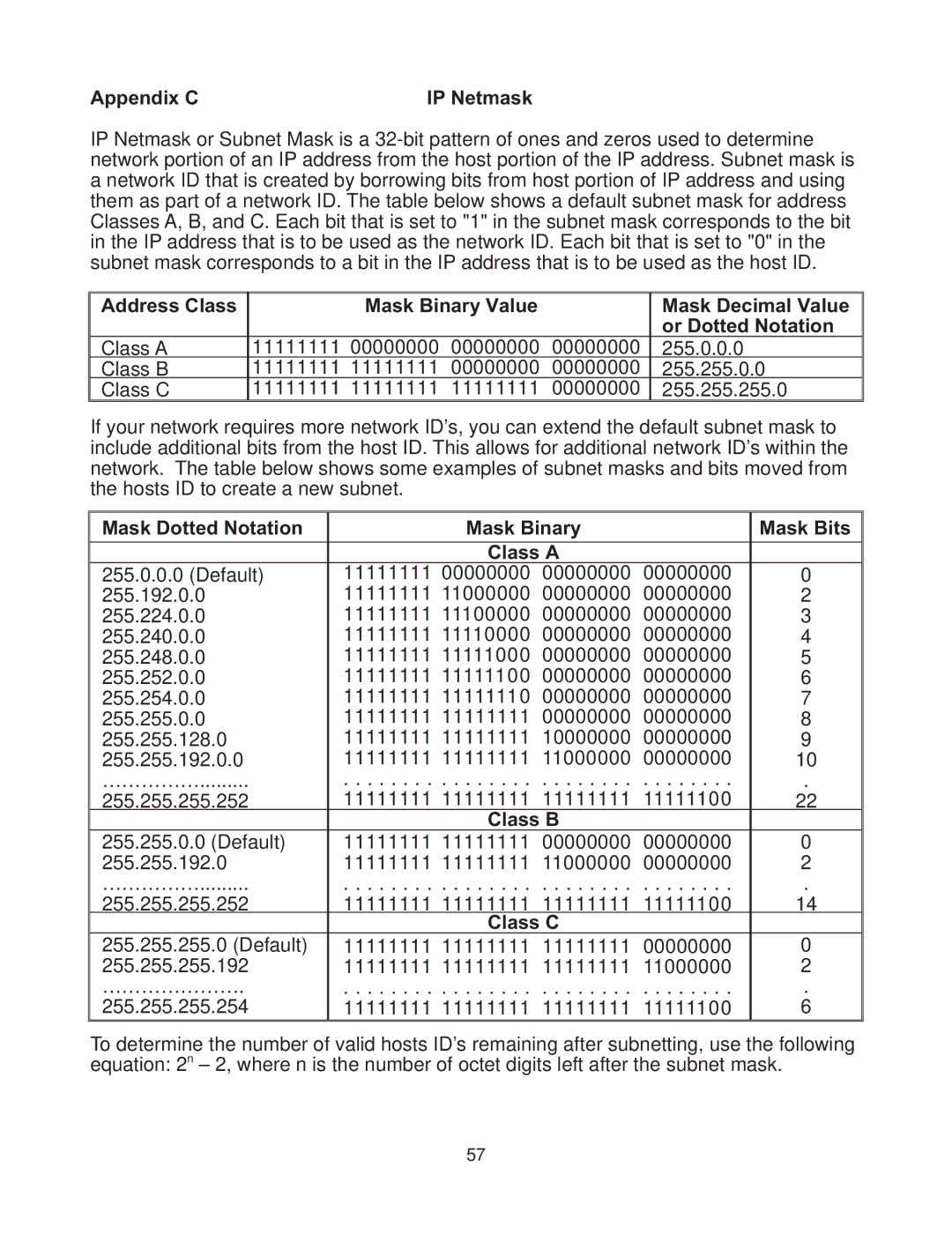
Appendix CIP Netmask
IP Netmask or Subnet Mask is a
| Address Class |
|
|
| Mask Binary Value |
|
| Mask Decimal Value |
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
|
| 11111111 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 |
| or Dotted Notation |
|
| ||||||
| Class A |
| 255.0.0.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Class B | 11111111 | 11111111 | 00000000 | 00000000 |
| 255.255.0.0 |
|
|
|
| ||||
| Class C | 11111111 | 11111111 | 11111111 | 00000000 |
| 255.255.255.0 |
|
|
|
| ||||
If your network requires more network ID’s, you can extend the default subnet mask to | |||||||||||||||
include additional bits from the host ID. This allows for additional network ID’s within the | |||||||||||||||
network. The table below shows some examples of subnet masks and bits moved from | |||||||||||||||
the hosts ID to create a new subnet. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Mask Dotted Notation |
|
|
| Mask Binary |
|
|
| Mask Bits |
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
|
|
|
|
| 11111111 | Class A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| 255.0.0.0 (Default) |
|
| 00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 |
|
| 0 |
|
|
| |||
255.192.0.0 |
|
|
| 11111111 | 11000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 |
|
| 2 |
|
|
| ||
255.224.0.0 |
|
|
| 11111111 | 11100000 | 00000000 | 00000000 |
|
| 3 |
|
|
| ||
255.240.0.0 |
|
|
| 11111111 | 11110000 | 00000000 | 00000000 |
|
| 4 |
|
|
| ||
255.248.0.0 |
|
|
| 11111111 | 11111000 | 00000000 | 00000000 |
|
| 5 |
|
|
| ||
255.252.0.0 |
|
|
