Remote Access Server
Patton Electronics Company, Inc
Contents
Drop and Insert 138
Interfaces 178
Sync PPP 276
Contents
Contents
Audience
Structure
Typographical conventions used in this document
General conventions
Mouse conventions
Chapter contents
Introduction
Introduction Logging into the HTTP/HTML Administration Pages
HTTP/HTML and Snmp Object Format
Saving HTTP/HTML Object Changes
Home
Introduction
Home
Operating Status Variables
Immediate Actions
Immediate Actions buttons
Import/Export
Export Configuration
Import/Export main window
Typical access server flash memory configuration data
Import Configuration
Alarms
Sample alarm indication
Displaying the Alarms window
Total System AlarmsX alarmTotal
Alarm Response Outputs
Alarms
Modify Response-Configuring the alarm response system
Alarm Syslog Priority syslogAlarmPriority
Alarm Snmp Trap IP 1 alarmTrapIp0
Alarm Snmp Trap IP 2 alarmTrapIp1
Alarm Snmp Trap IP 3alarmTrapIp2
Modify Alarms-Configuring alarm severity levels
Modify Alarms settings window
Authentication
ID suID
Displaying the Authentication window
Validated authentications auAuthenticationsValidTotal
Validated via primary server auAuthenticationsValidPrimary
Statistics section
Validated via static database auAuthenticationsValidStatic
Denied authentications auAuthenticationsDenied
Primary server timeouts auPrimaryServerTimeouts
Secondary server timeouts auSecondaryServerTimeouts
Configuration section
Validation auValidation
Timeout auTimeout
Host Address auHostAddress
Secondary Host Address auSecondaryHostAddress
Host Port auHostPort
Accounting Enable auAccountingEnable
Accounting Port auAcctPort
Radius Packet Format auRadiusPacketFormat
Radius Session ID Size auRadiusRunningIdSize
Setting Up Authentication
Radius Session ID auRadiusRunningId
Authentication Configuration screen
Host Address auHostAddress
Accounting Port auAcctPort
Static User Authentication
Adding Static Users
Modify Static User
Service IP suServiceIP
Service Port suServicePort
Service Mask suServiceMask
Filter ID suFilterId
DAX
Configuring the DAX
Circuit Type daxClockMode
Main Reference daxClockMainRef
Fallback Reference daxClockFallbackRef
DAX Clock Status alarm condition
Clock Status daxClockFailure
Dial
Dial
Dial
Dial
Phone
Dial
Introduction
Dial In main window
Call Sorting diPageSort
Call ID diactIndex
ML ID diactMultiIndex
State diactState
Duration diactSessionTime
Disconnect Reason diactTerminateReason
Modulation diactModulation
Dial Modulations window
Connect Speed diactTxSpeed
Username diactUsername
DSP Link diactDSPIndex
Connection Modulation diactModulation
Transmit Connection Speed diactTxSpeed
Error Correction diactErrorCorrection
Receive Connection Speed diactRxSpeed
Data Compression Protocol diactCompression
Locally Initiated Renegotiates diactLocalRenegotiates
Dial Telco window
Dial Telco window
WAN Link diactLinkIndex
Time Slot diactSlotIndex
Time Call Is/Was Active diactSessionTime
Termination Reason diactTerminateReason
