Overview
Client-to-CSM-to-Server Traffic Flow
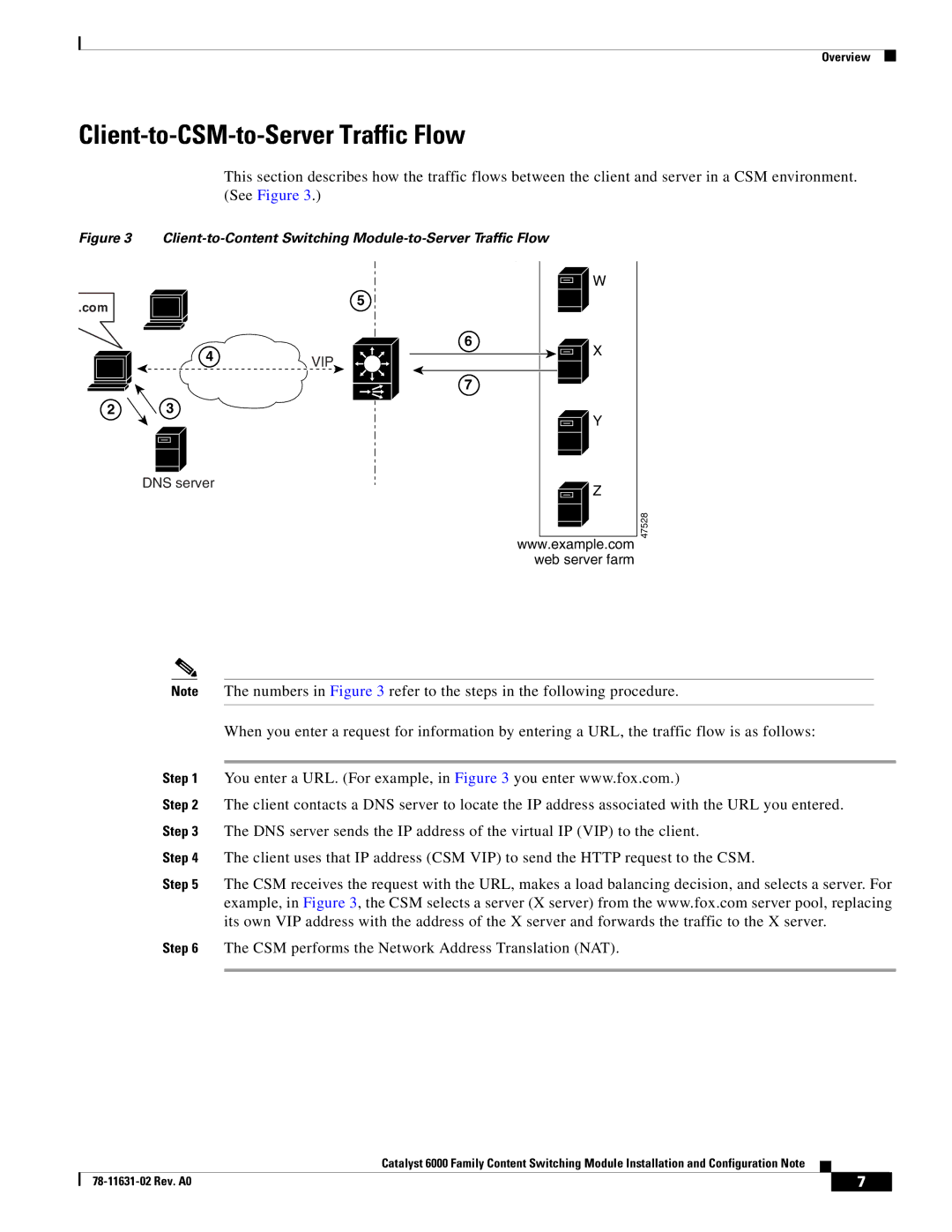
This section describes how the traffic flows between the client and server in a CSM environment. (See Figure 3.)
Figure 3 Client-to-Content Switching Module-to-Server Traffic Flow
.com | 5 |
|
4VIP
2 ![]()
![]() 3
3
DNS server
W
6![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() X
X
7
Y
Z
www.example.com web server farm
47528
Note The numbers in Figure 3 refer to the steps in the following procedure.
When you enter a request for information by entering a URL, the traffic flow is as follows:
Step 1 You enter a URL. (For example, in Figure 3 you enter www.fox.com.)
Step 2 The client contacts a DNS server to locate the IP address associated with the URL you entered. Step 3 The DNS server sends the IP address of the virtual IP (VIP) to the client.
Step 4 The client uses that IP address (CSM VIP) to send the HTTP request to the CSM.
Step 5 The CSM receives the request with the URL, makes a load balancing decision, and selects a server. For example, in Figure 3, the CSM selects a server (X server) from the www.fox.com server pool, replacing its own VIP address with the address of the X server and forwards the traffic to the X server.
Step 6 The CSM performs the Network Address Translation (NAT).
|
| Catalyst 6000 Family Content Switching Module Installation and Configuration Note |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
| 7 |
| |
|
|
|
|