Rugged Operating System ROS V3.5 User Guide
Registered Trademarks
Warranty
Copyright
Disclaimer of liability
Table Of Contents
DNP
109
Igmp
221
Page
Table Of Figures
WIN and TIN Form
160
Port Lldp Parameters Form 216
Document Conventions
Supported Platforms
Who Should Use This User Guide
How Chapters are organized
Firmware/User Guide Version Numbering System
Applicable Firmware Revision
Using the RS232 Port to Access the User Interface
Administration
ROS User Interface
Structure of the User Interface
Making Configuration Changes
ROS Secure Shell Server
ROS Web Server Interface
Using a Web Browser to Access the Web Interface
Log in to The Device with a Web Browser
ROS RS400
Main Menu via Web Server Interface
Structure of the Web Interface
Parameters Form Example
Updating Statistics Displays
Administration Menu
Administration Menu
IP Interfaces Table
IP Interfaces
Type
Mgmt
IP Address Type
Synopsis ###.###.###.### where ### ranges from 0 to Default
IP Address
Subnet
IP Gateways
Destination
Gateway
Web Server Users Allowed
IP Services
Inactivity Timeout
Telnet Sessions Allowed
SSH Sessions Allowed
Synopsis 1 to 254 or Disabled Default Disabled
Synopsis Disabled, Enabled Default Enabled
ModBus Address
Location
Login Banner
System Identification
System Name
Passwords
Synopsis Local, Radius Default Local
Auth Type
Admin Username
Administration Guest Username
Guest Password
Operator Password
Time Zone
Time and Date
Time
Date
NTP Server Address
Default UTC-000 Lisbon, London
NTP Update Period
Synopsis 1 to Default 60 min
Snmp Users
Snmp Management
Auth Key
Name
Auth Protocol
Priv Protocol
SecurityModel
Administration Priv Key
Synopsis snmpV1, snmpV2c, snmpV3 Default snmpV3
Snmp Security to Group Maps
Snmp Access
Synopsis Any 32 characters Default
Group
WriteViewName
Synopsis noView, V1Mib, allOfMib Default noView
SecurityLevel
ReadViewName
Administration NotifyViewName
Radius overview
User Login Authentication and Authorization
Vendor
Server
Radius Server Configuration
Default Primary
Synopsis ###.###.###.### where ### ranges from 0 to
Auth UDP Port
TACACS+
TACACS+ Server Configuration
TACACS+ Server Form
Auth TCP Port
Dhcp Server Address
Dhcp Relay Agent N/A for RMC30
Syslog
Configuring Local Syslog
Administration Dhcp Client Ports
Default Debugging
UDP Port
Configuring Remote Syslog Client
Configuring Remote Syslog Server
Synopsis 1025 to 65535 or Default
Severity
Facility
Problem One
Troubleshooting
Serial Protocols
1 ‘Raw Socket’ protocol features
2 ‘Preemptive Raw Socket’ protocol features
Serial Protocols Overview
6 ‘WIN’ protocol features
3 ‘Modbus’ protocol features
4 ‘DNP’ protocol features
5 ‘Microlok’ protocol features
RTU Polling
Serial Protocols Operation
Broadcast RTU Polling
Broadcast RTU Polling
Permanent and Dynamic Master Connection Support
Preemptive Raw Socket
Message Packetization
Use of Port Redirectors