Dial Protocol window
Shared Unique ID diactMultiIndex
LCP Authentication LCPAuthOptions
Protocol diactProtocol
IP Address diactIP
Port # on Remote Machine diactPort
Local-Remote VJ Protocol Comprsn diIpLocalToRemoteCompProt
Remote-Local VJ Protocol Comprsn diIpRemoteToLocalCompProt
Next Hop diForceNextHop
Dial In Details
Dial In Details window
Dial In Modify default window
Dial In Modify window modify Login, Service, and DNS objects
Modify Login
Login Technique diLoginTechnique
IP Address Pool diIpPool
Password Prompt diPasswordPrompt
Modify Service
Default Service diService
Username Prompt diUsernamePrompt
Modify Domain Name Server
Modify Attempts
Failure Banner diFailureBanner
Success Banner diSuccessBanner
Modify Configuration
Modify Maximum Time
Modify Isdn Configuration
110 diV110Enable
Modify V.92 Configuration
Modify Modem Configuration
V90diModemV90Enable
K56flexdiModemK56Enable
V34diModemV34Enable
V32diModemV32Enable
Billing Delay diBillingDelay
Guard Tone diModemGuardTone
CarrierLossDuration diModemCarrierLossDuration
Answer Tone LengthdiModemAnswerToneLength
Manage Dnis Window
Direct0-No compression will be used
Manage Dnis main window
Dnis Entry Window
Called Calling Number dnisPoolDesrcDialedNumber
Dnis Profiles
Login Technique dnisProfileLoginTechnique
Dnis Profiles Main Window
ID dnisIpProfileId
IP Pool dnisProfileAssignedIpPool
Service Port dnisProfileServicePort
Service IP dnisProfileServiceIP
Telnet Mode dnisProfileTelnetMode
Dovbs dnisProfileDOVBS
Status dnisIpProfileStatus
Add a Dnis Profile
Dnis Profile Entry Window
IP Pool dnisProfileSAssignedIpPool
Dovbs dnisProfileDOVBS
Service Port dnisProfileServicePort
Dnis IP Pools Window
ID dnisIpPoolId
IP Address Pool dnisIpPool
Status dnisIpPoolStatus
Dnis IP Pool Entry Window
Dnis IP Pools Entry window
Dial In User Statistics window
User Statistics Call Identification, Session
Call Identification
Session
Time Left In Session diactRemainingSession
Termination Reason diactTerminateReason
Dial
Dial
State at termination diactTerminateState
PPP Statistics
LCP Statistics
LCP Authentication LCPAuthOptions
Remote MRU diStatRemoteMRU
Local Multilink Mrru diStatLcpLocalMRRU
Remote Multilink Mrru diStatLcpRemoteMRRU
Local-Remote AC Comprsn diStatLocalToRemoteACComp
Remote-Local AC Comprsn diStatRemoteToLocalACComp
Transmit Frame Check Seq. Size diStatTransmitFcsSize
Receive Frame Check Seq. Size diStatReceiveFcsSize
Operational Status diIpOperStatus
Local-Remote VJ Protocol Comprsn diIpLocalToRemoteCompProt
Remote-Local VJ Protocol Comprsn diIpRemoteToLocalCompProt
Remote Max Slot ID diIpRemoteMaxSlotId
Primary Domain Name Server diactPrimaryDNS
Secondary Domain Name Server diactSecondaryDNS
Filters diStatIpFilterAtoJ
Phone
Data
Physical Layer
Error Correction diactErrorCorrection
Modulation Symbol Rate diactSymbolRate
Transmit Connection Speed diactTxSpeed
Receive Connection Speed diactRxSpeed
Locally Initiated Retrains diactLocalRetrains
Remote Initiated Renegotiates diactRemoteRenegotiates
