User’s Guide
Page
Installation Considerations
Standards Compliance
Limitation of Liability
Page
Contents
Features and Applications 125
Using ION Software
Hardware Reference 159
Environmental Conditions Unit Dimensions
Telnet and Hyperterminal
Standard Meter Security
Appendix a Technical Notes 183
Introduction
Firmware Revision History Using this Guide
ION 7500 and ION 7600 Meters
Introduction
Data Display and Analysis Tools
ION meter in an Enterprise Energy Management System
MeterM@il Internal E-Mail Server Feature
WebMeter Embedded Web Server Feature
Front Panel
XML Compatibility
Communications Protocols
ION Setup Software
Digital and Analog I/O Options
Digital Inputs
Analog Inputs and Analog Outputs
Meter is Factory-Configured and Ready to Operate
V203 Apr
Firmware Revision History
Using this Guide
Getting More Information
Before You Can Use this Guide
Online ION Enterprise Help
ION Enterprise Administrator Guide
Technical Notes
Application Notes
Displaying Data with the Front Panel
Configuring the Meter with the Front Panel
Displaying Data with the Front Panel
Using the Front Panel Buttons to Display Data
Navigation Buttons
Softkeys
Front Panel LEDs
Display Screen Types
Backlight Operation and Display Contrast
Status Bar
Event Log Displays
Phasor Diagram Displays
Nameplate Displays
Histogram Displays
Trend Displays
Trend Bar Graph Displays
Screens Shown in Display Cycle
Default Front Panel Display Screens
Additional Data Display Screens
Name Plt Name Plate Info
Phasors Phasors
Events Event Log
Setpoint Setpoint Status
EN50160 Data and Statistics Displays ION 7600 only
Trending Display Screens in the ION
Front Panel’s Setup Menu
Configuring the Meter with the Front Panel
Passwords
Using the Front Panel Buttons for Configuration
Setup Mode Timeout
Confirming Configuration Changes
Sub-Menu Register Default Description
Basic Setup Menu
Demand Setup Menu
Main Setup Menu
Sliding Window Demand Rolling Block Settings
Sliding Window sub-menu contains the following settings
Thermal sub-menu contains the following settings
Thermal Demand Settings
Demand Options sub-menu contains the following setting
Demand Options
Following settings can be configured in this option
Network Setup
Configuring Network Settings with BootP
Setting Description Default
89.123.40
Configuring Network Settings Through the Front Panel
Serial Communications Setup
Internal Modem Setup
COM Port Setting Options Default
Sag Limit
PQ Power Quality Setup
Swell Limit
Change Criteria
Numeric Format sub-menu contains the following settings
Format Setup Menu
General Format sub-menu contains the following settings
Numeric Format
Display Setup Menu
Time Setup Menu
Clock Setup
Use this item to set the meter’s display to local time
Set Meter Time
Factory Resets
Meter Resets
This sub-menu contains the following default resets
Peak dmd rset
Security Setup
User Resets
EN50160 Reset ION 7600 only
Password
Enabled
Web Config
Custom Front Panel Displays
Creating a Front Panel Reset
External Pulse Module #6
Maximum Module
To access the External Pulse modules #4 or #6 using Designer
Using The Front Panel
Default Meter Functionality
Default Meter Functionality
Basic Setup
Setup Function Default Register
Module Name Settings
Communications Setup
Communications Port Setup Register Function Default
Communications modules control the following channels
Communications Protocols
Modem Initialization String
Default Logging Capacity
Data Logging Setup
Changing the Log Depths
Log name Depth Interval
Changing the Frequency of Logging
Default Logging Configuration
Revenue Log
Parameter Description
