Emerson Process Management GmbH & Co. OHG3-6
X-STREAM XE
Instruction Manual
HASXEE-IM-HS
04/2010
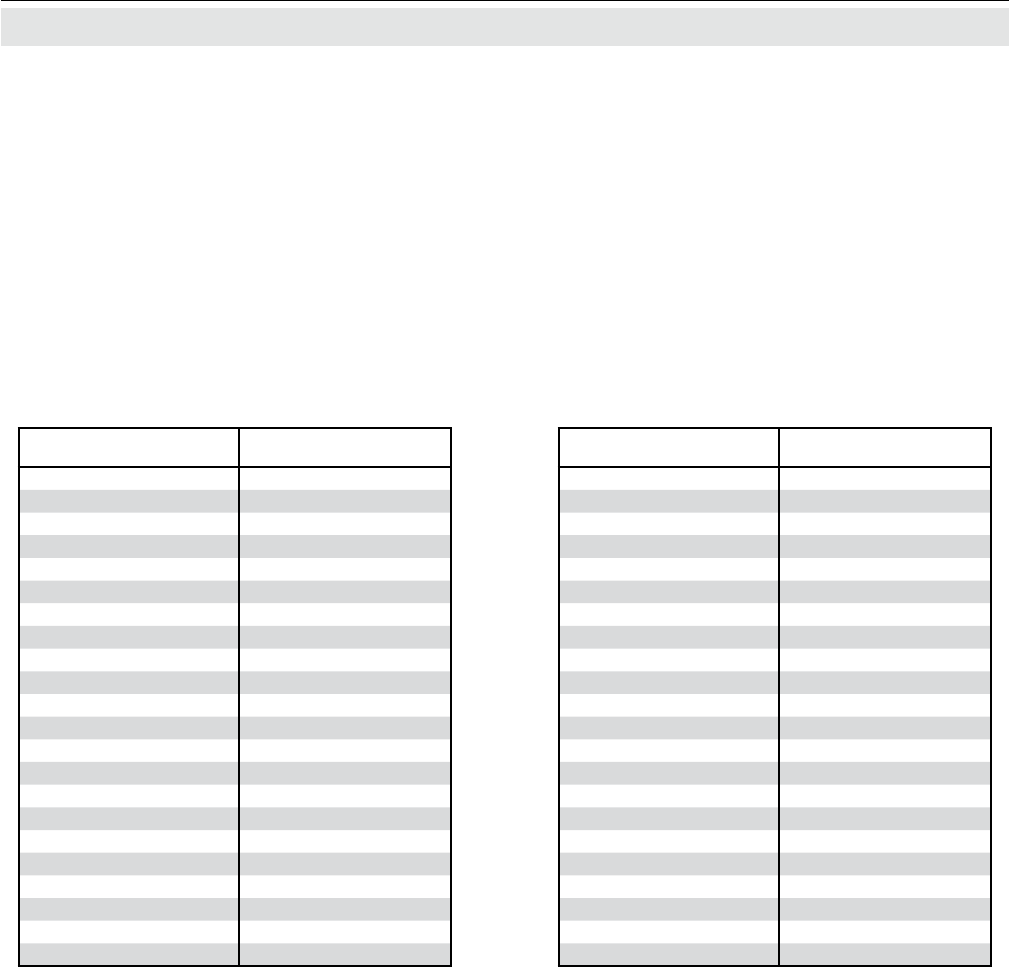
3.2 Oxygen Measurement3.2.1.1 Cross Interferences by Accompanying GasesThe table below shows, how accompanying gases interfere the paramagnetical oxygen measurement. If the concentration of such gases is already given at time of enquiry, this interference may be taken into account during factory startup and thus minimized (option).Tab. 3-1: Standard Paramagnetic Sensor -
Cross Interference by Accompanying Gases
100 % Gas Zero-level effect % O2
Acetylene C2H2-0.24
Allene C3H4-0.44
Ammonia NH3-0.26
Argon A -0.22
Bromine Br2-1.30
1.2-Butadiene C4H6-0.49
1.3-Butadiene C4H6-0.49
n-Butane C4H10 -1.11
i-Butene C4H8-0.85
cis 2-Butene C4H8-0.89
trans 2-Butene C4H8-0.92
Carbon dioxide CO2-0.27
Carbon monoxide CO +0.06
Chlorine Cl2-0.77
Cyclohexane C6H12 -1.56
Ethane C2H6-0.43
Ethylene C2H4-0.26
Helium He +0.30
n-Heptane C7H16 -2.10
n-Hexane C6H14 -1.70
Hydrogen H2+0.24
Hydrogen bromide HBr -0.61
100 % Gas Zero-level effect % O2
Hydrogen chloride HCl -0.30
Hydrogen ouride HF +0.10
Hydrogen iodide HI -1.10
Hydrogen sulphide H2S -0.39
Iodine I -2.40
Isobutane C4H10 -1.11
Isobutane C5H12 -1.49
Krypton Kr -0.51
Laughing gas N2O -0.20
Methane CH4-0.20
Neon Ne +0.13
Neoptane C5H12 -1.49
Nitric acid HNO3+0.43
Nitrogen dioxide NO2+28.00
Nitrous oxide NO +40.00
n-Octane C8H18 -2.50
n-Pentane C5H12 -1.45
Propane C3H8-0.86
Propylene C3H6-0.55
Vinyl chloride C2H3Cl -0.63
Water H2O -0.02
Xenon Xe -0.95