May
Technical Product Specification
Technical Product Specification
Contents
10.1
16.1
112
10.4
Tables
OOS LED DS9
121
Figures
Date Revision Description
Revision History
Document Organization
Introduction1
Acpi
Glossary
IDE
Application
Features Overview
Functional Description
ECC
Block Diagram
Low Voltage Intel Xeon Processor CPU-0 U35, CPU-1 U36
Intel E7501 Memory Controller Hub U22
Chipset
PCI Bus Master IDE Interface J24
Intel 82801CA I/O Controller Hub 3 U7
P64H2 Interfaces
Memory J8, J9, J10, J11
Intel 82870P2 64-bit PCI/PCI-X Controller Hub 2 U14, U24
Memory Ordering Rule for the MCH
Super I/O U28
4 I/O
Real-Time Clock
Timer0 Capabilities
Gigabit Ethernet U13
See , Component Layout #1 on page 100 for its location
Fibre Channel* U23 Optional
Firmware Hub U30, U33
PMC Connector J25, J26, J27
FWH 1 Backup/Recovery Bios
FWH 0 Main Bios
Flash ROM Backup Mechanism
Onboard Power Supplies
Ipmb Standby Power
Hardware Management Overview
Hardware Management Block Diagram
PCI Serr Ipmc
Sensor Data Record SDR
Hardware Sensors Sheet 1
Ipmc
CPU 0 Ierr Ipmc
Bios SMI
Hardware Sensors Sheet 2
BAT
Hardware Sensors Sheet 3
System Event Log SEL
IPMB-0
Ierr
SEL Events Supported by the MPCBL0001 SBC Sheet 1
Sensor
Event Remarks Type Type Code
SEL Events Supported by the MPCBL0001 SBC Sheet 2
PCI Perr
SEL Events Supported by the MPCBL0001 SBC Sheet 3
PCI Serr
SEL Events Supported by the MPCBL0001 SBC Sheet 4
Temperature and Voltage Sensors
Offset Event Remarks Type Type Code Data 1, Bit
Number
Sensor Thresholds for Ipmc Firmware
Sensor Name
Normal
+5VSB
Sensor Normal
Sensor Thresholds for Ipmc Firmware 1.7 and Above
Sensor Thresholds for Ipmc Firmware 1.14 and Above
Critical Interrupts
System Firmware Progress Post Error
Processor Events
Dimm Memory Events
Bus Device Function Hardware Component Subsystem
PCI Mapping for Hardware Component Subsystem
0XFF
CPU Failure Detection
System Acpi Power State
Ipmb Link Sensor
FRU Hot Swap
Health LED
Port 80h Post Codes
CPU Failure Behavior
CPU Identification
XXX
Field Replaceable Unit FRU Information
PMC Data
Variable Size bytes Data Type
Ipmc Firmware Code
Keying
Link Descriptors for E-Keying
Ipmc Firmware Upgrade Using KCS Interface
Ipmc Firmware Upgrade Procedure
Ipmc Firmware Code Process
Ipmc Firmware Upgrade via the Ipmb Interface Rmcp
OEM Ipmi Commands
Updating MPCBL0001 Firmware
Get Fibre Channel Port Selection
Reset Bios Flash Type
Reset Bios Flash Type
Set Fibre Channel Port Selection
Set Control State
Get HW Fibre Channel Port Selection
Get Fibre Channel Port Selection
Set Control State
Get Control State
Controls Identifier Table
Get Port80 Data
Hot-Swap Process
Hot-Swap Process
LED Status Meaning
Hot-Swap LED DS10
Ejector Mechanism
Hot-Swap LED DS11
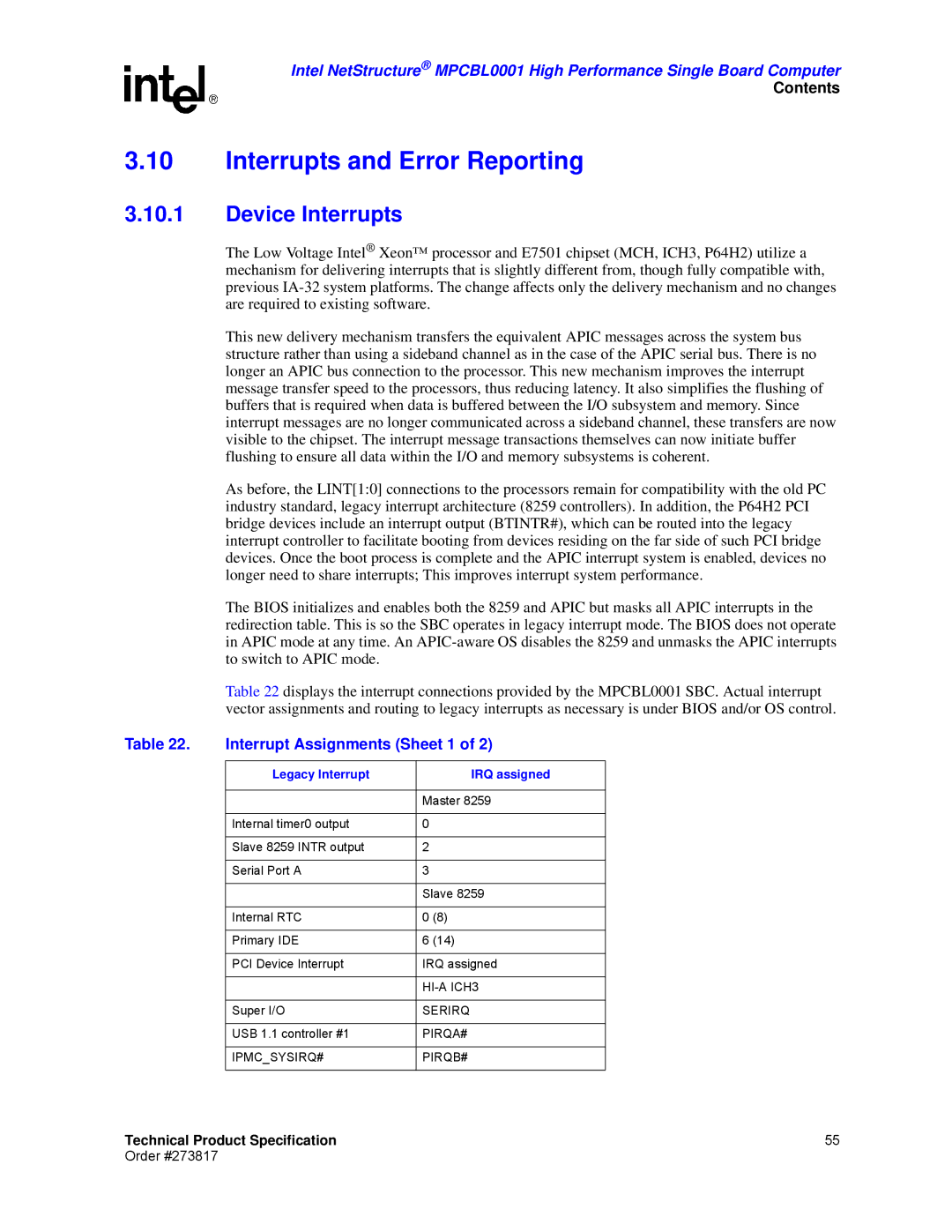
Legacy Interrupt IRQ assigned
Interrupts and Error Reporting
Device Interrupts
Interrupt Assignments Sheet 1
PBIRQ0
Interrupt Signals
Interrupt Assignments Sheet 2
HI-B P64H2 BTINTR# PIRQC# HI-C P64H2 BTINTR# PIRQD#
Error Reporting
Acpi
Reset Types
System States and Power States
Power States and Targeted System Power
Hard Reset Request
Reset Logic
Soft Reset Request
Reset Request
Warm Boot