| 11111111 | 11111100 | 00000000 | 00000000 |
|
| 6 |
|
|
| ||
255.254.0.0 |
|
|
| 11111111 | 11111110 | 00000000 | 00000000 |
|
| 7 |
|
|
| ||
255.255.0.0 |
|
|
| 11111111 | 11111111 | 00000000 | 00000000 |
|
| 8 |
|
|
| ||
255.255.128.0 |
|
|
| 11111111 | 11111111 | 10000000 | 00000000 |
|
| 9 |
|
|
| ||
255.255.192.0.0 |
|
|
| 11111111 | 11111111 | 11000000 | 00000000 |
|
| 10 |
|
|
| ||
| …………… |
|
|
| .. .. . .. . . . . . . . . . .. . .. .. . .. . . . . . . |
|
| . |
|
|
| ||||
255.255.255.252 |
|
|
| 11111111 | 11111111 | 11111111 | 11111100 |
|
| 22 |
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| Class B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| 255.255.0.0 (Default) |
|
| 11111111 | 11111111 | 00000000 | 00000000 |
|
| 0 |
|
|
| ||
255.255.192.0 |
|
|
| 11111111 | 11111111 | 11000000 | 00000000 |
|
| 2 |
|
|
| ||
| …………… |
|
|
| . .. . .. .. . . . . . . . . .. .. .. . . .. . . . . . . |
|
| . |
|
|
| ||||
255.255.255.252 |
|
|
| 11111111 | 11111111 | 11111111 | 11111100 |
|
| 14 |
|
|
| ||
| 255.255.255.0 (Default) |
|
| 11111111 | Class C |
|
|
|
| 0 |
|
|
| ||
|
|
| 11111111 | 11111111 | 00000000 |
|
|
|
|
| |||||
255.255.255.192 |
|
|
| 11111111 | 11111111 | 11111111 | 11000000 |
|
| 2 |
|
|
| ||
| …………………. |
|
|
| . .. . .. .. . . . . . . . . .. .. .. . . .. . . . . . . |
|
| . |
|
|
| ||||
255.255.255.254 |
|
|
| 11111111 | 11111111 | 11111111 | 11111100 |
|
| 6 |
|
|
| ||
To determine the number of valid hosts ID’s remaining after subnetting, use the following |
| ||||||||||||||
equation: 2n – 2, where n is the number of octet digits left after the subnet mask. |
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
57