Administration Guide
Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved 78-19576-01 B0
Placement Tips
Viewing System Summary Information Setup
Other Hardware Features
Introduction
Port Management
Dhcp
System Management
Firewall
VPN 122
Logging System Statistics 153
Appendix E IPSec NAT Traversal 183
Appendix G Specifications 189
Appendix H Where to Go From Here 199
Appendix F Bandwidth Management 186
Ports
RV0xx Series Router Features
Model
RV042 and RV042G RV082 RV016
RV042 and RV042G Status Lights
Introduction
RV042 and RV042G Ports
RV082 Ports and Status Lights
Ports
Port Description
Status Lights
Light Description
Other Hardware Features
Feature Description
Desktop Placement
Default Settings
Placement Tips
Parameter Default Value
Wall Mounting
RV042 and RV042G 58 mm apart RV082 and RV016 94 mm apart
Rack Mounting RV082 or RV016
RV082 Internet Port
Connecting the Equipment
RV042 and RV042G Internet Port
RV016 Internet 1 Port
Getting Started with the Configuration
Troubleshooting Tips
Features of the User Interface
Navigation
Pop-Up Windows
Setup Wizards
Saving the Settings
Help
Viewing System Summary Information
System Information
Cisco ProtectLink Web
Viewing System Summary Information
Configuration
Port Statistics
Port Information Window
Viewing System Summary Information
WAN Status
WAN information
Log Setting Status
Firewall Setting Status
VPN Setting Status
DMZ information
Setup
Setting Up the Network
Setup
Host Name and Domain Name
IP Mode
LAN Setting device IP address and subnets
Changing the device IP address
Enabling multiple subnets IPv4 only
Setup
WAN Setting Internet connection
DMZ Setting
Setup
Editing a WAN Connection
Page
Page
Page
Editing a DMZ Connection
IPv4 IPv6
Page
Changing the Administrator Username and Password
Setup
Setting the System Time
To open this page Click Setup Time in the navigation tree
Setting Up a DMZ Host
Setting Up Port Forwarding and Port Triggering
Port Range Forwarding
Port Range Forwarding, Port Triggering,
Setup
Adding a service
Port Triggering
Setting Up Universal Plug and Play UPnP
To open this page Click Setup UPnP in the navigation tree
Setup
Adding a service
Setting Up One-to-One NAT
Setup
Cloning a MAC Address for the Router
Editing the MAC Address Clone Settings
Assigning a Dynamic DNS Host Name to a WAN Interface
Editing the Dynamic DNS Setup
Setting Up Advanced Routing
Configuring Dynamic Routing, Configuring Static Routing,
Configuring Dynamic Routing
Dynamic Routing for IPv4
Data None, RIPv1, RIPv2 Broadcast, or RIPv2 Multicast
Configuring Static Routing
Dynamic Routing for IPv6
Prefix Length Pv6 only Enter the prefix length
Setting Up Advanced Routing
IPv6 Transition
To Go From Here
Setting Up the Dhcp Server or Dhcp Relay
Dhcp
Dhcp