TCPModbus Performance Determinants
Modbus Server and Client Applications
RTU
Worked Example
Use of Turnaround Delay
Concept of Links
DNP 3.0, Microlok, TIN and WIN Applications
Address Learning for DNP
Address Learning Address Learning for TIN
TIN Broadcast Messages
Broadcast Messages DNP Broadcast Messages
Transport for Protocols with Defined Links
Use of Differentiated Services Code Point Dscp
Transport Protocols
Transport for Raw Socket
Optical loop topology
Force Half Duplex Mode of Operation
Serial Protocols Menu
Serial Protocol Configuration and Statistics
Serial Ports Table
Serial Ports
ForceHD
Pack Timer
Serial Protocols Port
Protocol
Raw Socket
Default 0 ms
Pack Char
Flow Control
Transport
Rem Port
Call Dir
Max Conns
Loc Port
Preemptive Raw Socket Table
Preemptive Raw Socket
Synopsis 3 to Default 10 ms
Dyn Pack Timer
Dyn Pack Char
Synopsis 1 to maximum port number
Serial Protocols Timeout
Synopsis 10 to Default 10 s
Modbus Server
Send Exceptions
Response Timer
Modbus Client
Auxiliary TCP Port
Serial Protocols Forward Exceptions
WIN and TIN
TIN Transport
Serial Protocols TIN Mode
Message Aging Timer
Address Aging Timer
WIN Dscp
MicroLok
Synopsis TCP, UDP Default TCP
8 DNP
Learning
Mirrored Bits
Serial Protocols Aging Timer
Mirrored Bits Form
Device Address Table
Device Addresses
Synopsis 1 to maximum port number or Unknown
Synopsis Any 31 characters Default
Address
Remote IP Addr
Default Unknown
Synopsis Any 16 characters Default
Dynamic Device Addresses
Aging Time
Links Statistics
Connection Statistics
Serial Port Statistics
Overrun Errors
Packet Errors
Parity Errors
Framing Errors
Clearing Serial Port Statistics
Resetting Serial Ports
Problem Two
Problem Three
Problem Four
Page
Ethernet Ports
Controller Protection Through Link-Fault-Indication LFI
Ethernet Ports
Ethernet Ports Menu
Ethernet Ports Configuration and Status
Port Parameters Table
Port Parameters
Speed
Media
State
AutoN
LFI
Link Alarms
Port Rate Limiting Table
Port Rate Limiting
Ingress Frames
Port Mirroring
Port Mirroring Limitations
Ingress Limit
Target Port
Synopsis Disabled, Enabled Default Disabled
Port Mirroring
Source Port
Synopsis Off, On, OnwithPortGuard Default OnwithPortGuard
Link Detection Options
Fast Link Detection
Negative impact on overall system responsiveness
PoE Parameters when applicable
Pwr Limit
Admin
Powered
Class
Ethernet Ports Current
EoVDSL Parameters when applicable
ROS 106 RS400
Set Rate DS/US
Mode
SNR Mrgn
Port Status
Link
Link Rate DS/US
Resetting Ports
Ethernet Ports Name
Duplex
Page
Ethernet Statistics
Ethernet Statistics
OutOctets
Viewing Ethernet Statistics
Synopsis ----, Down, Up
InOctets
ErrorPkts
Ethernet Statistics InPkts
OutPkts
Ethernet Port Statistics Table
Viewing Ethernet Port Statistics
Ethernet Port Statistics Form
TotalInPkts
CRCAlignErrors
Ethernet Statistics InOctets
TotalInOctets
Pkt64Octets
