CLI Commands 2
Encapsulation encapsulation-type encapsulation-protocol
CLI Command Default Settings
Connectors, Cables, and Pin Assignments
Rear Panels
Figure E-1. Model 9720 CSU/DSU Rear Panel
Figure E-4. Model 9783 Router Rear Panel
RJ48C
Table E-1. DSL Network Interface Connector Pin # Signal
DSL Network Interface and Cable
Model 9783 COM Port Connector
Model 9720 and 9788 COM Port Connector
Ethernet Port Connector
Model 9720 and 9783 CSU/DSU Data Port Connector
Table E-5. Model 9720 and 9783 CSU/DSU Data Port Connector
Signal Number Direction Pin
Standard V.35 Straight-through Cable
Signal Mnemonic Number Direction Pin
Model 9788 CSU/DSU Data Port Connector
Table E-6. Model 9788 CSU/DSU Data Port Connector Circuit
Signal Plug Socket
EIA-530-A-to-V.35 Adapter
EIA-530-A-to-X.21 Adapter
Configuring an External Modem
Enter AT Command To configure the modem to
DB25-to-DB25 Crossover Cable
TXD RXD RTS DSR
CD Rlsd RXC DTR Xtxc
RXC DTR Xtxc
Pin
DB9-to-DB25 Crossover Cable
Pin
Connectors, Cables, and Pin Assignments December
Technical Specifications
COM Port
COM Port 9720
DSL Network Interface
Ethernet Port
Equipment List
Equipment
Description Model Number
FrameSaver DSL 9720 CSU/DSUs
FrameSaver DSL 9783 DSU/CSUs
FrameSaver DSL 9788 CSU/DSUs
FrameSaver DSL 9788 Routers
FrameSaver SLV Upgrade
FrameSaver DSL 9783 Routers
Optional Housing Mounting Kit Features
NMS Products
Description Part Number Feature Number
For connection to an external device with a DB9 connector
Cables
For use in the U.S
Equipment List December
Index
Numerics
IN-2
IN-3
COS
IN-4
IN-5
Idsl
IP SLV
IN-7
IN-8
IN-9
IN-10
PVC Rmon
SLV
Shdsl
SLM
IN-12
IN-13
IN-14