Historic Data Logging
Loss Log
Harmonics Logging
ION Enterprise Reporting
Time-of-Use Logging
Sag/Swell and Transient Logging
Meter logs the following ION output register values
EN50160 Compliance Logging ION 7600 only
Energy Pulsing Setup
Pulser Module Settings
Calibration Pulser Module Settings
Power Quality Configuration
Sag/Swell Module Settings
Setup Register Function Default
EN50160 Settings ION 7600 only
Transient Module Settings ION 7600 only
Fine Tuning Over Condition Monitoring
Setpoint Configuration
Relative Setpoint Module Settings
To a varying value
Meter Clock Configuration
On using the meter’s time synchronization functions
Number of seconds since 000000 UTC on Jan 1
Display Options Module Settings
Display Setup
Scroll Module Settings
Display Module Settings
Sliding Window Demand Module Settings
Demand Setup
Thermal Demand Module Settings
Changing the Parameters that are Displayed
Time of Use Configuration
Seasonal Settings
Time Of Use Module Settings
Setup Register Function
Creating a New Time Of Use Schedule
Manager in Designer from the Options menu
Factory Module Settings
How to TAG Your Meter
Setup Register Description
Factory Information
Third Party Protocols
Communications Protocol Configuration
Using the Modbus RTU Protocol
Factory Modbus Configuration
Changing the Modbus Configuration
Modbus Slave Module Settings
Modbus Slave Module Parameter Mapping
Default Meter Functionality
Refer to Appendix a for more
Default Meter Functionality
Default Meter Functionality
Default Meter Functionality
Default Meter Functionality
Importing Data using Modbus RTU
Modbus TCP Communications
Using the Modbus/TCP Protocol
Using the DNP 3.00 Protocol
Factory DNP 3.00 Configuration
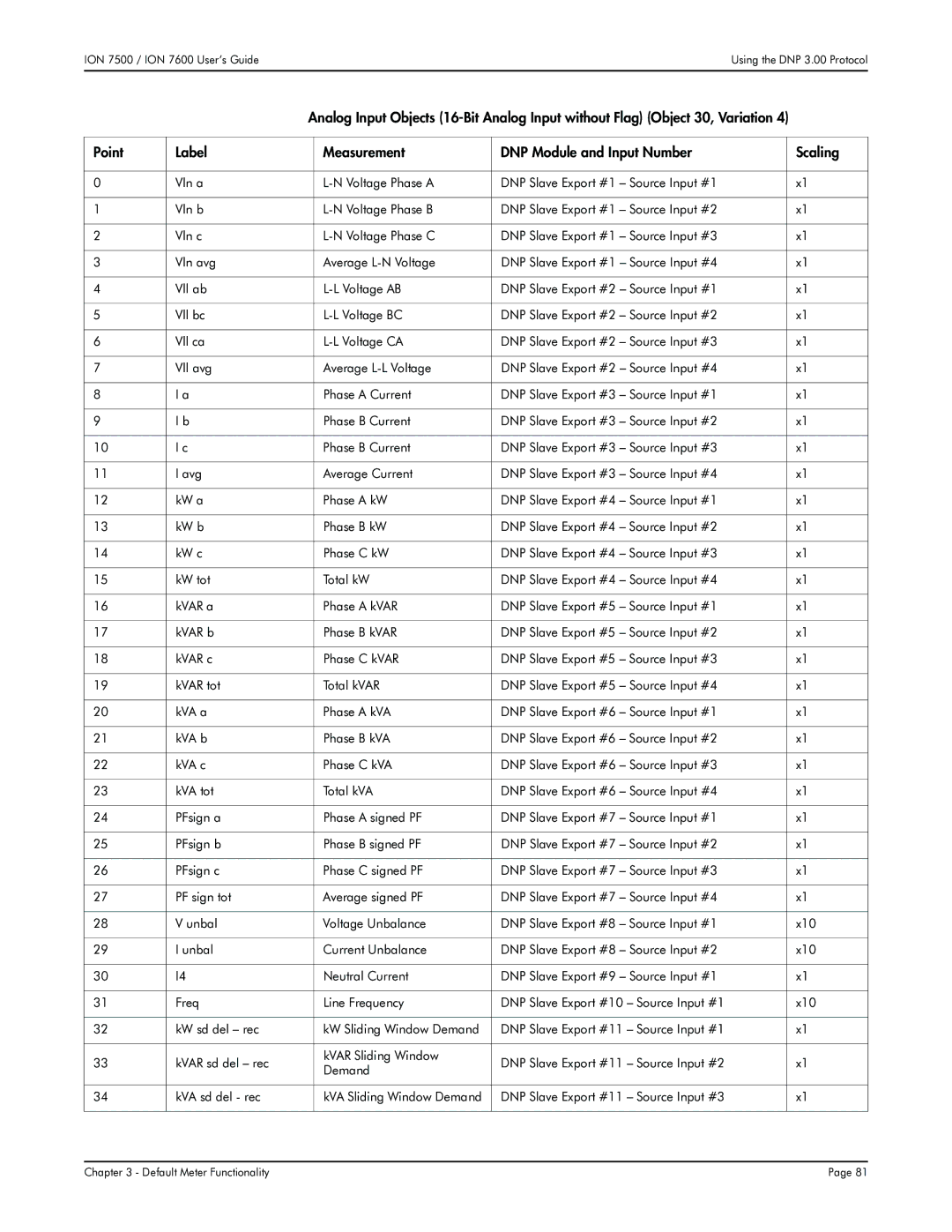
Vln a
ION 7500 / ION 7600 User’s GuideUsing the DNP 3.00 Protocol
Changing the DNP Configuration
DNP Slave Export Module Settings
DNP Options Module Settings
Importing Data using DNP
Setup Register Setting Function
Restoring the Factory Configuration
To restore the factory configuration
Click OK on the confirmation dialog box
Default Meter Functionality
Using ION Software
Software Security
ION Enterprise Software
Servers
ION Enterprise ION Management Console
Devices
Sites
Dialout Modems
Connection Schedules
Adding a new Server, Site, Device or Dialout Modem
Configuring Communications
Configuring Communications ION 7500 / ION 7600 User’s Guide
Generating a network diagram in Vista
ION Enterprise Vista
Displaying Data with Vista
Displaying Data if the Software is Not Fully Configured
Vista Diagram Elements
Power Quality
Historic Data Logging Enable
Summary of Data Provided in Vista
Volts/Amps
Harmonics Trending
Instantaneous Power
Long-Term Harmonics Min/Max Measurements
EN50160 Measurements ION 7600 only
Energy & Demand by Quadrant
Setup and Controls
Demand Max and Demand Min
Loss Compensation
Per Phase Over Current Monitoring
Setpoints
Over kW Sliding Window Demand Monitoring
Time-of-Use Tables
Voltage Unbalance Monitoring
TOU- Peak Demand Details
Inputs
Revenue Test Mode Values
Revenue Test Mode
Customizing the Vista Interface
Analog Inputs/Outputs
Custom Appearance of a User Diagram
Diagram Objects in a User Diagram
Basics of ION Architecture
ION Enterprise Designer
Module Linking Restrictions
ION Modules
ION Registers
Sequence of ION Module Execution
‘NOT AVAILABLE’ Value
Core Modules
ION Configuration Changes and Module Security
Fixed Module Links
Persistent Modules
Designer’s Main Configuration Screen
Changing Setup Registers with Designer
Viewing Real-time Data in Designer
To view real-time data of output registers
