Configuring
DLSw+ Configuration Examples
dlsw
ip address 10.2.24.3 255.255.255.0
int e1
ip address 150.150.2.2 255.255.255.0
dlsw transparent
Router C
dlsw
ip address 10.2.24.4 255.255.255.0
int e1
ip address 150.150.2.3 255.255.255.0
dlsw transparent
Router D
dlsw
DLSw+ with Ethernet Redundancy Enabled for Switch Support Configuration Example
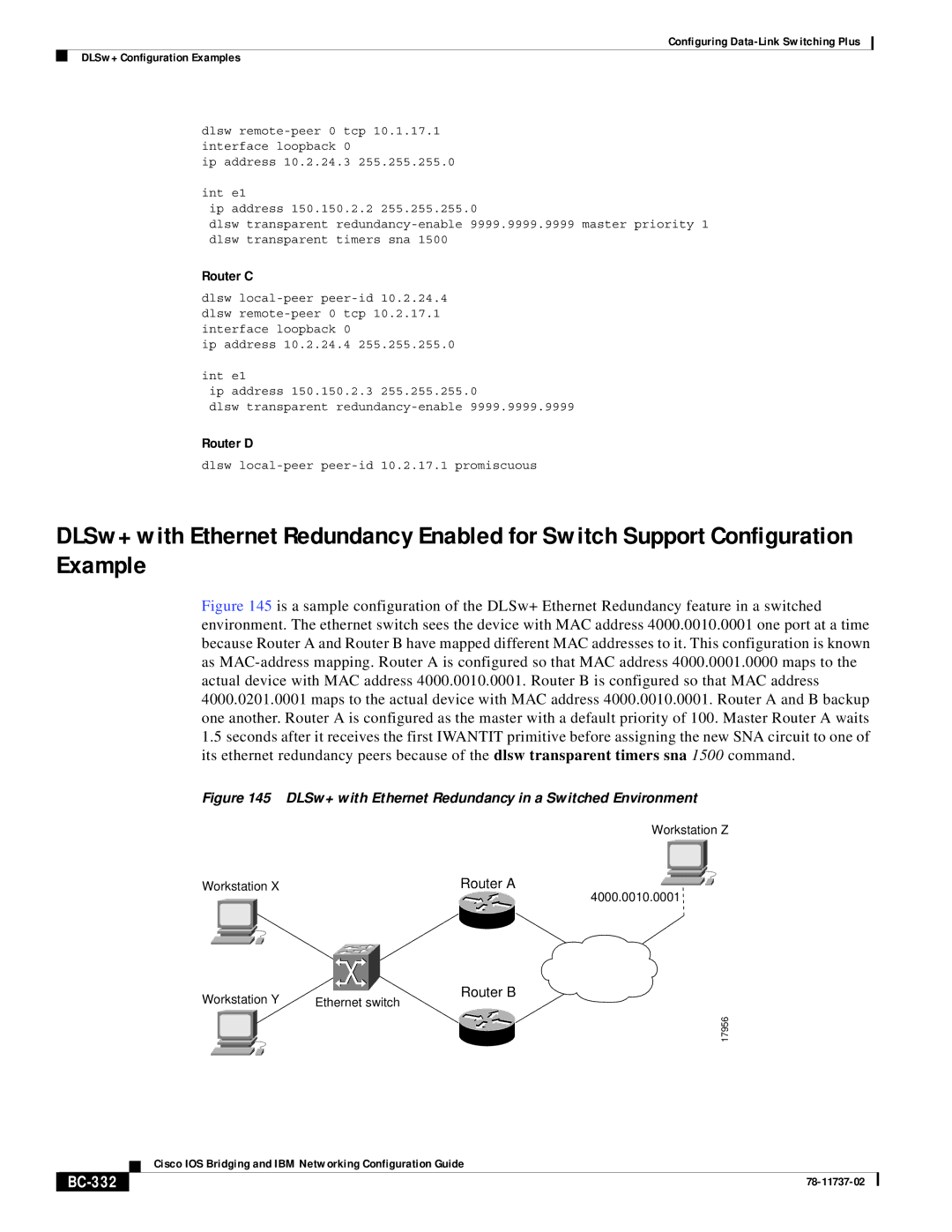
Figure 145 is a sample configuration of the DLSw+ Ethernet Redundancy feature in a switched environment. The ethernet switch sees the device with MAC address 4000.0010.0001 one port at a time because Router A and Router B have mapped different MAC addresses to it. This configuration is known as MAC-address mapping. Router A is configured so that MAC address 4000.0001.0000 maps to the actual device with MAC address 4000.0010.0001. Router B is configured so that MAC address 4000.0201.0001 maps to the actual device with MAC address 4000.0010.0001. Router A and B backup one another. Router A is configured as the master with a default priority of 100. Master Router A waits
1.5seconds after it receives the first IWANTIT primitive before assigning the new SNA circuit to one of its ethernet redundancy peers because of the dlsw transparent timers sna 1500 command.
Figure 145 DLSw+ with Ethernet Redundancy in a Switched Environment
Workstation Z
Workstation X | Router A |
4000.0010.0001
Workstation Y | Router B |
Ethernet switch |
17956
| Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide |
|