Using this Handbook
This handbook was produced for practical application of the SHARP
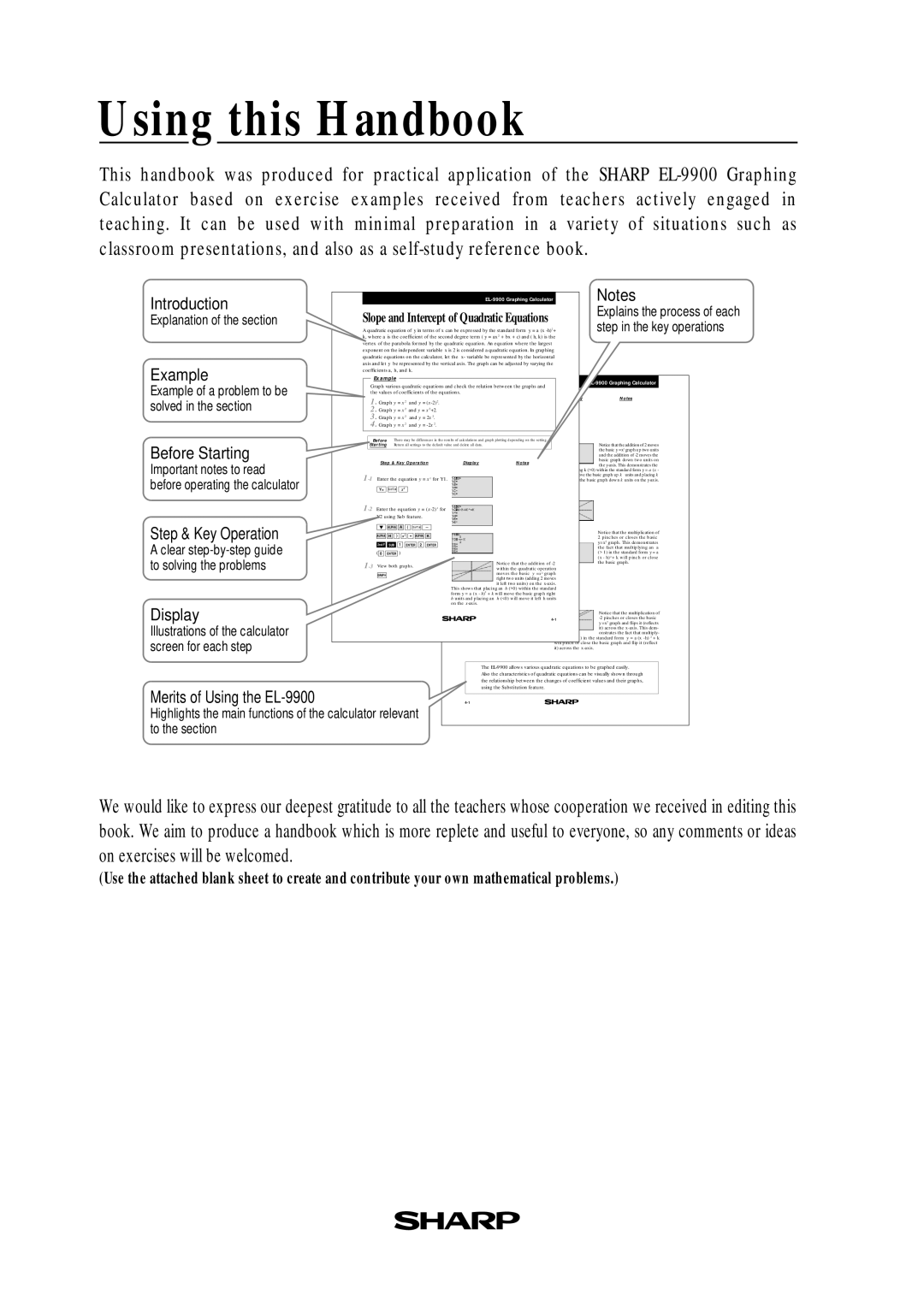
Introduction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||
| Slope and Intercept of Quadratic Equations |
| Explains the process of each | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Explanation of the section |
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| step in the key operations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| A quadratic equation of y in terms of x can be expressed by the standard form y = a (x |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| k, where a is the coefficient of the second degree term ( y = ax2 + bx + c) and ( h, k) is the |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| vertex of the parabola formed by the quadratic equation. An equation where the largest |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| exponent on the independent variable x is 2 is considered a quadratic equation. In graphing |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| quadratic equations on the calculator, let the x- variable be represented by the horizontal |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Example |
| axis and let y be represented by the vertical axis. The graph can be adjusted by varying the |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Example |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
| coefficients a, h, and k. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
Example of a problem to be |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
| Graph various quadratic equations and check | the relation between the graphs and |
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| the values of coefficients of the equations. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||
solved in the section |
| 1. Graph y = x 2 | and y = |
|
|
| Step & Key Operation |
|
|
|
| Display |
| Notes | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
| *Use either pen touch or cursor to operate. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Graph y = x | and y = x +2. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
|
| 2. |
|
|
|
| 2 |
| 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
|
| 3. Graph y = x 2 | and y = 2x 2. | Change the equation in Y2 to y = x +2. |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| 4. Graph y = x 2 | and y = |
|
|
| Y= |
|
|
|
|
|
| 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
|
|
|
| * | 2nd F |
| SUB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ENTER | 2 | ENTER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
| Before |
|
| There may be differences in the results of calculations and graph plotting depending on the setting. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Before Starting |
| Starting |
|
| Return all settings to the default value and | both graphs. |
|
|
|
|
| Notice that the addition of 2 moves | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| basic graph down two units on | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| the basic y =x2 graph up two units | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| GRAPH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| and the addition of | |||
Important notes to read |
|
| Step & Key Operation |
| Display |
|
|
|
|
| Notes |
|
|
|
|
| the | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| h)2 |
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| + k will move the basic graph up k units and placing k | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| fact that adding k (>0) within the standard form y = a (x - | ||||||
before operating the calculator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (<0)k will move the basic graph down k units on the | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Y= |
| X/θ /T/n | x2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| axis. |
|
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| the equation in Y2 to y = 2x2. |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