Remote Initiated Retrains diactRemoteRetrains
Dial Out
Dial Out
105
106
Dial Out Main Window
Call Sorting doPageSort
Active Calls doActive
Call ID doactIndex
User doactUsername
State doactState
Duration doactSessionTime
Disconnect Reason doactTerminateReason
109
Dial Out Details window
Modulation doactModulation
Speed doactTxSpeed
Dial Out Modify window
Dial Out Details window
TCP Type doServiceType
Login Technique doLoginTechnique
Password Prompt doPasswordPrompt
TCP Port doTcpPort
Login Attempts Allowed doAllowAttempts
Failure Banner doFailureBanner
Maximum Session Time doSessionTimeout
Maximum Idle Time doIdleTimeout
Time to Login sec doLoginTimeout
Call History Timeout min doLingerTime
Isdn doModemISDNEnable
V22 doModemV22Enable
V21 doModemV21Enable
Maximum Speed doModemMaxSpeed
Minimum Speed doModemMinSpeed
Guard Tone doModemGuardTone
Carrier Loss Duration doModemCarrierLossDuration
Retrain doModemRetrain
Dial Out Locations Window
Restrict Modification doModemRestrictMods
Status locationstatus
Add Location
Multilink locationConfigMultilink
Idle Timeout locationIdleTimeout
Maximum Session Time locationSessionTimeout
Authentication Technique locationAuthTechnique
View/Modify location details
Dialing Locations
Dial Out Modem Profiles Window
Add Modem Profile
Locations Link
Profile ID modemProfileId
Guard Tone modemGuardTone
Carrier Loss Duration modemCarrierLossDuration
RetrainmodemRetrain
Compression modemCompression
Billing Delay modemBillingDelay
Dial Out User Statistics Window
Status modemStatus
View modem profile
Password doactPassword
Call Identification
Call ID doactIndex
Username doactUsername
Minutes until timeout doactRemainingIdle
Dsp Link doactDSPIndex
Wan Link doactLinkIndex
Time Slot doactSlotIndex
126
PPP Statistics
Bad Address doStatBadAddresses
Bad Controls doStatBadControls
Packets too long doStatPacketTooLongs
Remote LCP Authentication doStatLcpAuth
Local MRU doStatLocalMRU
Remote MRU doStatRemoteMRU
Local Multilink Mrru doStatLcpLocalMRRU
Local PPP Protocol Compression doStatLocalToRemoteProtComp
Remote PPP Protocol Compression doStatRemoteToLocalProtComp
Local AC Compression doStatLocalToRemoteACComp
Remote AC Compression doStatRemoteToLocalACComp
Bad Packets doactErrorFrames
Number Called doactNumberDialed
Octets Sent doactSentOctets
Octets Received doactReceivedOctets
Error Correction Protocol doactErrorCorrection
Connection Modulation doactModulation
Tx Connection Speed doactTxSpeed
Rx Connection Speed doactRxSpeed
An example section of dialout
Callback
Dial-in Modify Configuration
Callback diCallbackConfig
Dial-in Main Window
Dial-in user waiting to be called back
Radius Configuration
Callback Configuration suCallbackConfig
Callback phone number suCallbackNumber
Accounting information
Dialout
Drop and Insert
Session Timeout drSessionTimeout
Call History Timeout drLingerTime
Drop and Insert main window
Active Calls drActive
How Drop and Insert works
Using Drop and Insert
