MGS3700-12C
Page
About This Users Guide
Intended Audience
Need More Help?
Document Conventions
Syntax Conventions
Icons Used in Figures
Dslam
Safety Warnings
Safety Warnings MGS3700-12C User’s Guide
Contents Overview
IP Application 335
Table of Contents
Chapter Initial Setup Example
115
Chapter Static MAC Forward Setup 137
173
Chapter Classifier 211
255
Chapter Loop Guard 295
335
357
413
Part VII Appendices and Index
Part
Page
Introduction
Getting to Know Your Switch
Backbone Application
Bridging Example
Backbone Application
Ieee 802.1Q Vlan Application Examples
High Performance Switching Example
Tag-based Vlan Example
Ways to Manage the Switch
IPv6 Support
Good Habits for Managing the Switch
Getting to Know Your Switch MGS3700-12C User’s Guide
Installation Scenarios
Hardware Installation and Connection
Desktop Installation Procedure
Rack-mounted Installation Requirements
Mounting the Switch on a Rack
Precautions
Attaching the Mounting Brackets to the Switch
Attaching the Mounting Brackets
Mounting the Switch on a Rack
Mounting the Switch on a Rack
Hardware Overview
Front Panel
Front Panel Connections
Label Description
Console Port
Gigabit Ethernet Ports
Mini-GBIC Slots
Default Ethernet Negotiation Settings
Auto-crossover
Transceiver Installation
Transceiver Removal
Power Connector
Management Port
AC Power Connection
DC Power Connection
Signal Slot
Connect a Sensor to the Signal Slot
Output
Rear Panel
LEDs
LED Descriptions
LED Color Statu Description
Configuring the Switch
Hardware Overview
Hardware Overview MGS3700-12C User’s Guide
Web Configurator
System Login
Web Configurator Layout
Web Configurator Login
Basic Setting Advanced Application IP Application Management
Navigation Panel Sub-links Overview
Link Description
Navigation Panel Links
Vlan
AAA
Dhcp
Saving Your Configuration
Change Your Password
Resetting the Switch
Switch Lockout
Reload the Configuration File
Resetting the Switch Via the Console Port
Logging Out of the Web Configurator
Help
Web Configurator MGS3700-12C User’s Guide
Overview
Initial Setup Example
Creating a Vlan
Setting Port VID
Initial Setup Network Example Port VID
Configuring Switch Management IP Address
Initial Setup Example Management IP Address
Click Basic Setting IP Setup in the navigation panel
Initial Setup Example MGS3700-12C User’s Guide
How to Use Dhcp Snooping on the Switch
Tutorials
Tutorial Settings in this Tutorial
Host Port Vlan Pvid Dhcp Snooping Connected Port Trusted
Tutorial Tag Untagged Frames
Tutorial Set the Dhcp Server Port to Trusted
How to Use Dhcp Relay on the Switch
Dhcp Relay Tutorial Introduction
Vlan
Tutorial Set Vlan Type to 802.1Q
Tutorial Create a Static Vlan
Configuring Dhcp Relay
Tutorial Add Tag for Frames Received on Port
How to Use PPPoE IA on the Switch
Troubleshooting
Configuring Switch a
Settings in This Tutorial
Tutorials
Configuring Switch B
Tutorials
Tutorials
How to Use Error Disable and Recovery on the Switch
Tutorials
How to Set Up a Guest Vlan
Creating a Guest Vlan
Tutorials
Enabling Ieee 802.1x Port Authentication
Enabling Guest Vlan
How to Do Port Isolation in a Vlan
Internet
Tutorials
Tutorials
Creating a Private Vlan Rule
Click Advanced Application Private Vlan
Tutorials MGS3700-12C User’s Guide