Dynamic IP used for Dhcp Server only
DNS used for Dhcp Server only
Wins used for Dhcp Server, IPv4 Only
About Static IP Addresses for IPv4 Only
Assigning static IP addresses by adding devices from a list
Assigning static IP addresses by entering devices manually
Using the Static IP List to Block Devices
DNS Local Database
Viewing the Dhcp Status Information
Dhcp Server
Client Table
Router Advertisement IPv6
Dhcp
Setting Up Dual WAN and Multi-WAN Connections
System Management
Mode Cisco RV042, RV042G, and RV082
System Management
Mode Cisco RV016
Interface Setting
Editing the Dual WAN and Multi-WAN Settings
Network Service Detection
Max Bandwidth Provided by ISP
Page
Adding a service
Page
Bandwidth Management Type
Managing the Bandwidth Settings
Max Bandwidth Provided by ISP
Appendix F, Bandwidth Management
Managing the Bandwidth Settings
Adding a service
Setting Up Snmp
Enabling Device Discovery with Bonjour
Enabling Device Discovery with Bonjour
Using Built-In Diagnostic Tools
To open this page Click System Management Diagnostic
DNS Name Lookup
Ping
Restoring the Factory Default Settings
Upgrading the Firmware
Restarting the Router
Backing Up and Restoring the Settings
Restoring the Settings from a Configuration File
Backing Up Configuration Files and Mirror Files
Copying a Startup File or Mirror File
Backing Up and Restoring the Settings
Configuring the Port Settings
Port Management
Port Management
Viewing the Status Information for a Port
Summary
Statistics
Configuring the General Firewall Settings
Firewall
Firewall
Restrict Web Features
Firewall
Configuring Firewall Access Rules
About Access Rules
Managing Access Rules
To delete all custom rules Click Restore to Default Rules
Configuring Access Rules
Services IPv4 and IPv6
Schedule IPv4 Only
Adding a service
Page
Using Content Filters to Control Internet Access
Forbidden Domains, Website Blocking by Keywords, Schedule,
Forbidden Domains
Website Blocking by Keywords
Schedule
Cisco ProtectLink Web
Getting Started with Cisco ProtectLink Web
Cisco ProtectLink Web
Specifying the Global Settings for Approved URLs and Clients
Approved URLs and Approved Clients
Approved URL Configuration
Approved Clients Configuration
To delete an entry Click the Delete icon
Enabling Web Protection for URL Filtering
Web Protection
URL Filtering
Business Hour Setting
Web Reputation
Updating the ProtectLink License
URL Overflow Control
License
License Information
VPN
Introduction to VPNs
Site to Site VPN Gateway To Gateway
Remote Access Client To Gateway
Configuration tasks
Gateway-to-Gateway VPN Tunnel Between RV0xx Series Routers
QuickVPN, page125 and Remote Access with PPTP, page125
Router
Remote Access with Cisco QuickVPN
Remote Access with Pptp
Viewing the Summary Information for VPN