Drop and insert diagram
Digital Signal Processing DSP
152
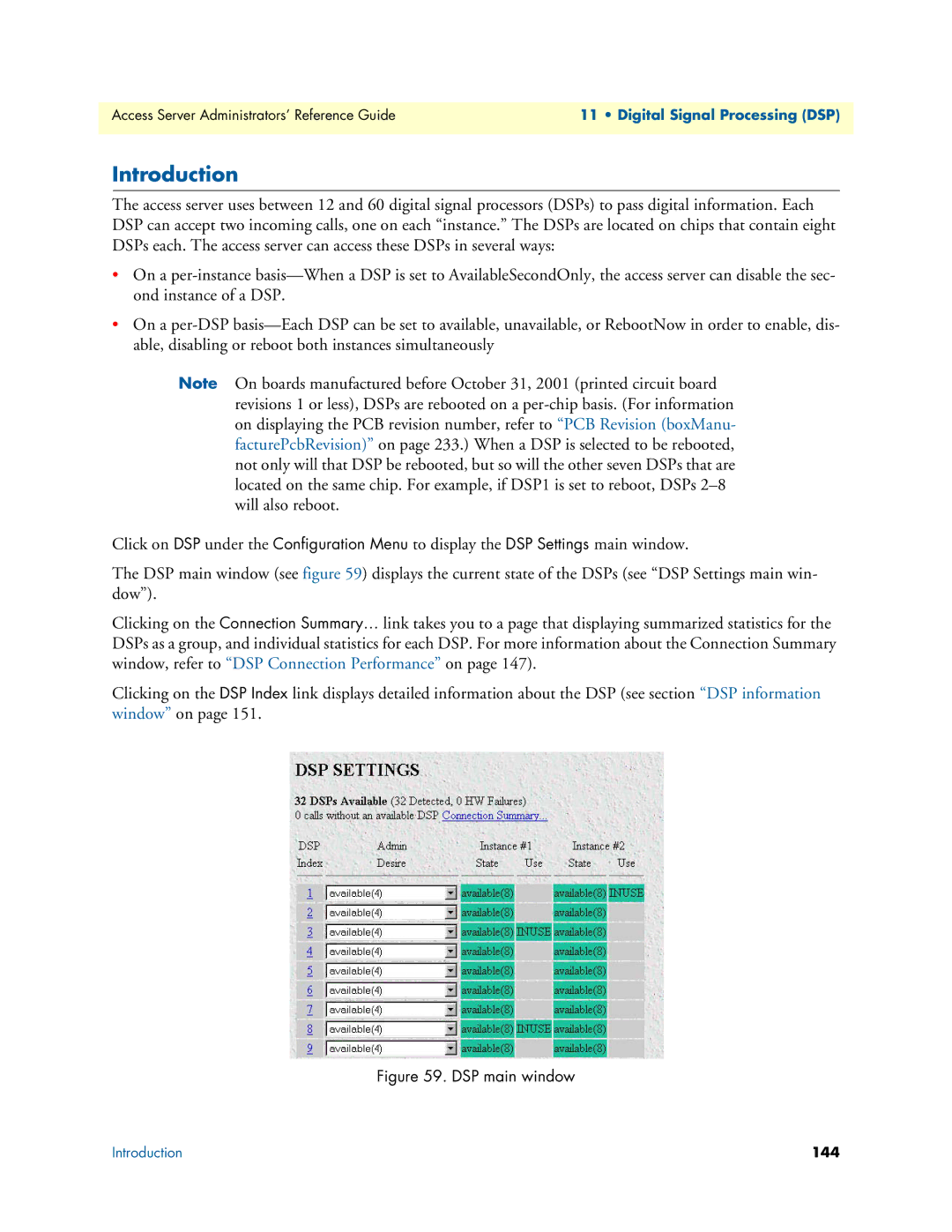
DSP main window
DSP Settings main window
Instance #1 Use dspUsefirst
Instance #2 State dspStateSecond
Instance #2 Use dspUseSecond
DSP Connection Performance
DSP Memory Capture
DSP PCM Capture
DSP Debugging Events
Connection Summaries
DSP Connection Totals
Reboot-A dspTotalRebootDueToFails
Reboot-B dspTotalRebootDueToError
Remote-Reneg dspRemoteRenegotiates
Local-Retrain dspLocalRetrains
DSP information window
DSP Status
Desired State dspDesiredState
Call Statistics
Debug Statistics
Ethernet
Ethernet Main Window
State boxEtherAState
Config
PrimaryIPAddress boxEtherAPrimaryIpAddress
PrimaryIpMask boxEtherAPrimaryIpMask
PrimaryIpFilters boxEtherAPrimaryIpFilters
Ethernet Modify Window
Ethernet Modify Window
Technique Configuration
Alignment Errors dot3StatsAlignmentErrors
Ethernet Statistics
FCS Errors dot3StatsFCSErrors
SQE Test Errors dot3StatsSQETestErrors
Other Errors dot3StatsInternalMacTransmitErrors
Carrier Sense Errors dot3StatsCarrierSenseErrors
Other Received Errors dot3StatsInternalMacReceiveErrors
Received Frames Too Long dot3StatsFrameTooLongs
Chip Set ID dot3StatsEtherChipSet
Filter IP
Defining a filter
Modify Filter
Name filterIpName
Direction filterIpDirection
Action filterIpAction
Source IP
Comparison filterIpSourceAddressCmp
Address filterIpSourceIp
Destination IP
Source Port
Destination Port
Port filterIpDestinationPort
Protocol filterIpProtocol
TCP Established filterIpTcpEstablished
An example of using a filter
IP Filter showing default for dialout
168
169
Frame Relay
Congestion frameEnableCongestion
Frame Relay main window
Frame Relay main window
Link X frDlcmiIfIndex
Hdlc Statistics on Link
Dlmi Window
Signalling frDlcmiState
Error Threshold N392 frDlcmiErrorThreshold
MultiCast Service frDlcmiMulticast
Data Link Protocol frDlcmiAddress
Dlci window
LMI Interface frDlcmiInterface
Bidirectional PollingfrDlc rDlcmiPollingBiDir
Polling Verification T392 frDlcmiPollingVerification
Congestion frameEnableCongestion
Dlci frCircuitDlci
Interface # FrameIPInterfaceNum
State frCircuitState
Interfaces
Interfaces main window
Number ifIndex
Admin Stat ifAdminStatus
Type ifType
Operational Status ifOperStatus
Interface Details
Description ifDescr
Max Transfer Unit ifMTU
Speed ifSpeed
Physical Address ifPhysAddress
Last Change ifLastChange
Received Errored Packets ifInErrors
Requested Errored Packets ifOutErrors
Received and Discarded w/No Errs ifInDiscards
Received w/Unknown Protocol ifInUnknownProtos
184
16 IP
186
IP main window
IP main window
Default Time-To-Live ipDefaultTTL
Discarded for Header Errors ipInHdrErrors
Discarded for Address Errors ipInAddrErrors
Forwarding ipForwarding
Discarded w/No Errors ipInDiscards
Reassembly Timeout ipReasmTimeout
Forwarded Datagrams ipForwDatagrams
Discarded for Unknown Protos ipInUnknownProtos
Modify
TCP
TCP main window
Retransmit-Timeout Algorithm tcpRtoAlgorithm