To configure ION module setup registers with Designer
Customizing Frameworks in Designer
Deleting Modules
Creating New Modules
Linking Modules
Follow these steps to create an ION module in the meter
Follow the steps below to link modules on the meter
Checking an Output Register’s Owner
Editing Existing Frameworks
Deleting the Link at a Module’s Input
Replacing a Link
ION Enterprise Reporter
Pre-configured Reports
Energy and Demand
Power Quality
Load Profile
EN50160
Report Creation and Generation
Creating a Report
Generating the Report
Creating a Time of Use Schedule
Adding a Shoulder Period
Changing Which Days are Holidays
ION Setup Software
Adding a Site, Group or Meter
Sites, Groups, and Meters
Configuring Communications ION 7500 / ION 7600 User’s Guide
Changing a setup register
Basic Meter Configuration
Displaying real-time data
Displaying Data with ION Setup
Displaying diagnostics data
Using ION Software
Time Synchronization Meter Security
Digital and Analog I/O
COM Port Available Connections Standard/Option
Communications
Computer Connections
RS-232 Connections
Meter Connections
External Modem Connections
RS-485 Connections
General Bus Wiring Considerations
Straight-Line Topology
Loop Topology
RS-485 Connection Methods to Avoid
Ethernet Connections
Configuring the Ethernet Module through the Front Panel
Meter Setup for Ethernet Communications
Configuring the Ethernet Module via Designer
Configuring the Ethernet Module in Designer
EtherGate Protocol
Internal Modem Connections
ModemInit Setup Register
Modem Initialization Strings
Problem Add to Modem Initialization String
Configuring the Comm 3 Module through the Front Panel
Configuring the Comm 3 Module via Designer
Configuring the Comm 3 Communications Module in Designer
Workstation with ION Enterprise and modem
ModemGate Protocol
Infrared Port Connections
ION MeterM@il Feature
ION WebMeter Feature
Internet Connectivity
WebMeter and MeterMail
Telnet and Hyperterminal
WebReach
Specifying a Port in an ION Module
Digital and Analog I/O
Optional Output Port Names Description
Standard Output Port Names Description
Standard Input Port Names Description
Optional Input Port Names Description
Output Modules
Using the Onboard Digital Outputs
Calibration Pulsing Relay DO4
Alarm LED
Energy Pulsing with LEDs
KWh Pulse -LED
Settings in the Digital Input modules are as follows
Using the Onboard Digital Inputs
Analog Outputs
Analog Inputs
Enabling or Customizing Time Synchronization
Time Synchronization
Meter Security
Entering the Password through the Front Panel
Standard Meter Security
Your revenue meter can be protected by anti-tamper sealing
Disabling and enabling password security
Changing the Meter Password
Data Logging
Data and Event Logging
Changing the Parameters that are Logged
Changing Waveform Recording
Event Logging
ION Event Priority Groups
Event Group Description Priority Number
External ION Events
Logging and Recording Capacity
Log Depth Interval
Logging Configurations for ION 7500 Revenue Applications
Alerting
Alerting ION Software via the Alarm Server
Alarm Server Command Line Arguments
Configuring the Alarm Server
Remote Site Event Notification
Server or LAN
Alerting via an Alphanumeric Pager
Alerting via a Numeric Pager
Alerting via Email
Calculating Power Availability Number of Nines
Hardware Reference
Rear View of Meter
Standard Model
+ N
+ 30 V max
General Specifications
Environmental Conditions
Environmental Condition Acceptable Range
Basic Model Rear View
Unit Dimensions
Basic Model Front View
Basic Model Side View
RJ11
Communications Specifications
COM1 Port
LEDs