To open this page Click VPN Summary in the navigation tree
Tunnel Status
Up a Remote Access Tunnel for VPN Clients Client To Gateway,
GroupVPN Status
VPN Clients Status
Setting Up a Gateway to Gateway Site to Site VPN
Local Group Setup and Remote Group Setup
Add a New Tunnel
VPN
IPSec Setup
Preshared Key, page 135 and Advanced settings for IKE with
Required fields for Manual mode
Required fields for IKE with Preshared Key
Advanced settings for IKE with Preshared Key
VPN
VPN
RV0xx
Local Group Setup
Remote Client Setup for Single User Tunnel Type
VPN
IPSec Setup
Required fields for IKE with Preshared Key
Advanced settings for IKE with Preshared Key
VPN
Managing VPN Users and Certificates
Users, Certificate Management, page148
Users
Certificate Management
Setting Up VPN Passthrough
Setting Up Pptp Server
IP Address Range
Pptp Server
Connection List
Setting Up the System Log and Alerts
Syslog section, Mail section,
Mail section
Log Setting, Buttons,
Syslog section
Logging System Statistics
Log Setting
Buttons
Viewing the System Log
Logging System Statistics
Basic Setup, Access Rule Setup, page160
Wizard
Basic Setup
Access Rule Setup
Wizard
Dtim Delivery Traffic
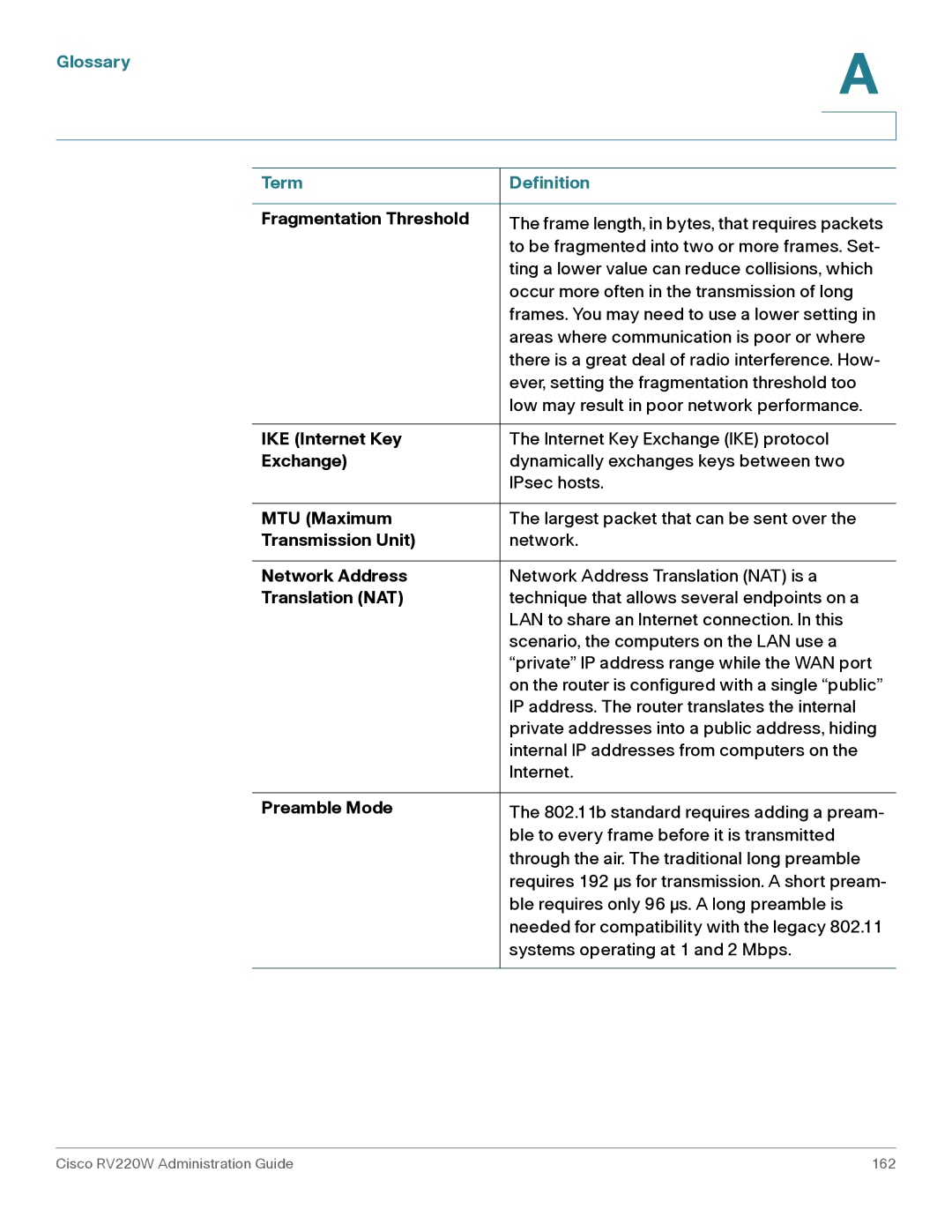
Term Definition
Beacon interval
Indication Message
Glossary Term Definition
Request to Send RTS
Radvd Router
Advertisement Daemon
Threshold
RIPng RIP next generation
Static routing
Vlan Virtual LAN
Firmware upgrade has failed
Your computer cannot connect to the Internet
Troubleshooting
Router does not have a coaxial port for the cable connection
Cisco QuickVPN for Windows
Introduction
Cisco QuickVPN Client Installation and Configuration
Using the Cisco QuickVPN Software
Cisco QuickVPN for Windows
Using the Cisco QuickVPN Software
Topology Options
VPN Hub and Spoke Topology
Hub and Spoke
VPN Mesh Topology
Mesh
WAN Setup
Other Design Considerations
LAN Setup
Gateway To Gateway Tunnel with a Dynamic IP Address
Configuring a VPN Tunnel on a Cisco RV0xx Series Router
Settings on the Site a Router
Example Sites with Static WAN IP Addresses
Field Value
Encryption Phase
MD5
Field Values
Encryption
Example Site with a Dynamic WAN IP Address
Authentication
Field Value
IPSec Setup Keying Mode IKE with Preshared Key Phase
IPSec NAT Traversal
Overview
Configuration of Router a
IPSec NAT Traversal
Configuration of Router B
Creation of New Services
Click the System Management tab
Click Add to List
Creation of New Bandwidth Management Rules
Bandwidth Management
Click Save
Performance
Specifications
RV042
Security
Specifications
Network
QoS
RV042G
Management
Environmental
Operating System Linux
VPN
Cisco RV082
IKE
Cisco RV016
Dhcp DNS NAT DMZ
Built-in Pptp server supporting 10 Pptp clients
Support
Product Documentation
Cisco Small Business