Retransmit-Timeout Minimum tcpRtoMin
Retransmit-Timeout Maximum tcpRtoMax
Established Resets tcpEstabResets
TCP Details
UDP
Handling of Netbios UDP Broadcasts boxNetbiosUdpBridging
Others Received with No Delivery udpInErrors
Received udpInDatagrams
Received With No Ports udpNoPorts
Errors icmpInErrors, icmpOutErrors
Block Icmp redirects boxBLockIcmpRedirects
Icmp Receive/Send Messages window
Total Received/Sent icmpInMsgs, imcpOutMsgs
Parameter Problems icmpInParmProbs, icmpOutParmProbs
Source Quenchs icmpInSrcQuenchs, icmpOutSrcQuenchs
Times Exceeded icmpInTimeExcds, icmpOutTimeExcds
Redirects icmpInRedirects, icmpOutRedirects
Addressing Information
Echo Replys icmpInReps, icmpOutReps
Time Stamps icmpInTimestamps, icmpInTimestamps
Address Mask Requests icmpInAddrMasks icmpOutAddrMasks
Entry Reassembly Maximum Size ipAdEntReasmMaxSize
Routing Information
Entry Interface Index ipAdEntIfIndex
Entry Subnet Mask ipAdEntNetMask
Destination ipRouteDest
Mask ipRouteMask
Gateway RouteGateway
Cost RouteCost
Interface ipRouteIfIndex
State RouteState
Adding a point-to-point route
Adding a static point-to-point route to a remote host
Adding a static routes to a remote network
Forwarding table window
Advanced…
Next Hop ipRouteNextHop
Type ipRouteType
Protocol ipRouteProto
IP Routing Destination window
Info ipRouteInfo
Route Destination ipRouteDest
Seconds Since Updated ipRouteAge
Address Translation Information
Tag RouteTag
Interface ipNetToMediaEntry
Net Address ipNetToMediaNetAddress
Physical ipNetToMediaPhysAddress
Type ipNetToMediaType
MFR Version
218
Line Signalling
MFR Version 2 main window
Country lineSigCountry
Interregister Signalling
MFR Version 2-Modify
MFR Version 2 Modify window
213
214
Interregister Signalling
216
A1010 A1111 A1212 A1313 A1414 A1515
218
RIP Version
RIP Version 2 main window
Route Changes Made rip2GlobalRouteChanges
Responses Sent rip2GlobalQueries
Address rip2IfConfAddress
Receive rip2IfConfReceive
Adding a RIP address
RIP Version 2-Configuration
Authentication Type rip2IfConfAuthType
Authentication Key rip2IfConfAuthKey
Domain rip2IfConfDomain
RIP Version 2 Statistics
Sent Updates rip2IfStatSentUpdates
Status rip2IfStatStatus
Snmp
Snmp window
Snmp window
ASN ParseErrors snmpInASNParseErrs
Error Status Too Big snmpInTooBigs
Error Status Read Only snmpInReadOnlys
Generated Errors snmpInGenErrs
Out
Generated Errors snmpOutGenErrs
Authentication Failure Traps snmpEnableAuthenTraps
Get Requests snmpOutGetRequests
Get Next Requests snmpOutGetNexts
System
System
System main window
Snmp and Http
Version boxSnmpVersion
Manufacturer
Message Blocks
Operating System Heap Memory
Total Size boxHeapSize
Free boxHeapFreeSpace
Largest boxHeapLargestSpace
Payable features
Installation
Enclosure System
Other
System Services sysServices
Web Settings boxBackgroundFlag
Physical Location sysLocation
Monitor Privilege boxMonitorPrivilege
System-Modify window
System-Modify window
Enable Payable FeaturesboxFeatureEnableKey