| Enter the equation y = | for |
| Y= |
|
|
|
|
| 2 | ENTER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||
| * | 2nd F |
| SUB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Y2 using Sub feature. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0 ENTER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
Step & Key Operation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ( X/θ /T/n — |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
| ALPHA |
| A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2 pinches2 | or closes the basic | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| x2 | + |
|
|
|
| View both graphs. |
|
|
|
|
| Notice that the multiplication of | |||||||||||||
|
|
| ALPHA |
| H | ) | ALPHA |
| K |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
A clear |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 ENTER | 2 ENTER |
|
|
| GRAPH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| y=x graph. This demonstrates | ||||||||
|
| 2nd F |
| SUB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||
| ( 0 | ENTER | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (x - h)2 + k will pinch or close | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| the fact that multiplying an a | |||
to solving the problems |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (> 1) in the standard form y = a | ||||
| View both graphs. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| within the quadratic operation |
| the basic graph. | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Notice that the addition of |
| ||||||||||||
|
|
| GRAPH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| moves the basic | y =x2 graph |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Change rightthe equationtwo unitsin(addingY2 to 2 moves |
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| y = |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| This shows that placing an h (>0) within the standard |
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| form y = a (x - hY=)2 + k will | move2nd F |
| theSUB |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| h units and placing an h (<0)* will move it left h units |
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
Display |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| on the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| GRAPH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| y =x2 graph and flips it (reflects | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| View both graphs. |
|
|
|
|
| Notice that the multiplication of | ||||||||||||
Illustrations of the calculator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ing an a | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| it) across the | |||
screen for each step |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| onstrates the fact that multiply- | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| will pinch or | close the basic graph and flip it (reflect | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| it) across the |
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| The |
| ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Also the characteristics of quadratic equations can be visually shown through |
| ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| the relationship between the changes of coefficient values and their graphs, |
| ||||||||||||||
Merits of Using the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| using the Substitution feature. |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Highlights the main functions of the calculator relevant to the section
We would like to express our deepest gratitude to all the teachers whose cooperation we received in editing this book. We aim to produce a handbook which is more replete and useful to everyone, so any comments or ideas on exercises will be welcomed.
(Use the attached blank sheet to create and contribute your own mathematical problems.)