Basic Configuration
Page
System Status and Port Statistics
Status
Port Status Summary
Lacp
Up Time
Status Port Details
Status Port Details
HOL
RX CRC
Basic Setting
System Information
100
101
MAX
MIN
RPM
General Setup
102
103
104
Introduction to VLANs
Select First , Sunday , November
Smart Isolation
105
Port Setup screen
Switch Setup Screen
106
Switch. Smart isolation does not work with Mstp and/or port
107
Vlan port isolation or private Vlan and Mrstp on
Based Vlan
Management IP Addresses
IP Setup
108
Basic Setting IP Setup
109
110
VID
111
In-band IP Addresses
Port Setup
Some web configurator screens
112
Make them
113
Half Duplex, 100M/Full Duplex and 1000M/Full Duplex
Queue tag. See Priority Queue Assignment in on page 106 for
Bpdu
114
Part
115
116
Introduction to Ieee 802.1Q Tagged VLANs
117
Tpid
CFI Vlan ID
Automatic Vlan Registration
Forwarding Tagged and Untagged Frames
Garp
Gvrp
Port Vlan Trunking
119
Ieee 802.1Q Vlan Terminology
Vlan Term Description Parameter
Static Vlan
Select the Vlan Type
120
Static Vlan Status
121
Vlan Details
Configure a Static Vlan
122
123
Active
124
125
Configure Vlan Port Settings
Gvrp
Subnet Based VLANs
126
Pvid
Untag Only
Configuring Subnet Based Vlan
127
Advanced Application Vlan Vlan Port Setting Subnet Based
128
Protocol Based VLANs
129
Configuring Protocol Based Vlan
130
131
Are not allowed to be used for protocol based VLANs
Create an IP-based Vlan Example
Port-based Vlan Setup
132
133
Configure a Port-based Vlan
134
135
Port Based Vlan Setup
Choose All connected or Port isolation
136
Configuring Static MAC Forwarding
Static MAC Forward Setup
137
138
Advanced Application Static MAC Forwarding
139
140
Static Multicast Forwarding Overview
Static Multicast Forward Setup
141
Configuring Static Multicast Forwarding
142
143
Advanced Application Static Multicast Forwarding
144
Filtering
Configure a Filtering Rule
145
146
MAC
Spanning Tree Protocol
13.1 STP/RSTP Overview
STP Terminology
147
How STP Works
148
STP Path Costs
Link Recommended Allowed Speed Value Range
STP Port States
Multiple Rstp
149
STP Port States
150
Multiple STP
Mstp Network Example
151
MST Region
MST Instance
152
Common and Internal Spanning Tree Cist
Spanning Tree Protocol Status Screen
153
Spanning Tree Configuration
154
Configure Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
Configuration screen to enable Rstp on the Switch
155
Rstp
156
Bridge Protocol Data Unit Bpdu
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Status
157
158
Configuration screen to enable Mrstp on the Switch
Configure Multiple Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
159
160
Multiple Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Status
161
162
Configure Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
163
Configuration screen to enable Mstp on the Switch
164
165
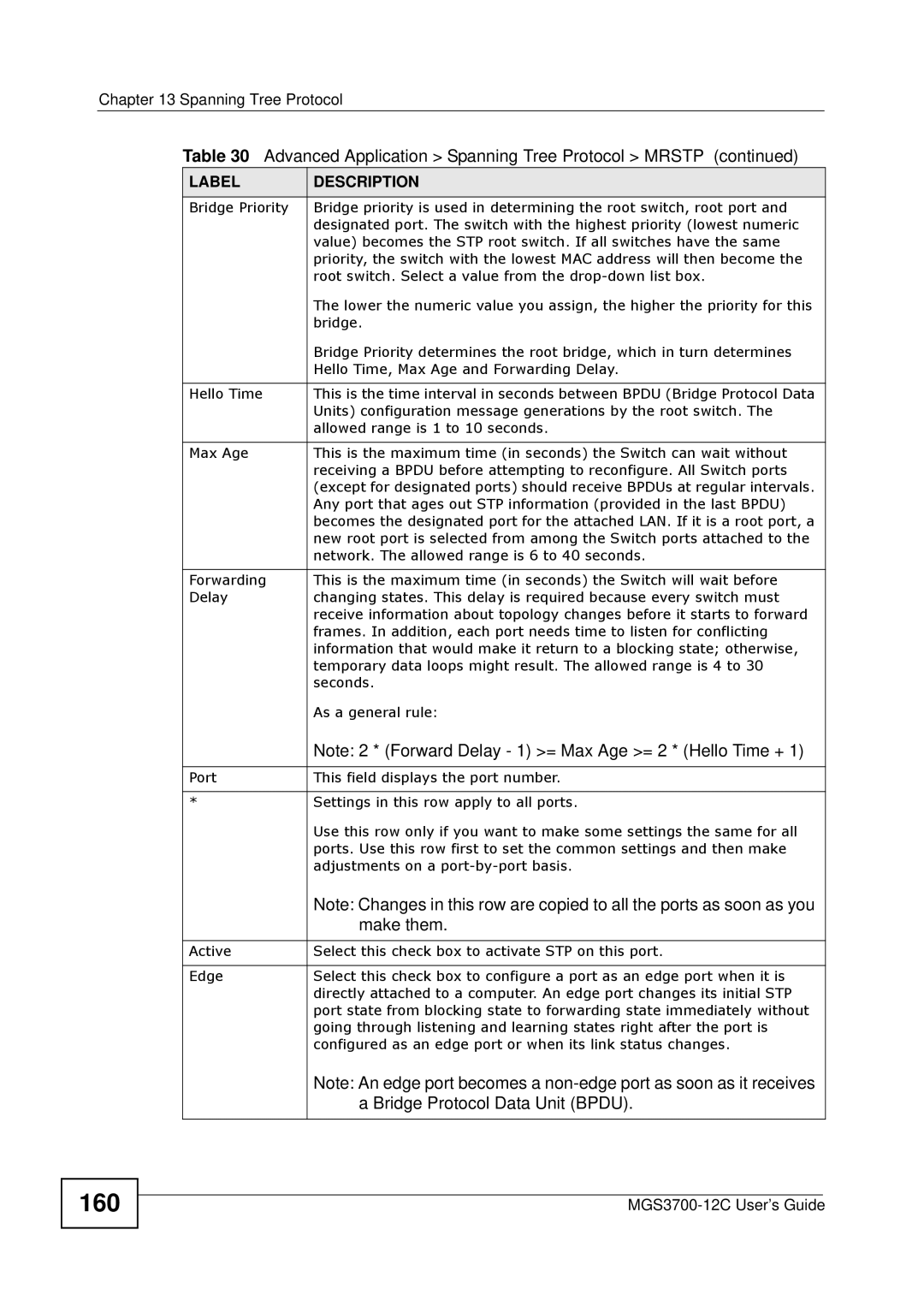
Bridge Priority
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol Status
166
CST
167
Msti
168
Bandwidth Control
Bandwidth Control Overview
CIR and PIR
169
Bandwidth Control Setup
170
171
172
Broadcast Storm Control
Broadcast Storm Control Setup
173
174
Mirroring
Port Mirroring Setup
175
176
RMirror Overview
RMirror
177