RS-232 Connections
RS-485 Connections
Specifications are as follows
Connections
Terminal connections on the meter are marked as follows
COM3 Port
COM2 Port
Internal Modem
RJ11
Specifications for the Ethernet ports are as follows
Specifications for the optical port are as follows
Ethernet Port
Optical Infrared
Protocol TCP/IP Port
IP Service Ports
AI1
Specifications
Specification Standard I/0
Mechanical Relay Outputs
Internal Excitation Additional External Excitation Optional
Operational Block Diagram
Solid-State Relay Outputs
RX1 RX2 RX2 RX3
Max Relays
Analog Outputs
I/O expansion card can be ordered with 4 analog outputs
Wh pulsing
Analog Inputs
Specification MA Analog Inputs
Power Supply
Electrical Specifications
Voltage Inputs
Potential Transformers PTs
Current Inputs
Specification 5A Option 1A Option
Installation Diagram
Installation Instructions
Retrofit Options
Terminal Cover
Installing the New Card
Communications Card
Removing the Existing Communications Card
Installing the I/O Card
Expansion Card
Final Steps
ION 7500 / ION 7600 User’s Guide Expansion Card
Tran Model
Environmental Conditions
Tran Model Front View
Tran Model Side View
Unit Dimensions ION 7500 / ION 7600 User’s Guide
Technical Notes
ION 7500 / ION 7600 User’s Guide
Basic Setup is required
Basic Setup is not required
To perform current probe basic setup
Calibration Menu and the KCTSTP/KCTRD Commands
Current Probe Basic Setup
Telnet and HyperTerminal Access
To perform current probe basic setup
Description of Kctstp and Kctrd Calibration Commands
Calibration Menu and the KCTSTP/KCTRD Commands
Calibration Menu and Help
Description
PH C
Example
None
Read all current probe setup registers
Introduction ION Modules in the Display Framework
Display Modules Display Options Module Scroll Modules
Screen Messages Adding New Trend Display Modules
ION Modules in the Display Framework
Introduction
Display Modules
Display Modules for ION 8000 Series, ION ION 7600 Meters
Screen Types Max. # Display Description Source Inputs
Changing ION 7300 Series Display Module Default Settings
Display Modules for ION 7300 Series Meters
Screen Types
Scroll Modules
Display Options Module
Display Framework Overview
Module Behavior in ION 8000 Series and ION ION 7600 Meters
Module Behavior in the ION 7300 Series Meters
Making a Framework Backup
Changing Default Display Frameworks
For the ION 8000 Series and ION 7500 / ION 7600 meters
For the ION 7300 Series
Adding a New Display Screen
Removing a Display Screen
To remove a data display screen
To add a new display screen in Designer
Changing Displayed Parameters in an Existing Screen
Changing Displayed Parameters using the Meter’s Front Panel
Before changing displayed parameters in an existing screen
Changing displayed parameters in an existing screen
Bar Graph Input Function Attributes
Creating Custom Trend Bar Graphs ION 7500 / ION 7600 only
Power Meter Module
Selecting and navigating the Trend Display screen
Trend Display Screen
Use the ESC key to exit the Trend Display
To change the logging interval for Trend Display data
Trending Data Log Screen
Screen Messages
Adding New Trend Display Modules
Screen Message Description
To create a Disk Simulator screen
Disk Simulator ION 8000 Series
To configure your custom display framework
Displaying Data from Other Meters
Customized Display Framework
Display
Custom Front Panel Displays Technical Note
Analog Input Module
Digital Input Module
Digital and Analog I/O Technical Note
Solutions
Onboard I/O for ION Meters
Meter Digital Analog Modbus Inputs Outputs Master ION
External I/O with Grayhill Products