Jabbers
Collisions
LateCollisions
OutUcastPkts
Ethernet Statistics OutMulticasts
OutBroadcasts
UndersizePkts
Clear Ethernet Port Statistics Form
Clearing Ethernet Port Statistics
Rmon History Controls
Remote Monitoring Rmon
Interval
Index
Requested Buckets
Granted Buckets
Synopsis Any 127 characters Default Monitor
Rmon History Samples
Ethernet Statistics Owner
Sample
StartTime
Synopsis Dddd days, Hhmmss
Number of good Broadcast packets received
Utilization
Rmon Alarms
ROS 126 RS400
Rising Thr
Variable
Rising Event
Startup Alarm
Falling Thr
Value
Rmon Events Table
Rmon Events
Last Time Sent
Synopsis none, log, snmpTrap, logAndTrap Default logAndTrap
Synopsis Any 31 characters Default public
Community
Rmon Event Log Table
Rmon Event Log
Synopsis Any 49 characters
Log
LogTime
LogDescription
Spanning Tree
Rstp Operation
State
Rstp States and Roles
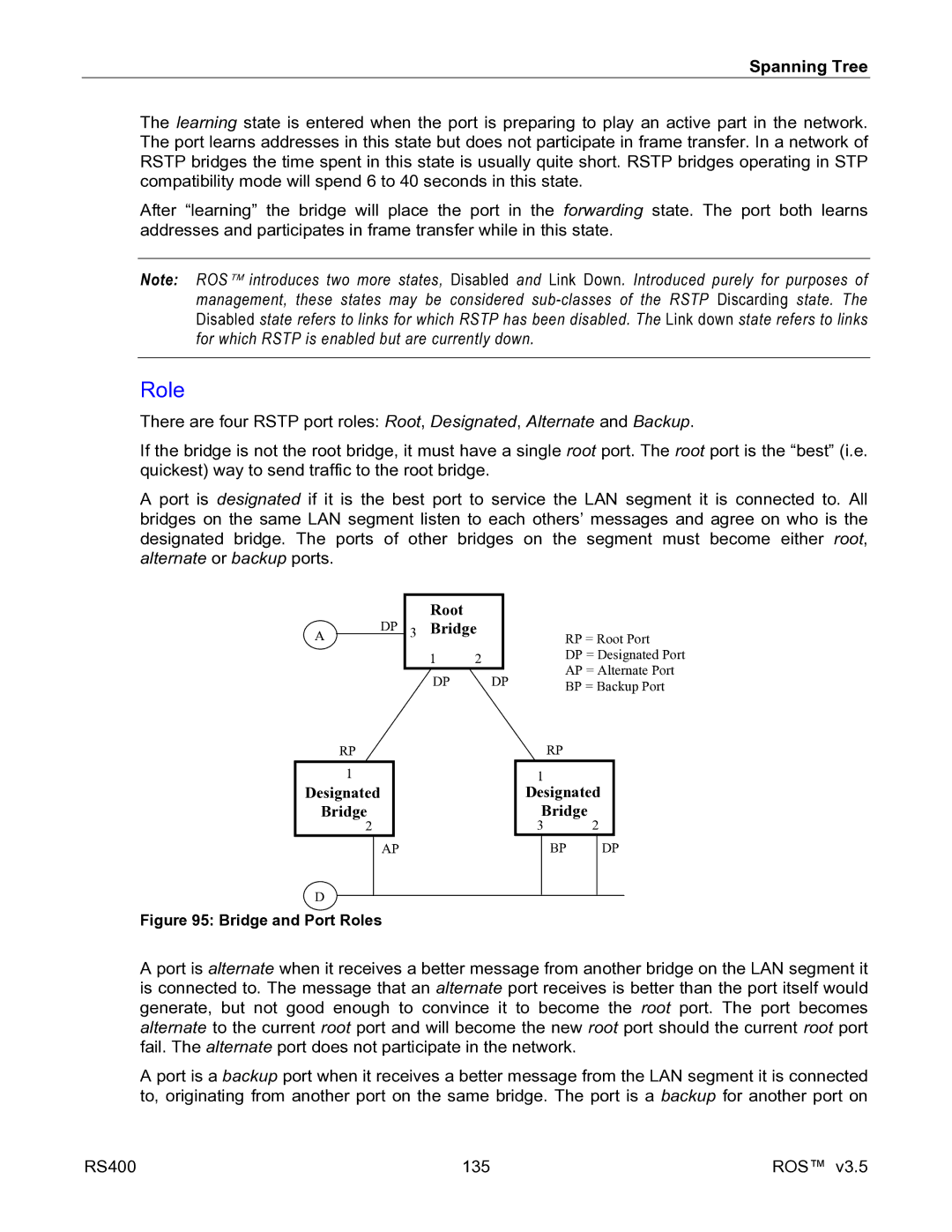
Bridge and Port Roles
Role
How Port Costs Are Generated
Edge Ports
Point-to-Point and Multipoint Links
Path and Port Costs
Bridge Diameter
STP vs. Rstp Costs
MST Regions and Interoperability
Mstp Operation
Msti Regional Root
Mstp Bridge and Port Roles 5.2.2.1 Bridge Roles
Cist Root
Cist Regional Root
Boundary Ports
Port Roles
Cist Port Roles
Msti Port Roles
Mstp versus Pvst
Isolation of Spanning Tree Reconfiguration
Benefits of Mstp
Load Balancing
Implementing Mstp on a Bridged Network
Identify required legacy support
Rstp in Structured Wiring Configurations
Rstp Applications
Select the design parameters for the network
Decide upon port cost calculation strategy
Rstp in Ring Backbone Configurations
Choose the root bridge and backup root bridge carefully
Identify desired steady state topology
Assign bridge priorities to the ring
Rstp Port Redundancy
Identify edge ports
Choose the root bridge
Spanning Tree Menu
Spanning Tree Configuration
ERSTP Enhancements
Synopsis STP, RSTP, Mstp Default Rstp
Bridge Rstp Parameters
Version Support
Max Age Time
Forward Delay
Bridge Priority
Hello Time
Synopsis STP 16 bit, Rstp 32 bit Default STP 16 bit
Bpdu Guard Timeout
Cost Style
Ports
Port Rstp Parameters
Rstp Cost
Spanning Tree Enabled
Priority
STP Cost
Spanning Tree
Digest
Synopsis Any 32 characters Default 00-0A-DC-00-41-74
MST Region Identifier
Revision Level
Instance ID
Bridge Msti Parameters
Port Msti Parameter Table
Port Msti Parameters
Ports
Bridge ID
Spanning Tree Statistics
Bridge Rstp Statistics
Bridge Status
Configured Max Age
Configured Hello Time
Configured Forward Delay
Learned Forward Delay
Port Rstp Statistics Table
Port Rstp Statistics
Role
Status
RX RSTs
RX Configs
TX Configs
Cost
Bridge Msti Statistics Table
Bridge Msti Statistics
Port Msti Statistics Table
Port Msti Statistics
Port Msti Statistics Form
Spanning Tree Role
Troubleshooting
Problem Five
Problem Six
Problem Seven
Problem Nine
Problem Eight
Native Vlan
Vlan Operation
