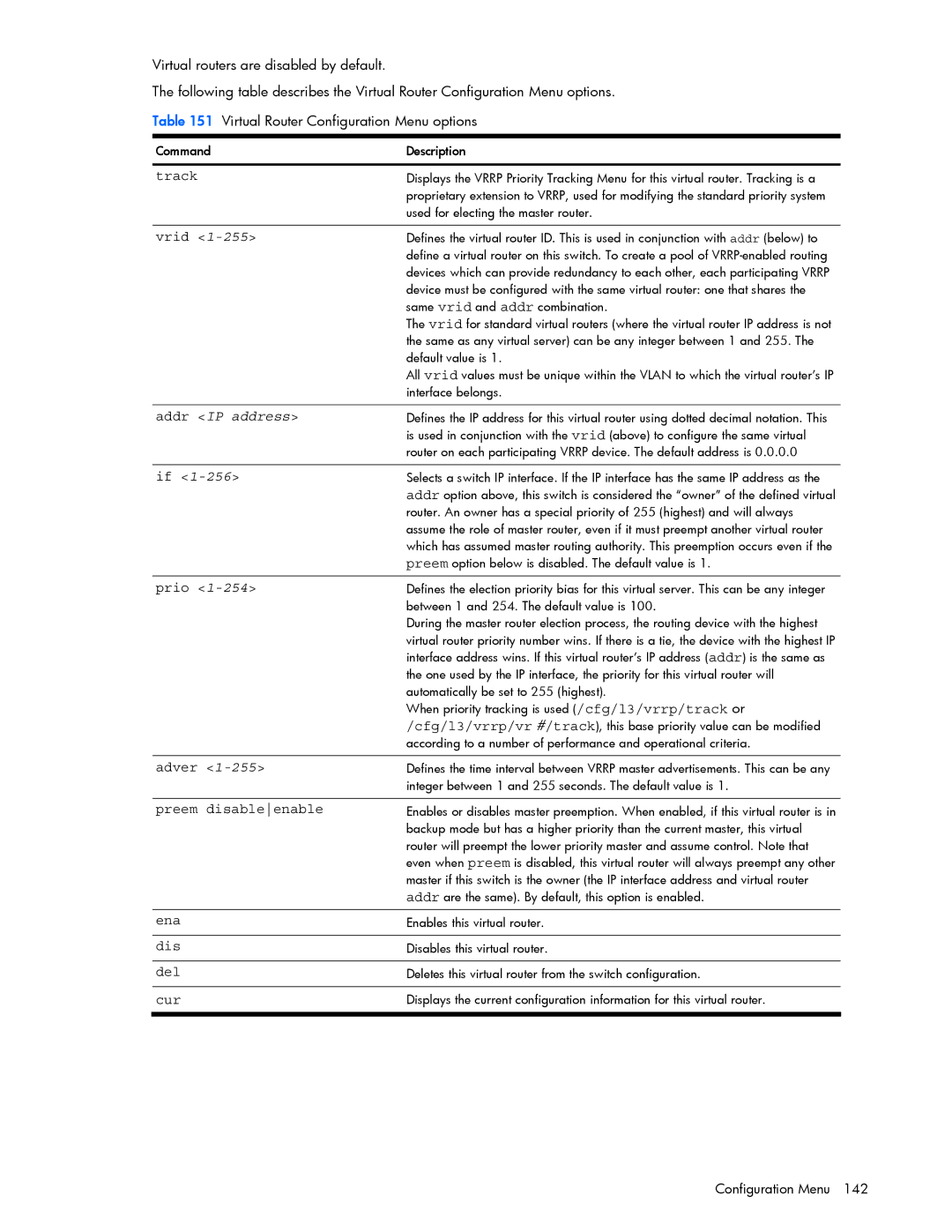
GbE2c specifications
The HP GbE2c is a high-performance Ethernet Switch designed to meet the increasing demands of data center environments. As a critical component in Hewlett-Packard's networking lineup, the GbE2c provides a seamless blend of speed, reliability, and advanced networking capabilities, making it an essential tool for enterprises aiming to enhance their network infrastructure.One of the standout features of the HP GbE2c is its support for Gigabit Ethernet, which allows for high-speed data transmission and reduced latency. This switch is designed to support the growing bandwidth needs of modern applications, ensuring that data is transmitted quickly and efficiently across the network. The GbE2c is particularly beneficial for organizations implementing virtualization technologies, as its Gigabit interfaces help in optimizing data flow between virtual machines.
The GbE2c also incorporates advanced Layer 2 and Layer 3 switching capabilities. This ensures that it can handle both basic and more complex networking tasks, such as routing traffic between different VLANs and enabling Internet Protocol (IP) addressing. The switch supports various protocols, enabling seamless integration into a wide range of network environments.
Additionally, the HP GbE2c is equipped with a robust management system that allows network administrators to easily configure and monitor network settings. With its user-friendly interface, administrators can gain insights into traffic patterns, performance metrics, and potential issues, helping to maintain optimal network performance.
Power efficiency is another key characteristic of the HP GbE2c. The switch is designed to minimize power consumption without sacrificing performance, making it a more sustainable choice for data centers aiming to reduce their carbon footprint. This energy-efficient design is crucial for enterprises looking to lower operational costs while maintaining a high level of service.
The HP GbE2c also boasts high availability features, including redundant power supplies and failover options, ensuring that the network remains operational even in the event of a component failure. This reliability is critical for businesses that require uninterrupted network access for their daily operations.
In summary, the HP GbE2c Ethernet Switch combines speed, versatility, and efficiency, making it an ideal choice for businesses seeking to enhance their networking capabilities. Its robust feature set, advanced management options, and focus on energy efficiency position it as a top-tier solution in the competitive networking landscape. Organizations can rely on the GbE2c to deliver high performance and reliability, thus meeting the demands of today's data-intensive environments.