RMirror Configuration
178
Source
179
180
Advanced Application Mirroring RMirror Source
Destination
181
182
Advanced Application Mirroring RMirror Destination
Connected Port
183
184
Link Aggregation
Link Aggregation Overview
Dynamic Link Aggregation
185
Link Aggregation ID Local Switch
Link Aggregation ID Peer Switch
Link Aggregation ID
186
Link Aggregation Status
187
188
Link Aggregation Setting
189
190
Port in an active trunk group
191
Link Aggregation Control Protocol
Dynamic link aggregation
Static Trunking Example
192
193
Trunking Example Physical Connections
194
Port Authentication
Port Authentication Overview
Ieee 802.1x Authentication
195
MAC Authentication
196
Port Authentication Configuration
197
Activate Ieee 802.1x Security
Before configuring it on each port
198
Guest Vlan
199
200
Guest Vlan Example
201
Activate MAC Authentication
202
Lower value, then it supersedes this setting. See Section
203
204
About Port Security
Port Security
205
206
Port Security Setup
Forwarding screen
207
Vlan MAC Address Limit
208
209
210
Configuring the Classifier
Classifier
About the Classifier and QoS
211
212
Untagged , Ethernet II tagged and Ethernet II untagged
213
Dscp
You configure the socket numbers
Viewing and Editing Classifier Configuration
214
215
Classifier Summary Table
Common Ethernet Types and Protocol Numbers
Common IP Protocol Types and Protocol Numbers
Classifier Example
216
Common TCP and UDP Port Numbers
Protocol Name TCP/UDP Port Number
217
Classifier Example
218
Policy Rule
Policy Rules Overview
DiffServ
Dscp and Per-Hop Behavior
Configuring Policy Rules
220
221
Advanced Application Policy Rule
222
TOS
Select Do not drop the matching frame previously marked for
Select Send the packet to priority queue to put the packets
Viewing and Editing Policy Configuration
223
224
Policy Example
225
226
Weighted Fair Queuing
Queuing Method
Queuing Method Overview
Strictly Priority Queuing
Weighted Round Robin Scheduling WRR
228
Configuring Queuing
229
230
Vlan Stacking
Vlan Stacking Overview
Vlan Stacking Example
231
Vlan Stacking Port Roles
232
Vlan Tag Format
Frame Format
233
Vlan Tag Format
Configuring Vlan Stacking
234
802.1Q Frame
VID Vlan ID FCS
Port-based Q-in-Q
235
Them
This screen at a time
236
Spvid
237
Selective Q-in-Q
Cvid
238
Multicast
Multicast Overview
IP Multicast Addresses
Igmp Filtering
Multicast Status
Igmp Snooping
Igmp Snooping and VLANs
240
Multicast Setting
241
Join multicast groups
242
You make them
Setting Igmp Filtering Profile screen
243
Igmp Snooping Vlan
244
245
Setting screen first
Screen
246
Igmp Filtering Profile
Start Address and End Address fields
247
MVR Overview
Profile
Types of MVR Ports
MVR Modes
How MVR Works
248
General MVR Configuration
249
250
Compatible
MVR Group Configuration
251
252
Mvlan
MVR Configuration Example
253
MVR Group Configuration Example
254
Authentication, Authorization and Accounting AAA
255
AAA Screens
Local User Accounts
Radius and TACACS+
256
Radius Server Setup
257
258
Shared Secret
TACACS+ Server Setup
259
260
AAA Setup
261
262
Method 2 and Method 3 fields
263
Vendor Specific Attribute
264
Supported VSAs
Function Attribute
265
Supported Radius Attributes
Tunnel Protocol Attribute
Attributes Used for Authentication
