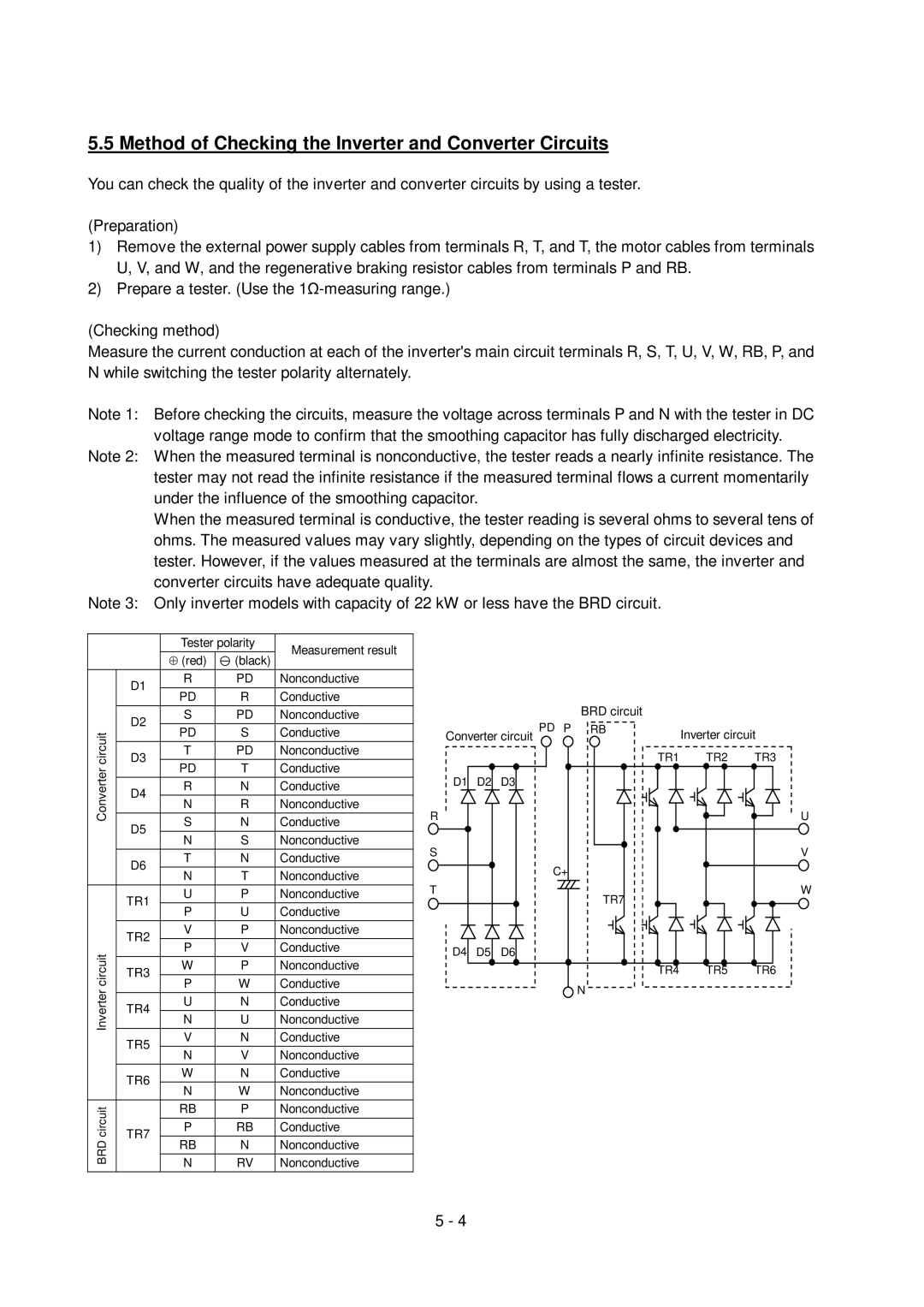
5.5 Method of Checking the Inverter and Converter Circuits
You can check the quality of the inverter and converter circuits by using a tester.
(Preparation)
1)Remove the external power supply cables from terminals R, T, and T, the motor cables from terminals U, V, and W, and the regenerative braking resistor cables from terminals P and RB.
2)Prepare a tester. (Use the
(Checking method)
Measure the current conduction at each of the inverter's main circuit terminals R, S, T, U, V, W, RB, P, and N while switching the tester polarity alternately.
Note 1: Before checking the circuits, measure the voltage across terminals P and N with the tester in DC voltage range mode to confirm that the smoothing capacitor has fully discharged electricity.
Note 2: When the measured terminal is nonconductive, the tester reads a nearly infinite resistance. The tester may not read the infinite resistance if the measured terminal flows a current momentarily under the influence of the smoothing capacitor.
When the measured terminal is conductive, the tester reading is several ohms to several tens of ohms. The measured values may vary slightly, depending on the types of circuit devices and tester. However, if the values measured at the terminals are almost the same, the inverter and converter circuits have adequate quality.
Note 3: Only inverter models with capacity of 22 kW or less have the BRD circuit.
Converter circuit
Inverter circuit
BRD circuit
| Tester polarity | Measurement result | ||
| (red) |
| (black) | |
|
|
| ||
D1 | R |
| PD | Nonconductive |
PD |
| R | Conductive | |
|
| |||
D2 | S |
| PD | Nonconductive |
PD |
| S | Conductive | |
|
| |||
D3 | T |
| PD | Nonconductive |
PD |
| T | Conductive | |
|
| |||
D4 | R |
| N | Conductive |
N |
| R | Nonconductive | |
|
| |||
D5 | S |
| N | Conductive |
N |
| S | Nonconductive | |
|
| |||
D6 | T |
| N | Conductive |
N |
| T | Nonconductive | |
|
| |||
TR1 | U |
| P | Nonconductive |
P |
| U | Conductive | |
|
| |||
TR2 | V |
| P | Nonconductive |
P |
| V | Conductive | |
|
| |||
TR3 | W |
| P | Nonconductive |
P |
| W | Conductive | |
|
| |||
TR4 | U |
| N | Conductive |
N |
| U | Nonconductive | |
|
| |||
TR5 | V |
| N | Conductive |
N |
| V | Nonconductive | |
|
| |||
TR6 | W |
| N | Conductive |
N |
| W | Nonconductive | |
|
| |||
| RB |
| P | Nonconductive |
TR7 | P |
| RB | Conductive |
RB |
| N | Nonconductive | |
|
| |||
| N |
| RV | Nonconductive |
|
|
| BRD circuit |
|
Converter circuit | PD | P | RB | Inverter circuit |
|
|
|
|
| TR1 | TR2 | TR3 |
D1 | D2 | D3 |
|
|
R |
|
|
| U |
S |
|
|
| V |
|
| C+ |
|
|
T |
| TR7 |
| W |
|
|
|
| |
D4 | D5 | D6 |
|
|
|
| TR4 | TR5 | TR6 |
|
| N |
|
|
5 - 4