Expander for ION 8000 Series Meters
Grayhill analog hardware module restrictions-power supplies
Digital Output Boards for ION 7300 Series Meters
Expansion Boards for the ION
Expansion Boards for Meters with Modbus Master Capability
Switch Setting Parameters
Power Requirements
Communications Considerations
Description Maximum draw per channel for I/O
Configuring Digital and Analog I/O
Digital Input Module Setup Registers
Configuring Digital Input
Digital Input Module
Specifying a Debounce Time
Detailed Operation Pulse or KYZ Input Mode
Configuring Digital Output
Digital Output Module Setup Registers
Digital Output Module
Calibration Pulser Module Setup Registers
Calibration Pulser Module
Detailed Operation
Detailed Module Operation
Pulse mode KYZ mode
Normal State
Pulse Width
Pulse mode
Maximum State
Overload State
Pulser Module
Pulser Module Setup Registers
Analog Input Module Setup Registers
Configuring Analog Input
Connecting Auxiliary Analog Inputs ION 7700 Meters
Analog Input Option Input Impedance Max Common Mode Voltage
Zero Scale
Analog Output Module Setup Registers
Configuring Analog Output
Analog Output Module
Analog Output Option Maximum Load
Setting Analog Zero and Full Scale Values
20 to
Considerations when scaling
20 mA
To 20 mA
1500 W 0mA 1000 W 4mA 20mA
Configuring ION Modules for Digital and Analog I/O
Configuring modules for digital or analog I/O
Assigning a port to a module
Making a port available
Energy Pulsing from ION Meters
Configuring the Meter for MeterM@il Technology
Setting Up the Network for the MeterM@il Feature
Introduction Viewing the MeterM@il Message
Email Alerts Email Data Logs
Setting Up the Network for the MeterM@il Feature
Network Administrator
ION Software Administrator
Recipient of the MeterM@il Message
Viewing the MeterM@il Message
Email Alerts
Here is an example of an email alert
Email Data Logs
XML Attachment
BootP Server
Automatically Configuring Meter Network Settings
Setting Up the Network for the MeterM@il Feature
Smtp Connection Timeout
Optional
‘Setting Up the Meter for the Smtp Server
Configuring the Meter for MeterM@il Technology
Setting Up the Meter for your Smtp Server
Click Send and save
Setting up the meter to send alerts
Configuring the MeterM@il Feature to Send Alerts
Configuring the MeterM@il Feature to Send Data Logs
Configuring the meter to send data logs
Additional ION Module Configurations
MeterM@il Internal Email Server Feature Technical Note
Factory Module
MeterM@il Technology in a Modbus Network
MeterM@il Internal Email Server Feature Technical Note
ION Meter Security
Overview of Security
ION Software Security ION Meter Security
Overview of Security
Icon Descriptions
Standard Advanced
Security Access Levels
ION Enterprise Software Security
Supervisor Operator Controller User View Only
Creating or modifying ION Enterprise user accounts
Entering the software user name and password
Creating or modifying ION Setup user accounts
ION Setup Software Security
ION Setup Software Security ION 7500 / ION 7600 User’s Guide
ION Meter Security
Meter Password
Configuring standard meter security in Designer
Configuring standard meter security in ION Setup
Advanced Meter Security ION 8000 Series
Entering an advanced security user name and password
Enter the appropriate password and click OK
Configuring advanced security using ION Enterprise
Configuring advanced users with ION Setup
Configuring advanced security using ION Setup
ION 7500 / ION 7600 User’s Guide
Device Security Access for ION Services
Launch ION Setup and connect to the appropriate meter
Service Function
Hardware Lock Security