System-Packet Holding Message Blocks
Buffer Size boxbuffersize
No. of Buffers boxbuffercount
No. Free boxbuffersfree
No. of Tasks Waited boxCountBufferTaskWait
No. of Times UnavailableboxCountBufferUnavailable
System Log
System Log Main Window
System Log main window
System Log-Modify
Daemons
Priority
Min Priority for Console RS-232 syslogConsolePriority
Min Priority for Flash Storage syslogFlashPriority
Min Priority for Snmp Trap Daemon syslogTrapPriority
Min Priority for RAM SyslogTablePriority
Unix Facility syslogUnixFacility
Maintenance
Call Trace syslogCallTrace
Maintain Flash Storage syslogFlashClear
System Log-Volatile Memory
Time slTick
Message slMessage
System Log-Non-Volatile Memory
What the System Log messages are telling you
Time slfTick
Message slfMessage
T1/E1 Link
Error Injection linkInjectError 263
Path Code Violations dsx1FarEndCurrentPCVs 271
T1/E1 Link Activity main window
T1/E1 Link Activity main window
Link dsx1LineIndex
Type dsx1LineType
Alarms Present
Physical Line Alarms dsx1LineStatus
Far End Alarm Failure
Circuit ID dsx1CircuitIdentifier
Alarm Indication Signal AIS Failure
Loss Of Signal Failure
TS16 Alarm Indication Signal Failure
Loss Of Frame Failure
Isdn Signaling Alarms linkSignalStatus
Snmp MIB definition
E1 TS16 AIS
Line Status-Configuration
Time Elapsed dsx1TimeElapsed
Valid Intervals dsx1ValidIntervals
WAN Circuit Configuration-Modify
Line Interface Settings
Circuit ID dsx1CircuitIdentifier
Line Type dsx1LineType
Line Coding dsx1LineCoding
Receive Equalizer linkRxEqualizer
Yellow Alarm Format linkYellowFormat
Signalling Settings
Signal Mode dsx1SignalMode
Line Build Out linkLineBuildOut
Test Settings
Loopback Config dsx1LoopbackConfig
Error Injection linkInjectError
Send Code dsx1SendCode
Line Status-Channel Assignment
Channel channelIndex
Desired Function channelfunction
Near End Line Statistics-Current
CurrentState ChannelState
Errored Seconds dsx1CurrentESs
Severely Errored Seconds dsx1CurrentSESs
Severely Errored Frame Seconds dsx1CurrentSEFSs
Line Errored Seconds dsx1CurrentLESs
Near End Line Statistics-History
Near End Line Statistics-Totals
Severely Errored Seconds dsx1TotalSESs
Severely Errored Frame Seconds dsx1TotalSEFSs
Line Errored Seconds dsx1TotalLESs
Bursty ErroredSeconds dsx1TotalBESs
Far End Line Statistics-Current
Far End Line Statistics-History
Severely Errored Seconds dsx1FarEndIntervalSESs
Severely Errored Frame Seconds dsx1FarEndIntervalSEFSs
Line Errored Seconds dsx1FarEndIntervalLESs
Bursty Errored Seconds dsx1FarEndIntervalBESs
Far End Line Statistics-Totals
Bursty Errored Seconds dsx1FarEndTotalBESs
Using Non-Facility Associated Signaling Nfas
Configuring Nfas
Degraded Minutes dsx1FarEndTotalDMs
RAS hosts 1 Nfas group containing 3 PRIs
Sync PPP
Sync PPP
WAN Circuit Configuration window
Line Status-Channel Assignment
PPP configuration
PPP Main Window
Ip Address pppServiceIpAddress
Ip Mask pppServiceIpMask
Default Settings
State pppActState
Authentication Technique pppDefaultAuthenticationTechnique
