Communicating Using A TCP/IP Connection
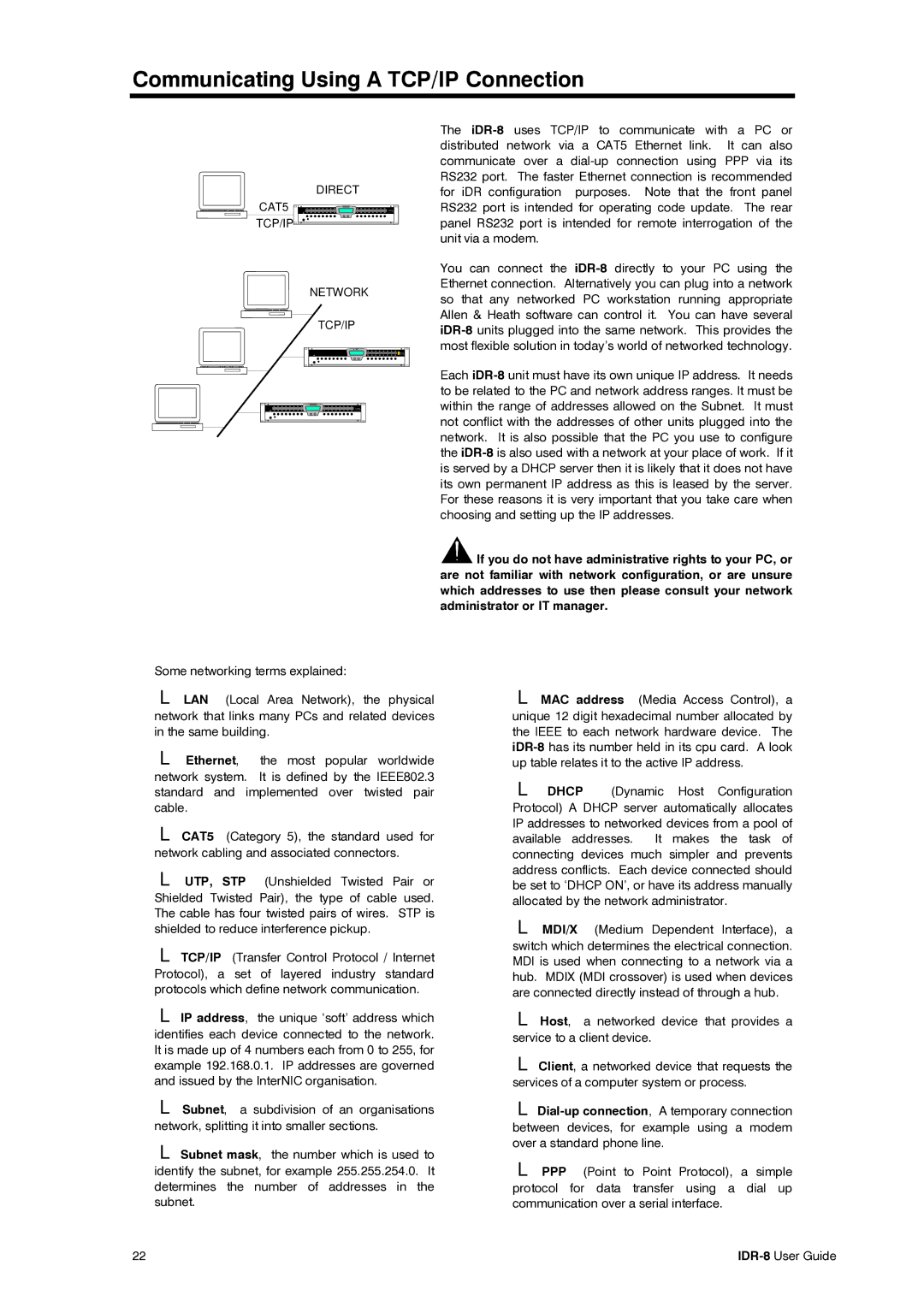
DIRECT
CAT5 | |
TCP/IP |
|
NETWORK
TCP/IP
The
You can connect the
Each
![]() If you do not have administrative rights to your PC, or are not familiar with network configuration, or are unsure which addresses to use then please consult your network administrator or IT manager.
If you do not have administrative rights to your PC, or are not familiar with network configuration, or are unsure which addresses to use then please consult your network administrator or IT manager.
Some networking terms explained:
LAN (Local Area Network), the physical network that links many PCs and related devices in the same building.
Ethernet, the most popular worldwide network system. It is defined by the IEEE802.3 standard and implemented over twisted pair cable.
CAT5 (Category 5), the standard used for network cabling and associated connectors.
UTP, STP (Unshielded Twisted Pair or Shielded Twisted Pair), the type of cable used. The cable has four twisted pairs of wires. STP is shielded to reduce interference pickup.
TCP/IP (Transfer Control Protocol / Internet Protocol), a set of layered industry standard protocols which define network communication.
IP address, the unique ‘soft’ address which identifies each device connected to the network. It is made up of 4 numbers each from 0 to 255, for example 192.168.0.1. IP addresses are governed and issued by the InterNIC organisation.
Subnet, a subdivision of an organisations network, splitting it into smaller sections.
Subnet mask, the number which is used to identify the subnet, for example 255.255.254.0. It determines the number of addresses in the subnet.
MAC address (Media Access Control), a unique 12 digit hexadecimal number allocated by the IEEE to each network hardware device. The
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) A DHCP server automatically allocates IP addresses to networked devices from a pool of available addresses. It makes the task of connecting devices much simpler and prevents address conflicts. Each device connected should be set to ‘DHCP ON’, or have its address manually allocated by the network administrator.
MDI/X (Medium Dependent Interface), a switch which determines the electrical connection. MDI is used when connecting to a network via a hub. MDIX (MDI crossover) is used when devices are connected directly instead of through a hub.
Host, a networked device that provides a service to a client device.
Client, a networked device that requests the services of a computer system or process.
PPP(Point to Point Protocol), a simple protocol for data transfer using a dial up communication over a serial interface.
22 |