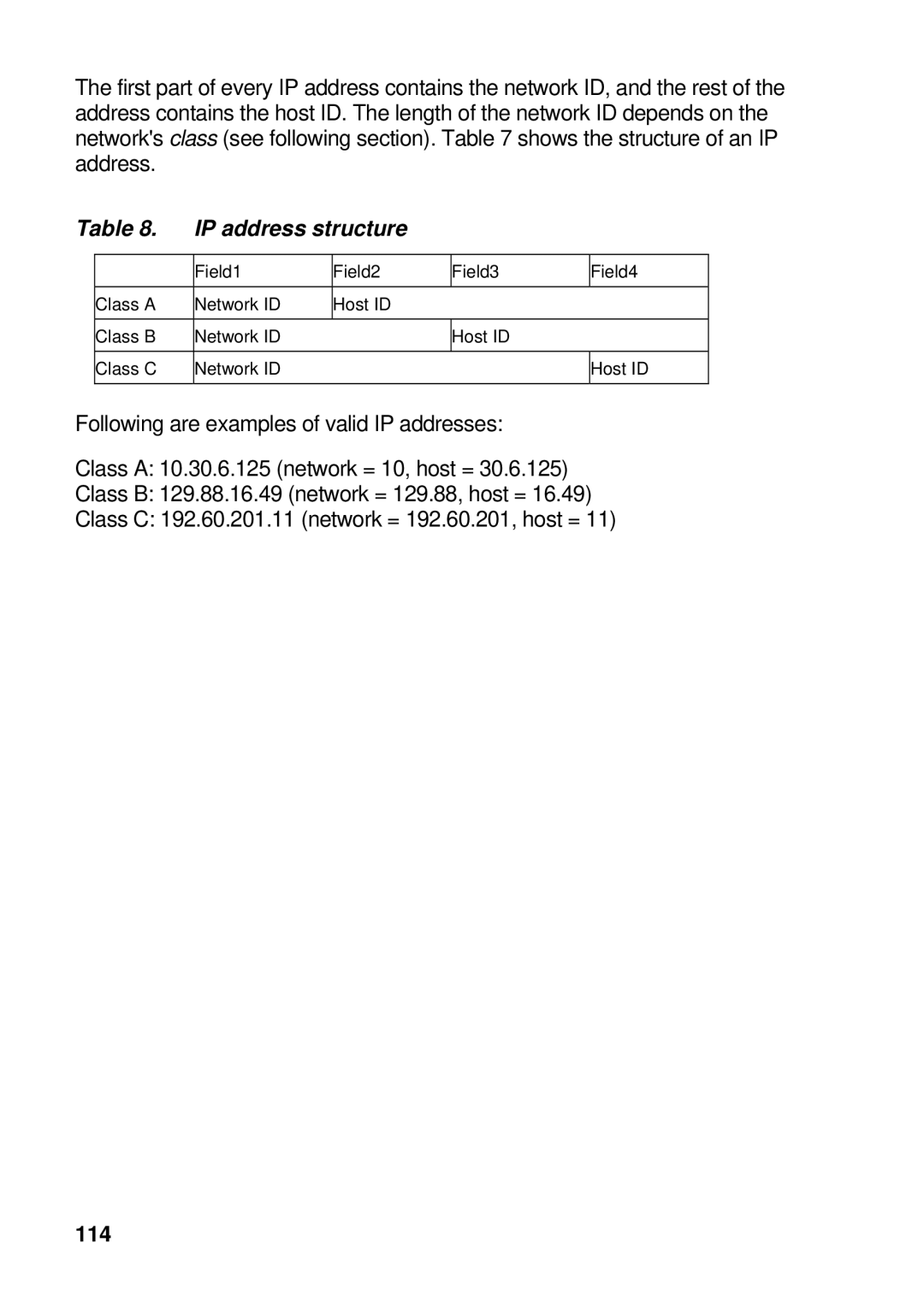
The first part of every IP address contains the network ID, and the rest of the address contains the host ID. The length of the network ID depends on the network's class (see following section). Table 7 shows the structure of an IP address.
Table 8. | IP address structure |
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Field1 | Field2 | Field3 | Field4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Class A | Network ID | Host ID |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Class B | Network ID |
| Host ID |
|
| Class C | Network ID |
|
| Host ID |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Following are examples of valid IP addresses:
Class A: 10.30.6.125 (network = 10, host = 30.6.125)
Class B: 129.88.16.49 (network = 129.88, host = 16.49)
Class C: 192.60.201.11 (network = 192.60.201, host = 11)