Reset Request Signal Activated Type
Reset Actions System Function Memory Status
Cold Boot
Power Good
Reset Actions
Contents
Reset Chain
WDT #1
Watchdog Timers WDTs
WDT #3
WDT #2
Hot-Swap LED
OOS Out Of Service LED
LED Status
Health LED
User Programmable LEDs
IDE Drive Activity LED
User Programmable LEDs
IDE Drive Activity LED
Network Speed LEDs
Network Link/Speed LEDs
Ethernet Controller Port State LEDs
Network Link LEDs
Fibre Channel Port State LED DS2, DS3
Setting the Default Color for the OOS and Health LEDs
Fibre Channel Port State LEDs
Ethernet Controller Port State LED
CMM Commands for FRU Control Options
Cold Reset
Warm Reset
Graceful Reboot
Returned Values from the Get Message Command
Diagnostic Interrupt
Byte Data Value Comments
Serial Port Buffering Overview
Diagnostic Interrupt Command Implementation
Description PC Ansi Codes
Using Serial Port Buffering
Configuring the Serial Port
Escape Sequences Not Buffered with Filter Enabled
Flow control No affect on serial buffering
Byte Data Field
0b = Get parameter
Response Data
Configuration of Buffering/Filtering
Get Serial Buffer Configuration Command NetFn=30h, Cmd=31h
Reading Buffered Data
Examples
Get Serial Buffer Command Net Function=30h, Command=30h
Contents
OFFSETLSB=0 OFFSETMSB=0
MPCBL0001 SBC Connector Locations
Connectors4
MPCBL0001NXX SBC Front Panel
MPCBL0001FXX SBC Front Panel
LED Descriptions
Connector Assignments
Backplane Description Details Connectors
Front Panel Description Details Connectors
Pin # Signal Name Description
Backplane Connectors
Power Distribution Connector Zone
Power Distribution Connector Zone 1 P10 Pin Assignments
Data Transport Connector Zone
Alignment Blocks
Data Transport Connector Zone 2 P23 Pin Assignments
Pin
USB Connector J12 Pin Assignments
Front Panel Connectors
USB Connector J12
Serial Port Connector J17
Connector Pin Serial Port Signal Number
Serial Port Connector J17 Pin Assignments
DB9 to RJ-45 Pin Translation
Fibre Channel SFP Copper Transceiver Module AMP, J34, J35
Fibre Channel SFP Optical Transceiver Module
Fibre Channel SFP Pin Assignments
PMC Connectors J25, J26, J27
J25 Bit PCI Pin Signal
PMC Connector Pin Assignments 32 Bit
J26 Bit PCI Pin Signal
J27 Bit PCI Pin Signal
PMC Connector Pin Assignments 64 Bit
PAR64
Pin # Signal Name
On-board Connectors
IDE Connector J24
IDE Connector Pin Assignments
Configuration Address Register Bit Assignments
Configuration Registers
Configuration Address Register MCH Configaddress
Configuration Data Register MCH Configaddress
Device Document Title/Number Section/Page/Table
Configuration Data Register Bit Assignments
I/O Address Assignments
Address Cross-References
Memory Map
Memory Map
Memory Device Address Size
SEL Eeprom
Ipmc Addresses
SMBus Addresses
Bit Ad dress W/R SMBus Description
Mechanical Specifications
Specifications6
Board Outline
Component Layout #1
MCH
Component Layout #2
Component Height
Backing Plate
Front Panel Dimensions FC SKU PMC and Connectors
Front Panel Dimensions FC SKU Screws and LEDs
Front Panel Dimensions Non FC SKU PMC and Connectors
Front Panel Dimensions Non-FC SKU Screws and LED
Environmental Specifications
Environmental Specifications