VLANs and Tags
Tagged vs. Untagged Frames
Vlan Ingress and Egress Rules
Edge and Trunk Port Types
Edge Type
Trunk Type
Egress Rules
Forbidden Ports List
VLAN-aware and VLAN-unaware operation modes
Gvrp Generic Vlan Registration Protocol
QinQ not supported in RS400 and RS8000/RS1600 families
Edge Switch
ROS 174 RS400
Traffic Domain Isolation
Vlan Applications
Reduced Hardware
Administrative Convenience
VLAN-aware
Vlan Configuration
Synopsis No, Yes Default Yes
Global Vlan Parameters
VID
Static VLANs
Synopsis Any 19 characters Default
Vlan Name
Forbidden Ports
Port Vlan Parameters Table
Port Vlan Parameters
VLANs Ports
Synopsis Edge, Trunk Default Edge
Synopsis Untagged, Tagged Default Untagged
Synopsis Adv&Learn, Adv Only, Disabled Default Disabled
Dynamic
Vlan Summary
Explicit
Implicit
Don’t need VLANs at all. How do I turn them off?
Page
Inspection Phase
Classes of Service
CoS Operation
Determining The CoS Of a Received Frame
Forwarding Phase
Global CoS Parameters
CoS Configuration
CoS Weighting
Synopsis 8421, Strict Default
Port CoS Parameter Table
Port CoS Parameters
Inspect TOS
Default CoS
Synopsis Normal, Medium, High, Crit Default Normal
Priority to CoS Mapping
Priority to CoS Mapping Form
CoS
TOS Dscp to CoS Mapping Table
Dscp to CoS Mapping
CoS Access Priorities Table
CoS Access Priorities RS8000 and RS1600 families only
Crit Access Priority
Normal Access Priority
Page
Igmp
Router and Host Igmp Operation
Multicast Filtering
Active Mode
Switch Igmp Operation
Passive Mode
Igmp Snooping Rules
Igmp and Rstp
Processing Joins
Combined Router and Switch Igmp Operation
Processing Leaves
Configuring Igmp Parameters
Multicast Filtering Configuration and Status
Router Forwarding
Multicast Filtering Mode
Query Interval
Router Ports
Configuring Static Multicast Groups
Synopsis ##-##-##-##-##-## where ## ranges 0 to FF Default
MAC Address
Synopsis ##-##-##-##-##-## where ## ranges 0 to FF
Viewing IP Multicast Groups
Joined Ports
Troubleshooting
Problem Six
Page
MAC Address Tables
MAC Address Tables
Synopsis Normal, Medium, High, Crit
Viewing MAC Addresses
Synopsis 0 to 65535 or Multi, Local
Synopsis Static, Dynamic
Age Upon Link Loss
Configuring MAC Address Learning Options
Configuring Static MAC Address Table
Synopsis 15 to Default 300 s
MAC address that is to be statically configured
Purging MAC Address Table
Page
Network Discovery
Lldp Operation
Network Discovery Menu
Network Discovery Menu
Tx Interval
Reinit Delay
Tx Delay
Global Lldp Parameters
Port Lldp Parameters Table
Port Lldp Parameters
Lldp Global Remote Statistics
Lldp Neighbor Information
Lldp Statistics
Page
PPP over Modem Operation
Remote Dial-in For Monitoring
PPP over Modem
Router Concentration
Router Concentration
Assigning IP Addresses For PPP
11.1.4 PAP/CHAP Authentication 11.1.4.1 Users Profiles
Using PAP
Using Chap
Static Routes