Additional Revenue Metering Security
Anti-Tamper Seals
Default Web Pages Custom Web Pages
Using the Setup Page Setup Errors
Hardware Framework
Web Browser User
Viewing WebMeter Data on the Internet Configuring your Meter
Default Web Pages
Viewing default web pages
Viewing WebMeter Data on the Internet
Creating custom web pages
Custom Web Pages
Viewing custom web pages
For example http//10.1.50.42/webpage1.html
Configuring your Meter
Using the Setup
Configuring your meter with the Setup
Undo Changes
Setup Errors
Automatic Configuration via a BootP Server
Configuring Meter Network Settings
Smtp Mail Server Address mandatory for MeterM@il
WebMeter Network
WebMeter Network ION 7500 / ION 7600 User’s Guide
Enabling/disabling web browser configuration of the meter
Enabling/Disabling Meter Web Browser Configuration
Enabling/disabling web server functionality of the meter
Enabling/Disabling Meter Web Server Functionality
Below is a typical application of the WebMeter feature
Using WebMeter in a Modbus Network
Hardware
Framework
Factory Module
Modbus Import Module
Web Page Module
AT Commands for the Conexant Modem
Conexant Modems in ION Meters
Cellular Phone Compatibility 289
ION meter
ION Meter Internal Modem Types
AT Commands for the Multi-Tech Modem
Multi-Tech Internal Modem Settings
Multi-Tech Modems in ION Meters
International support
Configures the modem for pulse non-touch-tone
Registers
Register Unit Range Default Description
Configuration settings for certain types of connections
AT Commands for the Conexant Modem
Command Group Members Description
Conexant Modems in ION Meters
Mod Modulation Possible Rates bps
AT+MS Commands Select Modulation
Changing the Internal Modem Settings
Changing the Local Modem Settings
Cellular Phone Compatibility
AT command B1
AT command S10=100
Description Increases disconnect time on loss of carrier
Description If rate drops to 1200, use Bell protocol
Introduction Availability on the Meter Front Panel
Resetting and Pausing Power Availability
Detailed Behavior
Terminology
Availability Features Comments Versions
Availability Framework Release History
Firmware
Availability on the Meter Front Panel
Sample Availability Framework Behaviors
Assumptions
Power Operating Range Supply 36S 35S Phase
Sag/Swell Module Configuration
Blade Powered
Meter
Resetting and Pausing Power Availability
Resetting Availability with Vista
Resetting Availability with ION Setup Software
ION 7500 / ION 7600 meters only
Resetting Availability through the Meter Front Panel
Pausing Availability
Detailed Behavior
Terminology
Detailed Behavior ION 7500 / ION 7600 User’s Guide
EN50160 External Controls
Default EN50160 Measurements
Power Frequency
Default EN50160 Measurements
Power Frequency Default Measurements
Source Module Type Description
Register Label Description
Magnitude of Voltage Supply
Register Source Module Type Description
Voltage Magnitude Default Measurements
Parameter
Flicker
Register Label Source Module Type Description
Flicker Default Measurements
Register Label Description
Voltage Dips Default Measurements
Supply Voltage Dips
Register Labels
ION 7500 / ION 7600 User’s GuideSupply Voltage Dips
Short and Long Interruptions
Interruptions Default Measurements
Register Label Current Observation Period
Register Label Previous Observation Period
Overvoltages Default Measurements
Temporary Overvoltages
Overvoltages / Duration t 1s = t 1 min = 1 min
Temporary OvervoltagesION 7500 / ION 7600 User’s Guide
Unbalance Default Measurements
Supply Voltage Unbalance
Register Label Module Type Description
Odd Harmonics Not Multiples Order Threshold Even Harmonics