Authentication Side pppDefaultAuthenticationSide
Authentication Username pppDefaultAuthenticationUsername
Authentication Password pppDefaultAuthenticationPassword
Compression pppDefaultIpCompression
PPP Link Window
Link frDlcmiIfIndex
Status framerelStatus
Link Configuration
Authentication Side pppAuthenticationSide
Authentication Username pppAuthenticationUsername
Authentication Password pppAuthenticationPassword
Security Level pppAccessLevel
Link Compression pppLinkCompression
Allow Magic Number Negotiation pppMagicNumber
Bad Address pppStatBadAddresses
Bad Controls pppStatBadControls
LCP AuthenticationpppStatLcpAuth
ACC Map pppStatLocalToPeerACCMap
Peer-Local ACC Map pppStatPeerToLocalACCMap
Local-Remote AC ComprsnpppStatLocalToRemoteACComp
Remote-Local AC Comprsn pppStatRemoteToLocalACComp
Transmit Frame Check Seq. Size pppStatTransmitFcsSize
Receive Frame Check Seq. Size pppStatReceiveFcsSize
Operational Status pppIpOperStatus
Remote Max Slot ID pppIpRemoteMaxSlotId
Local Max Slot ID pppIpLocalMaxSlotId
Octets Sent pppActSentOctets
Octets Received pppActReceivedOctets
Modify Link Configuration Window
Link Configuration
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol L2TP
L2TP Configuration
Static Authentication
Radius Authentication
L2TP Radius Authentication
Configuration Example
Cisco Configuration
This will enable the use of tunnel authentication
Contacting Patton
Patton Electronics Company contact information
About window
License
End User License Agreement
Definitions
Warranty
Title
Term
Grant of License
Appendix a Supported Radius Attributes
Access-Accept Attributes
Access-Request Attributes
Access-Challenge Attributes
Accounting-Start Attributes
Accounting-Stop Attributes
Appendix B MIB trees
Model 2960 MIB Tree Structure
Appendix C Technical Reference
Configuring a Radius server
What Is RADIUS?
Radius Client/Server Architecture
Radius Services
Radius Authentication Procedure
Radius Standards
RADIUS-Where Can I Get It?
Radius Resources
Configuring Radius
Configuring Radius Authentication
Overview
Authentication window
Using Snmp with the Access Server
Finding the Snmp Name
Finding the branch where the Snmp parameter resides
MIB tree for Model 2960 access server
Configuring Non-Facility Associated Signaling Nfas
Configuring Nfas
Configuring Frame Relay
Line Configuration
WAN Channel Assignment main screen
Configuring Frame Relay link parameters
Configuring PVCs
Configuring Permanent Virtual Circuits
Click on Submit Query
Configuring IP routing with a Frame Relay Link
IP routing with Frame Relay example
Link Status and the IP Forwarding
Click Add Route
Configuring Dnis
Setting up IP address pools by configuring Dnis Ip Pools
Setting up a Dnis user profile
Setting up a Dnis group
Configuring a leased line/dedicated line connection
Configuring the RAS
Configuring the remote end using Microsoft Windows
Modem properties window
Under the Options tab set Redial attempts to a high number