N300 Wireless Dual Band ADSL2+ Modem Router DGND3300v2 User Manual
Planning a VPN
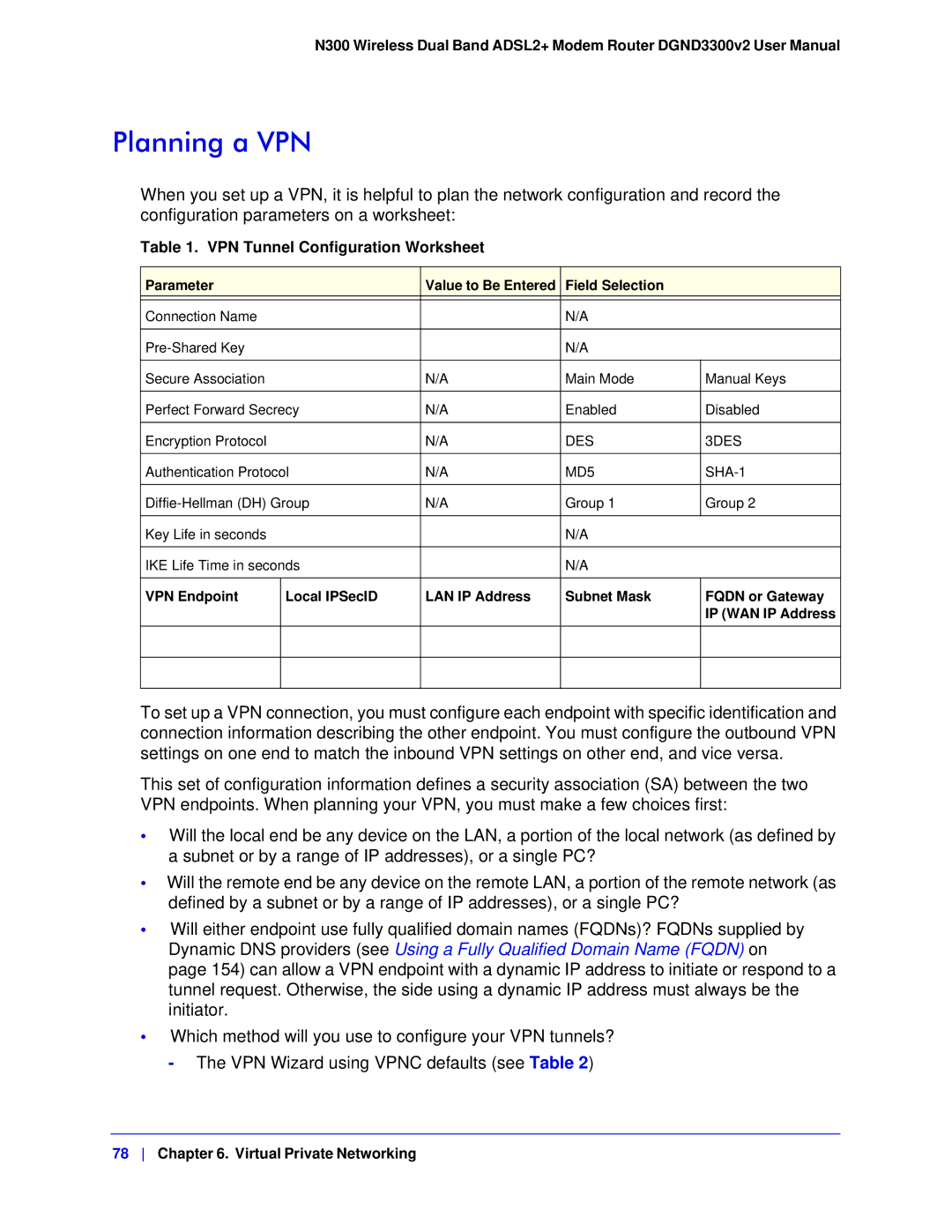
When you set up a VPN, it is helpful to plan the network configuration and record the configuration parameters on a worksheet:
Table 1. VPN Tunnel Configuration Worksheet
Parameter |
| Value to Be Entered | Field Selection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Connection Name |
|
| N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| N/A |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Secure Association |
| N/A | Main Mode | Manual Keys |
|
|
|
| |
Perfect Forward Secrecy | N/A | Enabled | Disabled | |
|
|
|
|
|
Encryption Protocol |
| N/A | DES | 3DES |
|
|
|
| |
Authentication Protocol | N/A | MD5 | ||
|
|
|
| |
N/A | Group 1 | Group 2 | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Key Life in seconds |
|
| N/A |
|
|
|
|
| |
IKE Life Time in seconds |
| N/A |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
VPN Endpoint | Local IPSecID | LAN IP Address | Subnet Mask | FQDN or Gateway |
|
|
|
| IP (WAN IP Address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
To set up a VPN connection, you must configure each endpoint with specific identification and connection information describing the other endpoint. You must configure the outbound VPN settings on one end to match the inbound VPN settings on other end, and vice versa.
This set of configuration information defines a security association (SA) between the two VPN endpoints. When planning your VPN, you must make a few choices first:
•Will the local end be any device on the LAN, a portion of the local network (as defined by a subnet or by a range of IP addresses), or a single PC?
•Will the remote end be any device on the remote LAN, a portion of the remote network (as defined by a subnet or by a range of IP addresses), or a single PC?
•Will either endpoint use fully qualified domain names (FQDNs)? FQDNs supplied by Dynamic DNS providers (see Using a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) on
page 154) can allow a VPN endpoint with a dynamic IP address to initiate or respond to a tunnel request. Otherwise, the side using a dynamic IP address must always be the initiator.
•Which method will you use to configure your VPN tunnels?
-The VPN Wizard using VPNC defaults (see Table 2)
78 Chapter 6. Virtual Private Networking