RIC-155
Page
RIC-155
Limited Warranty
Please observe the following precautions
General Safety Instructions
Connection of AC Mains
General Safety Practices
Connection of DC Mains
Connection of Data and Telecommunications Cables
Ports Safety Status
Electromagnetic Compatibility EMC
Conventions
Canadian Emission Requirements
Supplementary Information
Safety
Manufacturers Name Manufacturers Address
Product Name
Configuring RIC-155
Installing RIC-155
Quick Start Guide
To configure RIC-155
Configuring RIC-155
Contents
Appendix A. Connector Wiring Appendix B. Traffic Separation
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics
Application
Chapter Introduction
Overview
Versions
Fiber Optic Interface Options
Features
10/100BaseT Interface
STM-1/OC-3c Interface
Status Reporting
Alarm Relay
Management
Internal Bridge
RIC-155 3D View
Physical Description
Functional Description
RIC-155 Block Diagram
Technical Specifications
Temperature 50C / 32-122F Humidity Up to 90%, non-condensing
Alarm Types Major and minor Connector DB-9, female
Introduction
Introduction
Chapter Installation and Setup
Site Requirements and Prerequisites
Connecting the Interface Cables
Package Contents
Connecting AC Power
Connecting the Power Cable
Connecting DC Power
Connecting the Power Cable
To turn on RIC-155
Controls and Indicators
Chapter Operation
Turning On RIC-155
Name Function Location
RIC-155 Normal Indicator Status
Indicator Status
RIC-155 LEDs
RIC-155 Default Settings
Default Settings
Uplink
Configuration Alternatives
Parameter Default Value
Managing RIC-155 via Terminal Port
To prepare RIC-155 for network management
Managing RIC-155 via Ethernet Ports
Preparing the Terminal
Starting Terminal Session for a First Time
To start a ConfiguRAD session
Menu Map
Loging on
To enter the user name and password
Navigating the Management Menus
To choose an option terminal session
To choose an option ConfiguRAD session
Choosing Options
Correcting Entries
Navigating Tables
Turning Off RIC-155
Logging Out
Operation Turning Off RIC-155
To access the Management menu
Chapter Configuration
Configuring RIC-155 for Management
To access the Configuration menu
To enter device information
Entering Device Information
To define the IP parameters
Configuring the Host Parameters
To configure the network managers
Configuring the Network Managers
To define the management access method
Controlling the Management Access
To enable or disable management ports
Configuring the RIC-155 for Operation
Configuring Control Port Parameters
Configuring the Clock Source
Configuring the Security Timeout
Enabling and Disabling Pop-up Alarms
Changing the Control Port Data Rate
Configuring the Ethernet Interface
Configuring the Physical Ports
Configuring the STM-1/OC-3c Interface
10E-5,10E-6,10E-7,10E-8,10E-9
10E-3,10E-4,10E-5
J1 Path Trace
Uplink Port Loss of Signal
Uplink Port Signal Loss
Line Excessive Error Defect
Line Signal Degraded Error
Mbps, 8 Mbps, No Limit
Configuring the Internal Bridge
Configuring Fast Ethernet Bridge
To configure the Fast Ethernet bridge
