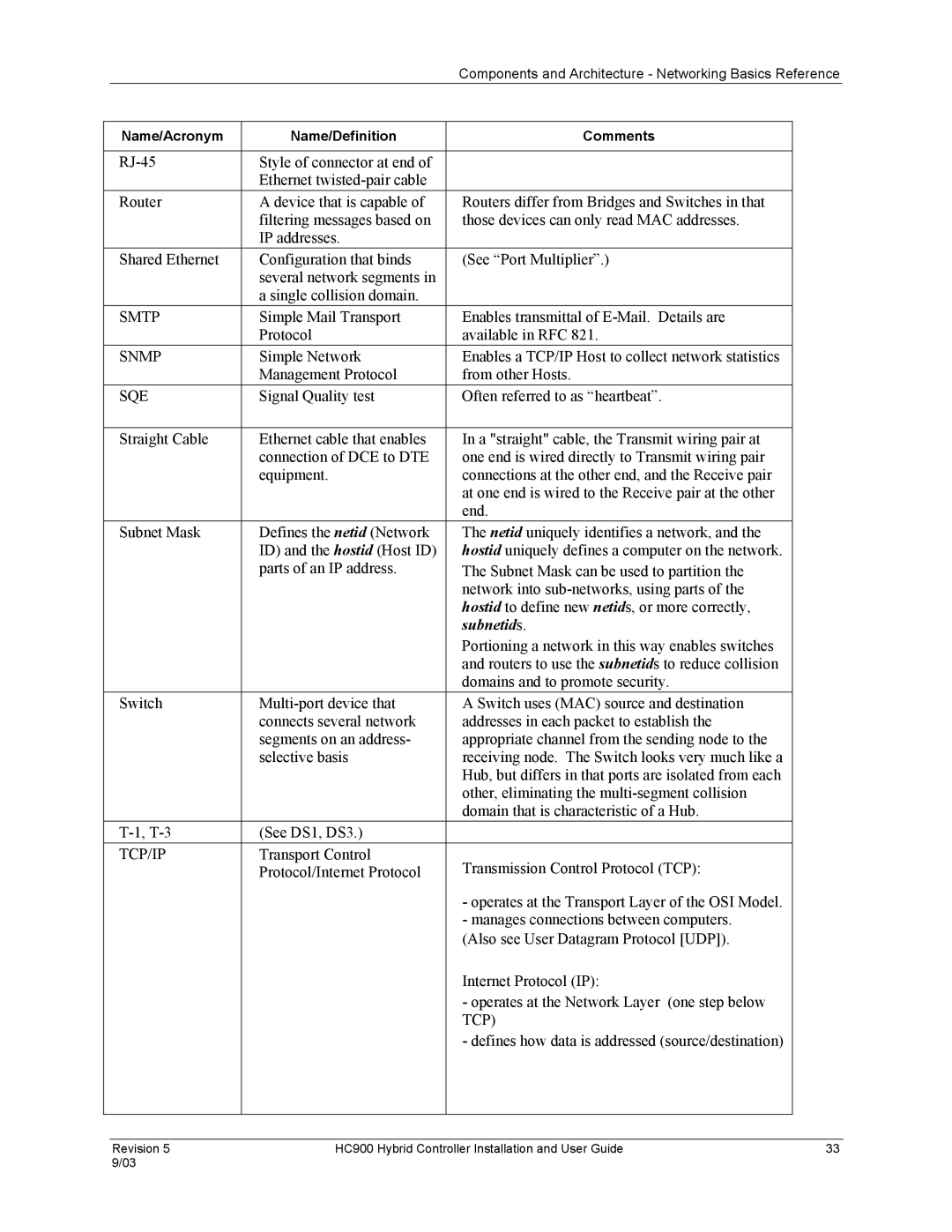
HC900 specifications
The Honeywell HC900 is a robust control solution designed to meet the demands of process industries. This flexible and powerful platform provides a comprehensive set of features tailored for process control and monitoring applications. The HC900 is particularly suited for batch control, continuous processes, and discrete applications, making it a versatile choice for a variety of industries, including oil and gas, chemicals, and electricity generation.One of the main features of the HC900 is its modular design. This allows users to customize their control systems by selecting from a range of I/O modules, communication options, and control strategies. The system supports both analog and digital inputs and outputs, enabling seamless integration with existing infrastructures. Additionally, the modular approach enhances scalability, allowing users to expand their systems as their needs evolve.
The HC900 is equipped with advanced control technologies, including adaptive control, multivariable control, and real-time data logging. These capabilities facilitate fine-tuned control over complex processes, improving efficiency and reducing waste. The system can manage multiple process loops simultaneously, providing operators with a holistic view of their operations.
Another significant characteristic of the HC900 is its intuitive user interface. The system features a graphical display that allows operators to monitor system performance easily and make adjustments quickly. This user-friendly design minimizes training requirements and encourages efficient operation across different experience levels.
Furthermore, the HC900 incorporates sophisticated data management tools. With built-in logging and reporting functions, users can track process variables and generate comprehensive reports for analysis and regulatory compliance. This data-centric approach fosters informed decision-making and enhances overall operational effectiveness.
From a communication standpoint, the HC900 supports a variety of protocols, making it compatible with many industry-standard devices. This interoperability ensures that users can integrate the HC900 into their existing systems without hassle, streamlining migration and upgrade processes.
Additionally, the HC900 is built with reliability in mind. Its rugged design ensures durability, capable of withstanding harsh environments while maintaining consistent performance.
In summary, the Honeywell HC900 stands out as a powerful and flexible control solution, equipped with modular design, advanced control technologies, and user-friendly interfaces that cater to the diverse needs of process industries. With its comprehensive data management capabilities and robust communications options, the HC900 is an excellent choice for organizations striving for efficiency and reliability.