Harmonic Voltage
Register Label
Harmonics Default Measurements
Register Label Source Module Description
Interharmonic Voltage
Interharmonics Default Measurements
Mains Signaling Voltage
Mains Signaling Evaluation Module Settings
Mains Signaling Default Measurements
More details about this module
EN50160 Synchronization Mode & Synchronization Timing
EN50160 Reset
EN50160 External Controls
Enabling the EN50160 Calculations
EN50160 External Controls ION 7500 / ION 7600 User’s Guide
Configuring the Modbus Network
Modbus Master Devices
Modbus Slave Devices
Connecting the Modbus Slave Devices
Configuring the Modbus Network
Configuring the Modbus Slave Devices
Configuring the Modbus Master Device
Pasting the Modbus Master Framework into the Meter
Multiple Modbus Master Devices
Customizing the Modbus Master Framework
Select EditCopy to framework
Select EditPaste from Framework
Customizing your Vista Diagram
Customizing the Modbus Master Front Panel Display
Controlling the Data Logging Capabilities
Output Register Module
Modbus Import Module Configurations
Using HyperTerminal
Using Telnet
Telnet Menu
Factory Terminal Menu
Using Telnet
To connect to the meter
Type in the meter IP address in the Host Name box
To access menus
Telnet Menu
Telnet menu options are
Using HyperTerminal
Factory Terminal menu options are
Factory Terminal Menu
Factory Terminal Menu ION 7500 / ION 7600 User’s Guide
EtherGate
ION Meter as an Ethernet Gateway
Serial Ethernet
EtherGate
Add the ION Gateway Meter to Your ION Enterprise Network
Install the Gateway Meter and Serial Network Devices
Add an EtherGate Site to Your ION Enterprise Network
New Ethernet Gateway
EtherGate Checklist
ModemGate
ION Meter as a ModemGate
ModemGate
General network installation and basic setup
Modem Site
ModemGate Checklist
Add a Modem Site to an ION Enterprise Network
Add Meters to the Modem Site
Site
Configure the ION Gateway Meter for ModemGate
ION Meter as a ModemGate Technical Note
Diagnostics Module Output Registers Event Logging
Diagnostics and Event Logging
Changing Default Blackout Settings
ION Time Synchronization GPS Time Synchronization
Time Synchronization & Timekeeping Technical Note
Clock Module Settings
Clock Source Used for Synchronization
Type of Time Used for Synchronization
Daylight Savings Time Adjustment
Time Zone Adjustment
Communications Port Used for Synchronization
Modem
ION Time Synchronization
Time Synchronization ION or GPS
GPS Time Synchronization
Configuring for GPS Time Synchronization
GPS Time Synchronization Format
GPS Receiver Comm Module Protocol Register Setting
Supported GPS Receivers
On Time Mark OTM ‘Protocol’ Register
Ascii Time String Sohdddhhmmssqcrlf
Explanation of GPSARBITER-VORNE Ascii Time String
Ascii Time String below left1
11NNCRLF
Diagnostics Module Output Registers
Diagnostics and Event Logging
Event Logging ION 7500 / ION 7600 User’s Guide
Time-Synchronization Blackout
Changing Default Blackout Settings
Time-Synchronization Blackout Considerations
Default value 150 2 minutes 30 seconds in seconds
TimesyncBlackoutIntervalmins
TimesyncBlackoutDurationsecs
Upgrading ION Device Firmware
Device Upgrader
Before You Upgrade
Device Upgrader
Checking the Log Server before upgrading
Ensuring the Log Server is caught up
Configuring device transmit delay
Modifying the transmit delay for Ethernet devices
Laptop computer considerations
Upgrading Your ION Devices
Downloads
Upgrading Your ION Devices ION 7500 / ION 7600 User’s Guide
Numerics
Index
Index
IP service ports 168 IrDA
Passwords 32, 44, 147, 255 default
XML 15, 236
Page
70000-0176-01