4.6 Packet Commands
The WRITE (10) command receives and writes data for the specified number of blocks from the specified logical block address.
Logical Block Address specifies the head logical block address used to start writing.
Transfer Length specifies the number of blocks to be transferred and written.
When Transfer Length is 0, the command does not carry out data transfer. It simply ends normally without writing any data.
4.6.24 WRITE AND VERIFY command
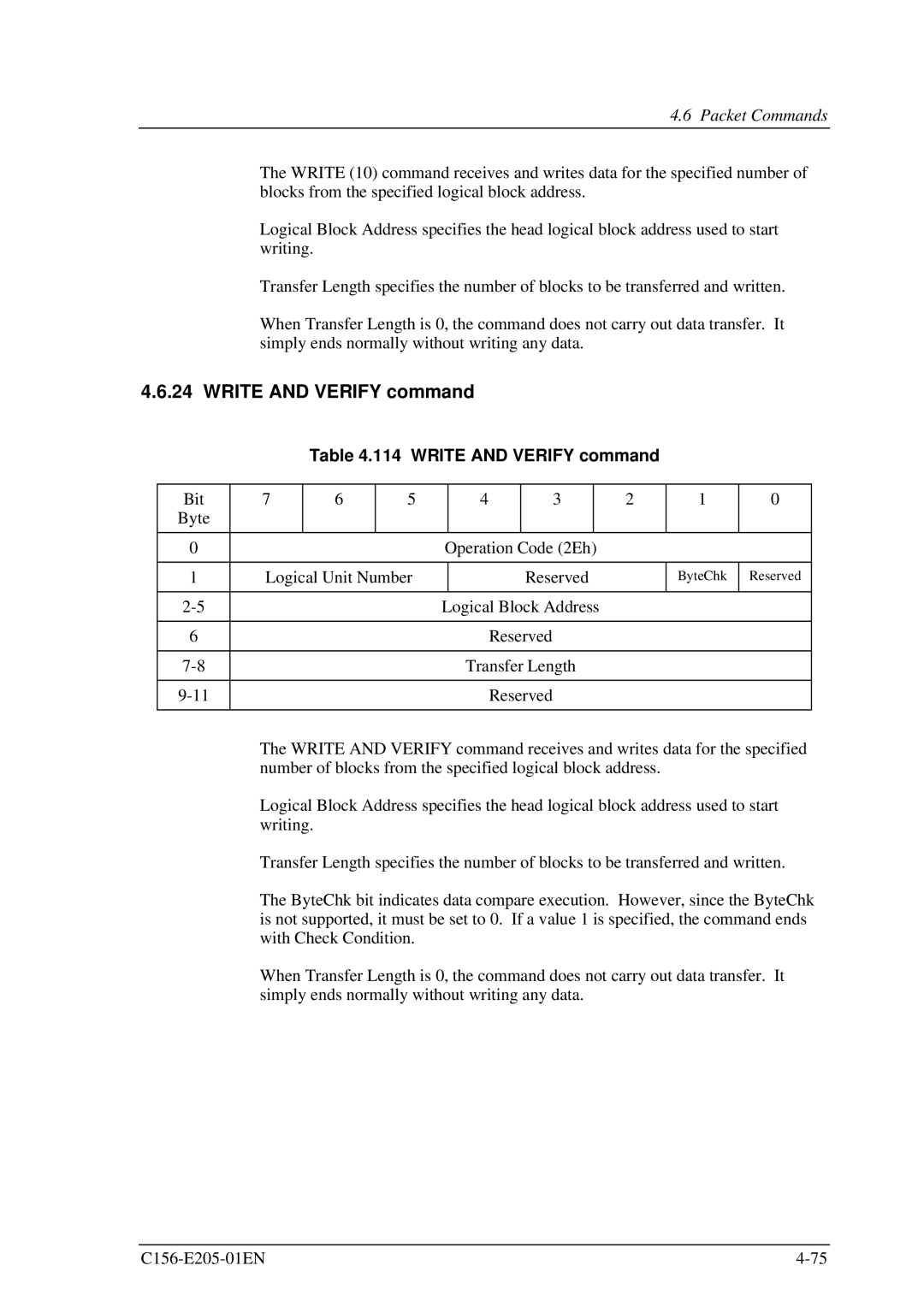
Table 4.114 WRITE AND VERIFY command
Bit | 7 | 6 | 5 |
| 4 |
| 3 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 |
Byte |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
0 |
|
|
| Operation Code (2Eh) |
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
1 | Logical Unit Number |
|
|
| Reserved |
| ByteChk | Reserved | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
| Logical Block Address |
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
6 |
|
|
|
|
| Reserved |
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
| Transfer Length |
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
| Reserved |
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The WRITE AND VERIFY command receives and writes data for the specified number of blocks from the specified logical block address.
Logical Block Address specifies the head logical block address used to start writing.
Transfer Length specifies the number of blocks to be transferred and written.
The ByteChk bit indicates data compare execution. However, since the ByteChk is not supported, it must be set to 0. If a value 1 is specified, the command ends with Check Condition.
When Transfer Length is 0, the command does not carry out data transfer. It simply ends normally without writing any data.