MP-11x & Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
3.3.2.4.2Number Normalization Examples
Two examples are provided below for number normalization. The examples are based on the following assumptions: a PBX with prefix (local) number 333 and a
Modifying E.164 Numbers to PBX Format for Outbound Calls: Outbound calls refer to calls made by Office Communications Server 2007 users (OCS clients) connected through IP to the Office Communications Server 2007.
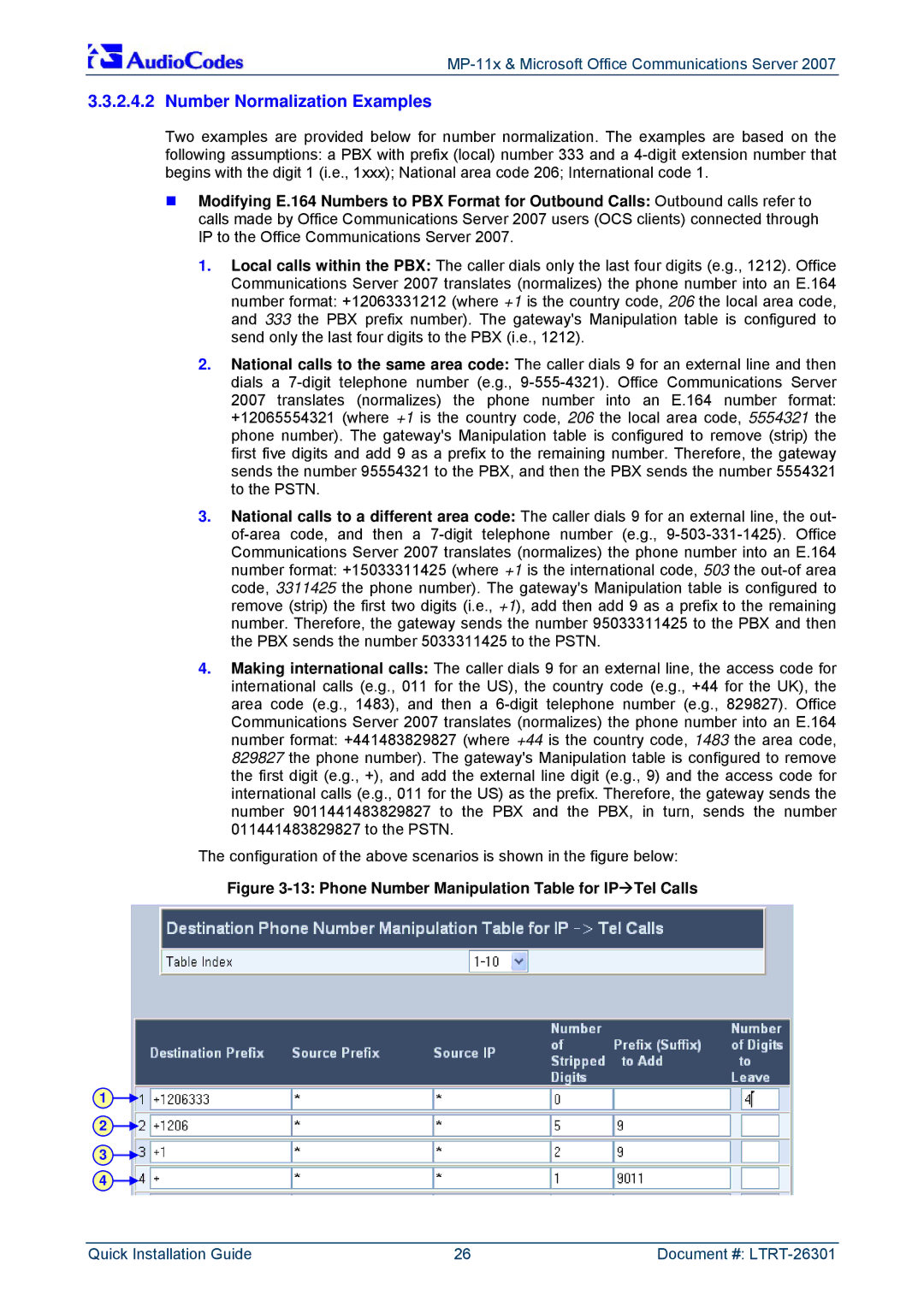
1.Local calls within the PBX: The caller dials only the last four digits (e.g., 1212). Office Communications Server 2007 translates (normalizes) the phone number into an E.164 number format: +12063331212 (where +1 is the country code, 206 the local area code, and 333 the PBX prefix number). The gateway's Manipulation table is configured to send only the last four digits to the PBX (i.e., 1212).
2.National calls to the same area code: The caller dials 9 for an external line and then dials a
2007 translates (normalizes) the phone number into an E.164 number format: +12065554321 (where +1 is the country code, 206 the local area code, 5554321 the phone number). The gateway's Manipulation table is configured to remove (strip) the first five digits and add 9 as a prefix to the remaining number. Therefore, the gateway sends the number 95554321 to the PBX, and then the PBX sends the number 5554321 to the PSTN.
3.National calls to a different area code: The caller dials 9 for an external line, the out-
4.Making international calls: The caller dials 9 for an external line, the access code for international calls (e.g., 011 for the US), the country code (e.g., +44 for the UK), the area code (e.g., 1483), and then a
The configuration of the above scenarios is shown in the figure below:
Figure 3-13: Phone Number Manipulation Table for IPÆTel Calls
1![]()
2
3
4
Quick Installation Guide | 26 | Document #: |