Please do not try to modify the base address and interrupt which assigned by the PCI PnP BIOS, it may cause resource confliction in your system.
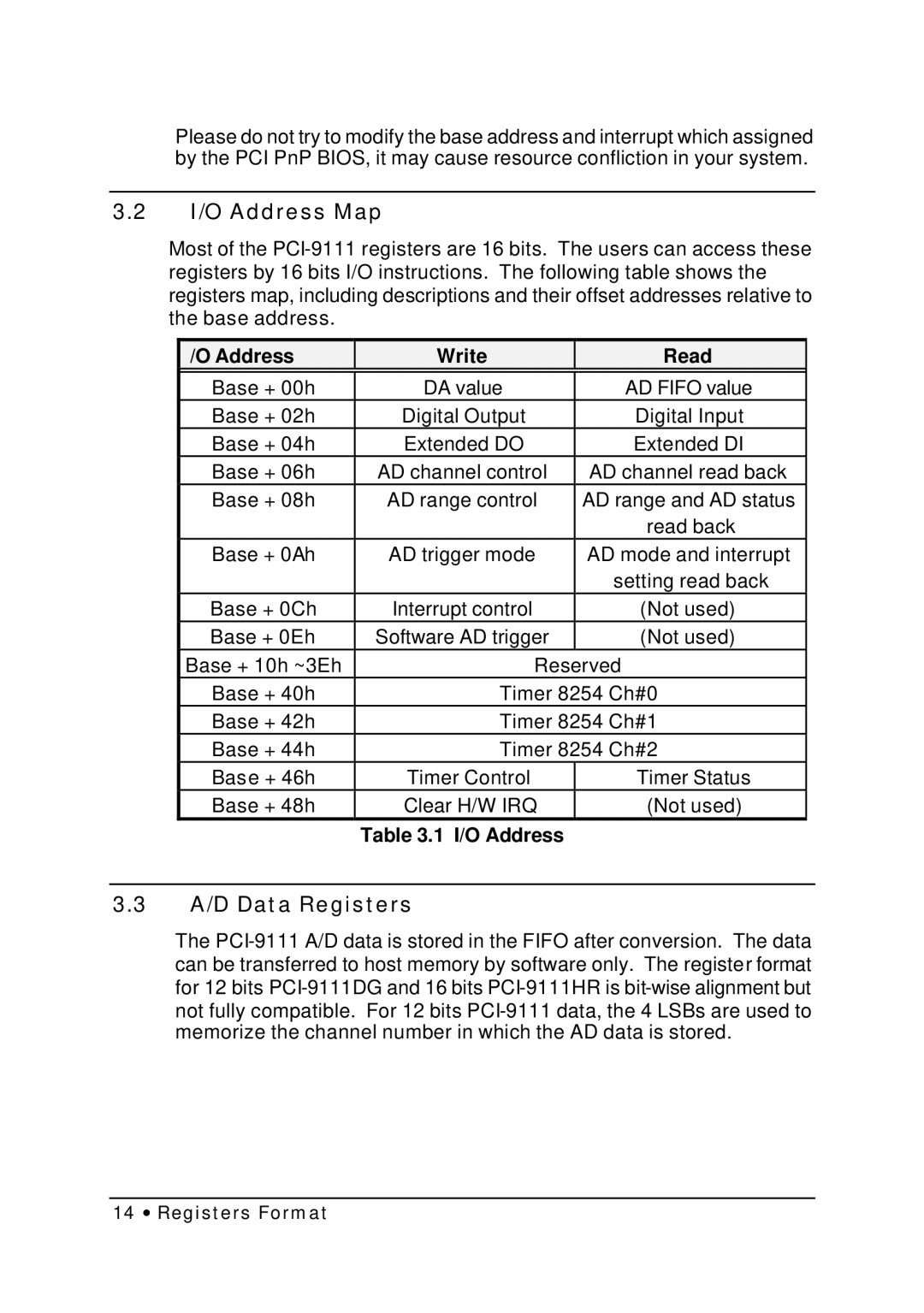
3.2I/O Address Map
Most of the
I/O Address | Write | Read |
|
|
|
Base + 00h | DA value | AD FIFO value |
Base + 02h | Digital Output | Digital Input |
Base + 04h | Extended DO | Extended DI |
Base + 06h | AD channel control | AD channel read back |
Base + 08h | AD range control | AD range and AD status |
|
| read back |
Base + 0Ah | AD trigger mode | AD mode and interrupt |
|
| setting read back |
Base + 0Ch | Interrupt control | (Not used) |
Base + 0Eh | Software AD trigger | (Not used) |
Base + 10h ~3Eh | Reserved | |
Base + 40h | Timer 8254 Ch#0 | |
Base + 42h | Timer 8254 Ch#1 | |
Base + 44h | Timer 8254 Ch#2 | |
Base + 46h | Timer Control | Timer Status |
Base + 48h | Clear H/W IRQ | (Not used) |
Table 3.1 I/O Address
3.3A/D Data Registers
The
14 ∙ Registers Format