Attributes Used for Authenticating Privilege Access
Attributes Used to Login Users
Attributes Used by the Ieee 802.1x Authentication
Attributes Used for Accounting
267
Attributes Used for Accounting System Events
Attributes Used for Accounting Exec Events
Attributes Used for Accounting Ieee 802.1x Events
268
Radius Attributes Exec Events via
IP Source Guard Overview
IP Source Guard
269
Dhcp Snooping Overview
270
Trusted vs. Untrusted Ports
Dhcp Snooping Database
271
Configuring Dhcp Snooping
Dhcp Relay Option 82 Information
272
ARP Inspection Overview
ARP Inspection and MAC Address Filters
Configuring ARP Inspection
IP Source Guard
273
Syslog
IP Source Guard Static Binding
274
275
IP Source Guard Static Binding
276
Dhcp Snooping
277
Configure screen. See .5 on
278
279
Dhcp Snooping Configure
280
Dhcp requests will not succeed
281
Vlan too
Dhcp Snooping Port Configure
282
Dhcp Snooping Vlan Configure
283
Dhcp Snooping Configure screen. See .5 on
284
285
ARP Inspection Status
Delete
ARP Inspection Vlan Status
286
ARP Inspection Log Status
287
ARP Inspection Vlan Configure screen, you can
ARP Inspection Configure
288
289
Syslog rate and Log interval
290
ARP Inspection Port Configure
Interval
ARP Inspection Port Configure
291
ARP Inspection Vlan Configure
292
293
294
Loop Guard
Loop Guard Overview
295
STP
Switch in Loop State
296
Loop Guard Setup
297
298
Vlan Mapping
Vlan Mapping Overview
Vlan Mapping Example
299
Enabling Vlan Mapping
300
301
Configuring Vlan Mapping
Translated VID field
302
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Overview
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
303
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Mode
304
Configuring Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
305
UDLD, and Pagp on the access ports only
306
SFlow Overview
SFlow
307
SFlow Configuration
308
SFlow Collector Configuration
309
310
Error Diable
Error-Disable Recovery Overview
CPU Protection Overview
311
CPU Protection Configuration
Error Disable Screen
312
Error-Disable Detect Configuration
313
Errdisable CPU protection screen
314
Error-Disable Recovery Configuration
315
316
PPPoE
PPPoE Intermediate Agent Overview
PPPoE Intermediate Agent Tag Format
317
Sub-Option Format
318
PPPoE IA Circuit ID Sub-option Format User-defined String
PPPoE IA Remote ID Sub-option Format
32.2.1.2 WT-101 Default Circuit ID Syntax
Port State
319
PPPoE IA Circuit ID Sub-option Format Defined in WT-101
PPPoE Intermediate Agent
PPPoE
320
321
PPPoE IA Per-Port
Application PPPoE Intermediate Agent Port screen or for a
322
Advanced Application PPPoE Intermediate Agent Port
Untrusted
323
Advanced Application PPPoE Intermediate Agent Port
PPPoE IA Per-Port Per-VLAN
324
PPPoE IA for Vlan
325
326
Private Vlan Overview
Private Vlan
327
Configuring Private Vlan
328
329
330
Green Ethernet Overview
Green Ethernet
331
Configuring Green Ethernet
332
333
334
IP Application
335
336
Static Routing Overview
Static Route
337
Configuring Static Routing
338
339
340
DiffServ Overview
Differentiated Services
341
DiffServ Network Example
Two Rate Three Color Marker Traffic Policing
342
TRTCM-Color-blind Mode
343
TRTCM-Color-aware Mode
Activating DiffServ
344
PIR?