PPP Configuration Menu
PPP Configuration
Country Code
Modem Settings
AT Commands
Synopsis Any 48 characters Default
Remote IP Address
PPP Control
PPP Status
Local IP Address
PPP over Modem Server Name
Synopsis Any 15 characters Default Server
Outgoing PAP Password
Synopsis Any 15 characters Default
User Name
PPP Users
Remote Subnet
PPP over Modem Password
Synopsis Any 9 characters Default
Remote Net
Synopsis 0 to 2147483647 bps or Offline
PPP Statistics
Current Status
Modem Speed
Authentication
PPP over Modem Tx LCP Packets
Connected User
Clearing PPP Statistics
Resetting PPP
Can connect to the server, but I can’t ping or telnet to it
Am having performance problems
Page
Diagnostics
Using the Alarm System
Viewing and Clearing Alarms
Active Alarms
Passive Alarms
Alarms and the Critical Failure Relay
Synopsis Any 127 characters
Viewing CPU Diagnostics
Total Powered Time
Synopsis MMM DD Hhmm
RAM Available
Diagnostics CPU Usage
Temperature
RAM Total
Viewing the System Log
Viewing and Clearing the System Log
Viewing Product Information
Loading Factory Default Configuration
Resetting the Device
RS900 v2, 40-00-0066, RS900 v2
ROS 244 RS400
Summary Of CLI Commands available in ROS
Using the CLI Shell
Entering and Leaving the Shell
Getting Help for a Command
Viewing Files
Listing files
Viewing and Clearing Log Files
Pinging a Remote Device
Tracing Events
Enabling Trace
Displaying Trace settings
Executing Commands Remotely Through RSH
Starting Trace
Viewing Dhcp Learned Information
Resetting the Device
Upgrading Firmware using XModem
Upgrading Firmware and Managing Configurations
Upgrading Firmware
Checking Status of Download
Upgrading Firmware Using a Tftp Client on Your Workstation
Example of an Upgrade using ROS Tftp Client
Upgrading Firmware Using ROS Tftp Client
Capturing Configurations
Capturing Configurations with XModem
Capturing Configurations with Tftp
Using SQL Commands
Getting Started
Finding the Correct Table
Retrieving Parameter from a Table
Retrieving a Table with Where Clause
Changing Values in a Table
Setting Default Values in a Table
Using RSH and SQL
Using RSH and SQL
Standard MIBs
Module Name
Groups Supported
Proprietary MIB Module Name
RuggedCom proprietary MIBs
Appendix B Snmp Trap Summary
IfInUcastPkts
IfInErrors
TcpInSegs
IfInOctets
UdpNoPorts
UdpInErrors
TcpRetransSegs
UdpInDatagrams
EtherStatsOversizePkts
EtherStatsCRCAlignErrors
EtherStatsMulticastPkts
EtherStatsUndersizePkts
Dot1dTpPortOutFrames
Dot1dBasePortDelayExceededDiscards
Dot1dBasePortMtuExceededDiscards
Dot1dTpPortInFrames
IfHCOutBroadcastPkts
RcDeviceStsTemperature
0x10
Request
0x040x03
Response
Modbus Memory Map
Alarms
Page
Serial
Uint32
Text
Cmd
Uint16
PSStatusCmd
Alarm
Read Data from device using PortCmd
Performing write actions on the device using PortCmd
See ROS
Read Power Supply Status from device using PSStatusCmd
See Lldp
Msti
Tagging 169