To configure the Ethernet management and data bridge ports
Configuring the Bridge Ports
Configuring Ethernet Management and Data Bridge Ports
To access the Bridge Port menu
To configure the POS port
Configuring the POS Bridge Port
Displaying the System Status
Displaying the RIC-155 Status
To display the system information
Displaying the Ethernet Port Status
Displaying the Port Status
To display the Ethernet port status
Parameters Values
Displaying the STM-1/OC-3c Port Status
DATA/MNG Port Status Parameters
To display the STM-1/OC-3c port status
STM-1/OC-3c Port Status Parameters
Changing the Password
To change the current password
Additional Tasks
Displaying the RIC-155 Inventory
21. User Access Menu
Installing a New Software Release via Tftp
Installing Software Releases
To install a new software release via Tftp
To install a new software release via Xmodem
Installing a New Software Release via Xmodem
Displaying the Software Version
Transferring Configuration Files
To upload a configuration file
To download a configuration file
Resetting RIC-155
Switching Software Versions
To switch software versions
To reset RIC-155
Resetting RIC-155 to Factory Defaults
Resetting RIC-155
To reset RIC-155 to the defaults
To display the Ethernet statistics
Chapter Troubleshooting Diagnostics
Monitoring Performance
Displaying the Ethernet Statistics
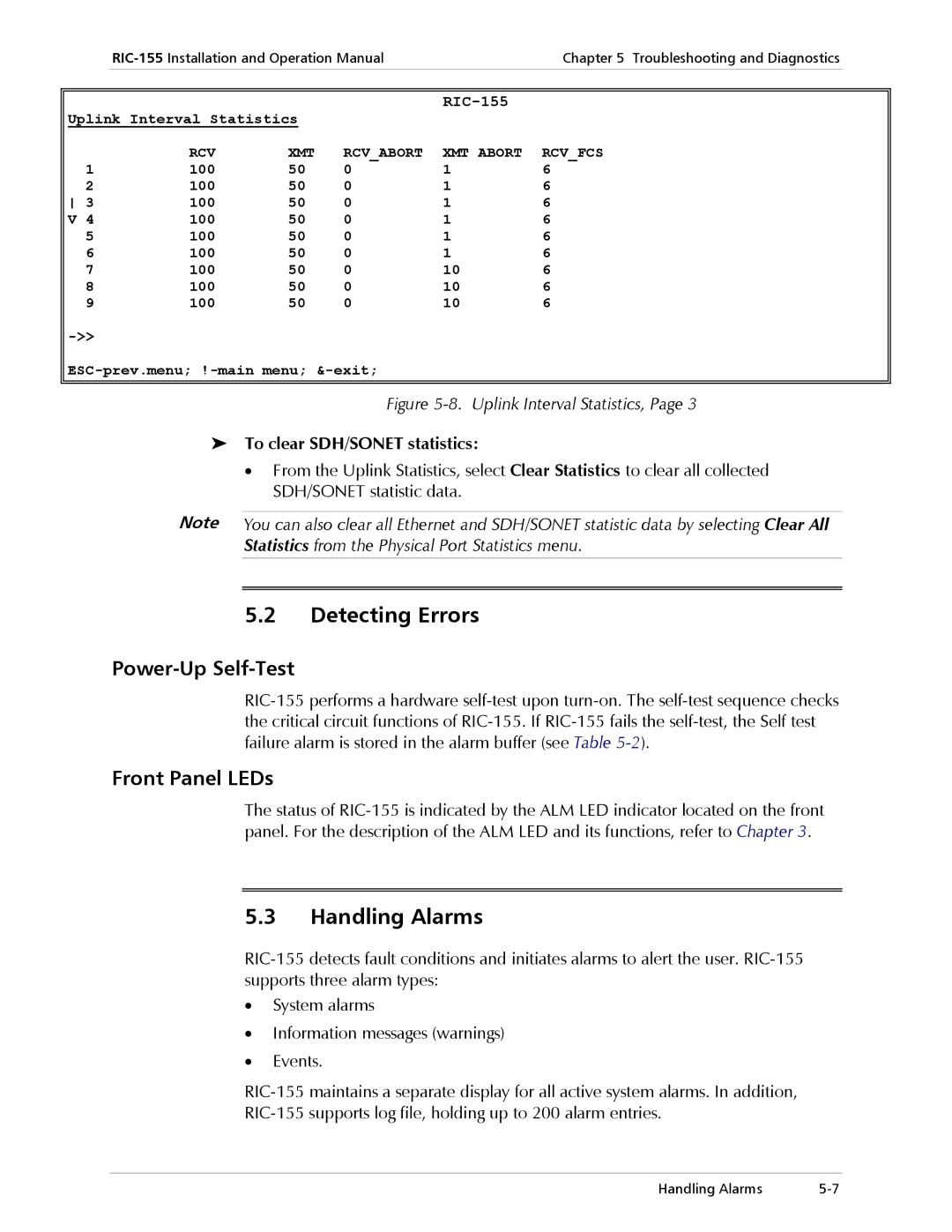
To display the current SDH/SONET statistics
Displaying SDH/SONET Statistics
Display Description Range
Uplink Statistics Screen,
Uasl
RCV Abort
1explains all SDH/SONET statistics parameters
To display SDH/SONET statistics for all intervals
Front Panel LEDs
Detecting Errors
Handling Alarms
Power-Up Self-Test
To display the event log file
Displaying System Alarms
To display the system alarms
Working with the Log File
To configure the alarm severity
Configuring Alarm Severity
To clear the event log
Terminal Message Description Severity
Masking Port Alarms
To mask RIC-155 alarms
RIC-155 Alarms and Warnings
Number Terminal Message Description
RIC-155 Events
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Handling Alarms
Table A-1. ETH and MNG-ETH Connector Pinout
Appendix a Connector Wiring
Ethernet Connectors
Alarm Relay Connector
Pin Alarm Relay Function
Control Connector
Table A-2. Alarm Connector Pinout
Table A-3. Control Connector Pinout
MNG only
Appendix B Traffic Separation
Port-Based Traffic Separation
None
All
Port-Based/VLAN-Based Traffic Separation
Local Mng Only
Uplink and Host Ports
Default Tagging
Table B-1. Default Tagging Modes
Tagging Modes of the Bridge Ports
None
Forwarding Mode Port Filter
Management Access Mode None MNG Only All Local MNG Only
Internal Operation Modes of the Bridge Ports
All
MNG Only
Managing RIC-155 via MNG Port
Configuring for a Typical Application
Local MNG Only
Figure B-9. Managing RIC-155 via MNG Port
Managing RIC-155 via Data Port
Figure B-10. Managing RIC-155 via Data Port
Index
STM-1/OC-3c interface, 1-2,1-6
RADview-Lite,3-5
Excellent Good Fair Poor Very Poor
Customer Response Form
Page
Error Report
Page
Page
International Headquarters