345
IP Application DiffServ
Configuring 2-Rate 3 Color Marker Settings
346
DSCP-to-IEEE 802.1p Priority Settings
Default DSCP-IEEE 802.1p Mapping
347
Dscp Value
Configuring Dscp Settings
348
Dhcp Configuration Options
Dhcp Overview
Dhcp Modes
349
Dhcp Status
Dhcp Relay
Dhcp Relay Agent Information
350
Configuring Dhcp Global Relay
General Setup
351
Relay Agent Information
352
Global Dhcp Relay Configuration Example
VLAN1VLAN2
Configuring Dhcp Vlan Settings
353
Example Dhcp Relay for Two VLANs
General Setup screen
354
Dhcp Relay for Two VLANs Configuration Example
Dhcp Relay for Two VLANs
356
Management
357
358
Maintenance Screen
Maintenance
359
Load Factory Default
Save Configuration
Settings to the current configuration on the Switch
360
Firmware Upgrade
Reboot System
361
Restore a Configuration File
362
Backup a Configuration File
FTP Command Line
Filename Conventions
363
FTP Command Line Procedure
Example FTP Commands
364
Filename Conventions
Command Description
GUI-based FTP Clients
FTP Restrictions
365
366
Access Control
Access Control Overview
Access Control Main Screen
Access Control Overview
About Snmp
368
Snmp Commands
Snmp v3 and Security
Supported MIBs
369
Snmp Traps
370
Snmp System Traps
Option Object Label Object ID Description
371
Snmp InterfaceTraps
372
AAA Traps
373
Snmp Switch Traps
Snmp IP Traps
374
Configuring Snmp
CFM
375
Version
Specify in this section to create accounts on the Snmp
Manager
Security level or higher than the security level settings on
376
Configuring Snmp Trap Group
377
Setting Up Login Accounts
378
SSH Overview
379
How SSH works
380
SSH Implementation on the Switch
Requirements for Using SSH
Introduction to Https
381
Internet Explorer Warning Messages
Https Example
382
Netscape Navigator Warning Messages
383
Security Certificate 1 Netscape
Security Certificate 2 Netscape
Main Screen
Service Port Access Control
385
Remote Management
386
HTTP/ICMP
387
SNMP/SSH Https
388
Diagnostic
Diagnostic
389
390
Syslog
Syslog Overview
391
Syslog Severity Levels
Syslog Setup
392
Syslog Server Setup
393
394
ZyXEL Clustering Management Specifications
Cluster Management
Cluster Management Status Overview
395
Cluster Management Status
396
397
Cluster Member Switch Management
Manager
Uploading Firmware to a Cluster Member Switch
398
FTP Upload to Cluster Member Example
399
FTP Parameter Description
Clustering Management Configuration
400
Based Vlan
401
Candidate list
402
MAC Table Overview
MAC Table
403
Viewing the MAC Table
404
405
406
ARP Table
ARP Table Overview
How ARP Works
407
Viewing the ARP Table
408
Configure Clone
Configure Clone
409
410
411
412
Troubleshooting Product Specifications
413
414
Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs
Troubleshooting
415
Switch Access and Login
416
417
Advanced Suggestions
Switch Configuration
418
Product Specifications
Hardware Specifications
Specification Description
419
Feature Description
Firmware Specifications
420
421
Queuing
422
Feature Specifications
423
424
MVR
Standards Supported
425
Standard Description
BRIDGE-MIB, Q-BRIDGE-MIB
426
EMC
Fan Module Removal and Installation
427
428
Appendices Index
429
430
431
Commonly Used Services
Name Protocol Ports Description
432
433
434
Certifications
Copyright
435
436
FCC Warning CE Mark Warning
ZyXEL Limited Warranty
437
438
Index
439
Numbers
ARP
440
441
442
MIB
443
Mrstp
444
445
SPQ
446
Trtcm
447
Vlan 104
448