1-15
Ad-Hoc Network
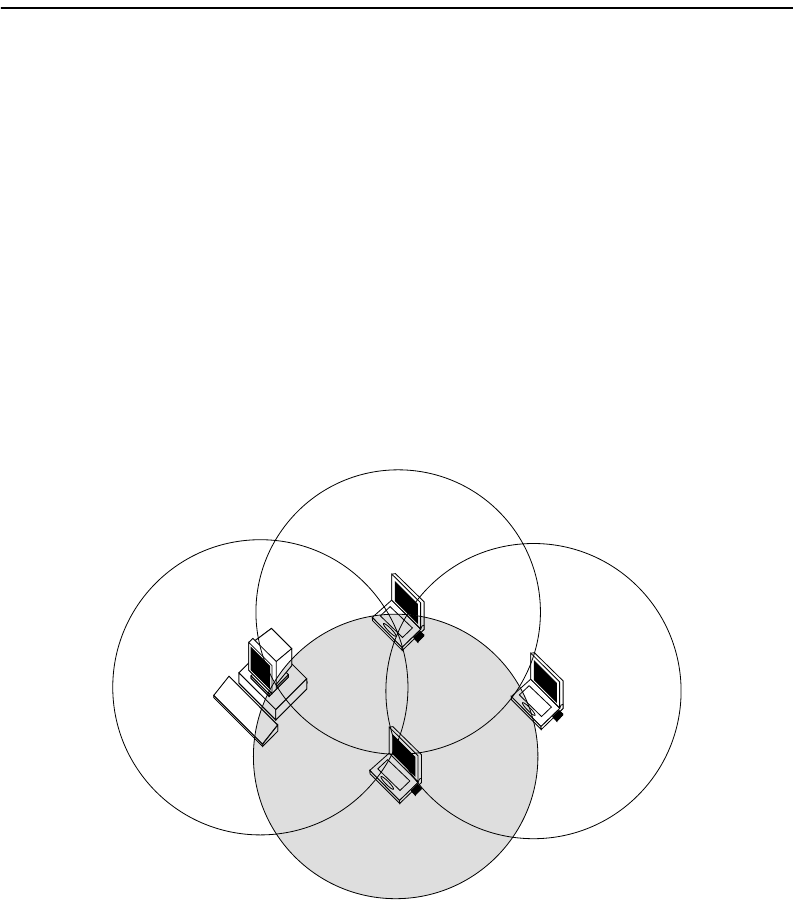
Ad-Hoc NetworkWireless ad-hoc networks do not include APs. Instead, the ad-hoc network is a loose
association, or workgroup, of computers that can communicate with each other using the
PC Card in Ad-Hoc Mode. Figure1-8 shows an ad-hoc network.
The ad-hoc network is also known as a peer-to-peer network or independent network. The
size of the ad-hoc network coverage area is determined by various factors, such as
proximity and obstacles in the environment. In Figure1-8, Client D has a coverage area
(shown in gray) that touches all the other clients. This client can communicate with the
other clients. Client C’s coverage area does not touch Client A. These clients cannot
communicate unless they move closer together.
The number of clients that the ad-hoc network can support is determined by the network
utilization of each client. For example, a large number of clients could use the network for
reading e-mail with very good network performance, but a few clients transferring large
files could slow the network response time for all the clients.
Figure 1-8: Ad-Hoc Network
Client A
Client B
Client D
Client D
Client C