Chapter 6 Enrolling and Managing Certificates
Viewing a Certificate
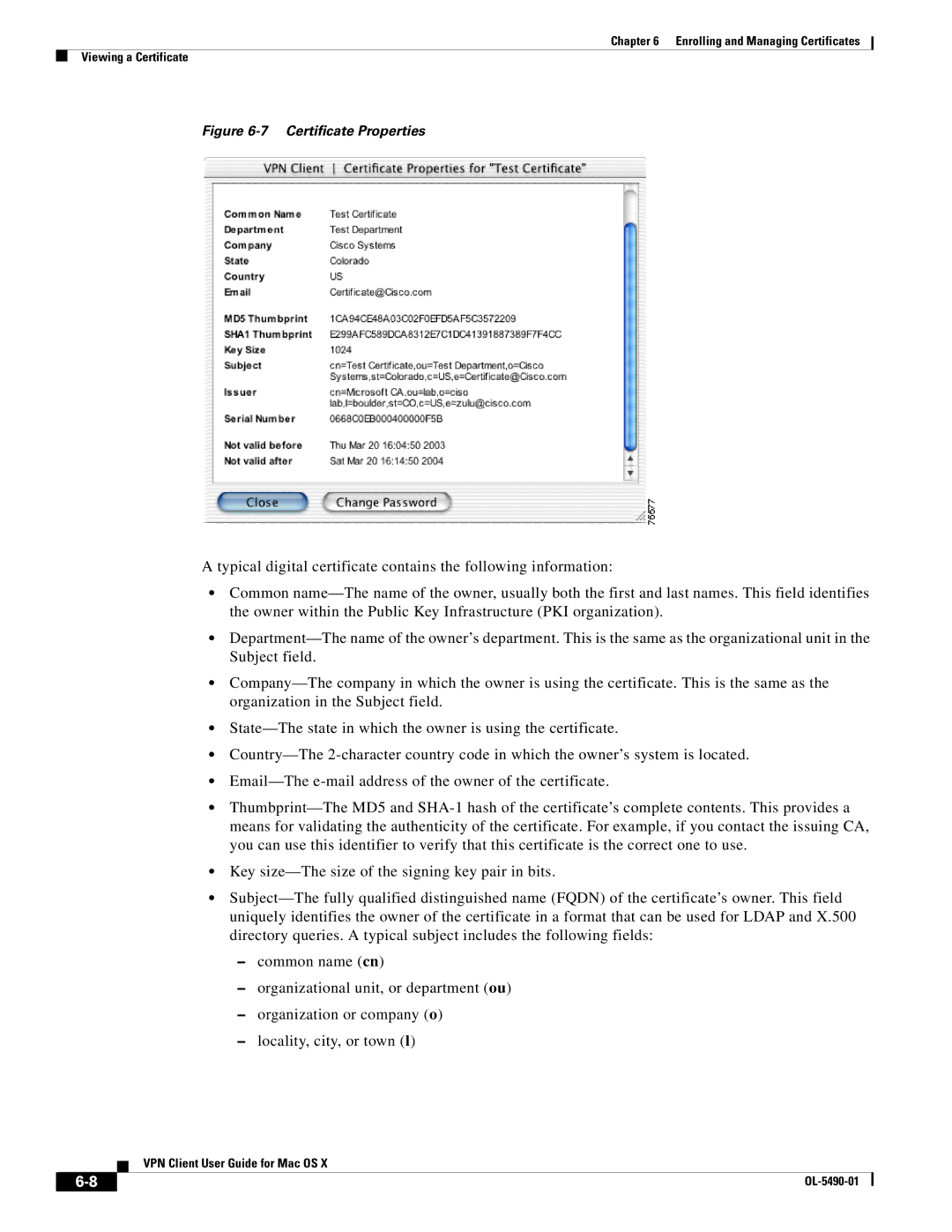
Figure 6-7 Certificate Properties
A typical digital certificate contains the following information:
•Common name—The name of the owner, usually both the first and last names. This field identifies the owner within the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI organization).
•Department—The name of the owner’s department. This is the same as the organizational unit in the Subject field.
•Company—The company in which the owner is using the certificate. This is the same as the organization in the Subject field.
•State—The state in which the owner is using the certificate.
•Country—The 2-character country code in which the owner’s system is located.
•Email—The e-mail address of the owner of the certificate.
•Thumbprint—The MD5 and SHA-1 hash of the certificate’s complete contents. This provides a means for validating the authenticity of the certificate. For example, if you contact the issuing CA, you can use this identifier to verify that this certificate is the correct one to use.
•Key size—The size of the signing key pair in bits.
•Subject—The fully qualified distinguished name (FQDN) of the certificate’s owner. This field uniquely identifies the owner of the certificate in a format that can be used for LDAP and X.500 directory queries. A typical subject includes the following fields:
–common name (cn)
–organizational unit, or department (ou)
–organization or company (o)
–locality, city, or town (l)
VPN Client User Guide for Mac OS X