Reliability Specifications
Mean Time Between Failure Mtbf Specifications
General Assumptions
Power Consumption
Total Measured Power
Environmental Assumptions
Weight
Board Layer Specifications
Cooling Requirements
Introduction
Bios Features
Bios Flash Memory Organization
Copying and Saving Cmos Settings
System Management Bios Smbios
Redundant Bios Functionality
Legacy USB Support
Bios Updates
Booting without Attached Devices
Recovering Bios Data
Boot Options
CD-ROM and Network Boot
Bios Security Features
Fast Booting Systems
Quick Boot
Supervisor and User Password Functions
Remote Access Configuration
Function Key Escape Code Equivalents
Main Menu
Bios Setup
Bios Setup Program Menu Bar
Bios Setup Program Function Keys
Main Menu
Feature Options Description
Bios ID
Advanced Menu
Advanced Menu
CPU Configuration Submenu
Picmg
CPU Configuration Submenu
IDE Configuration Submenu
IDE Configuration Submenu Sheet 1
Primary IDE Master/Slave Submenu
IDE Configuration Submenu Sheet 2
Primary IDE Master/Slave Submenu
Floppy Configuration Submenu
Floppy Configuration Submenu
SuperIO Configuration Submenu
SuperIO Configuration Submenu
Acpi Configuration Submenu
Acpi Configuration Submenu
Advanced Acpi Configuration Submenu
Advanced Acpi Configuration Submenu
System Management Configuration Submenu
System Management Configuration Submenu
Event Logging Configuration Submenu
Event Logging Configuration Submenu
Fibre Channel Routing Picmg Submenu
Fibre Channel Routing Picmg Configuration Submenu
Remote Access Configuration Submenu Sheet 1
Remote Access Configuration Submenu
VT-UTF8
Remote Access Configuration Submenu Sheet 2
USB Configuration Submenu
USB Configuration Submenu
131
USB Mass Storage Device Configuration
PCI Configuration
USB Mass Storage Device Configuration
Boot Menu
Boot Menu
Boot Settings Configuration Submenu
PCI Configuration Submenu
Boot Settings Configuration Submenu
Boot Device Priority Submenu
Hard Disk Drive Priority Submenu
OS Load Timeout Timer
Boot Device Priority Submenu
Hard Disk Drive Submenu
Security Menu
OS Load Timeout Timer Submenu
Security Menu
Exit Menu
Exit Menu
Explanation of Error Message
Error Messages
Bios Error Messages
Bios Error Messages
EC-EE
Bootblock Initialization Code Checkpoints
Port 80h Post Codes
Checkpoint Description
Post Code Checkpoints Sheet 1
Post Code Checkpoints Sheet 2
Number of Beeps Description
Bios Beep Codes
DIM Code Checkpoints
Acpi Runtime Checkpoints
Copying BIOS.bin from the SBC
Bios Configuration
Bios Image Updates
Procedures to Copy and Save Bios Including Cmos Settings
Error Messages
Saving BIOS.bin to the SBC
Error Message
Bios Image Command Behavior
Bios Utility Command Line Options
Command Line Parameter Description
Flashdos Utility Command Line Options
Jumpers
Jumper/Connector Locations
PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse Header
J18 Pin Assignments
J16 Jumper Assignments
J37 Jumper Assignments
J40 Jumper Assignments
Digital Ground to Chassis Ground Connectivity
Connecting Digital Ground to Chassis Ground
References
Serial Over Lan SOL
SOL Architecture
SOL Block Diagram
Serial Console Redirection over Front Panel and LAN
Bios
Architectural Components
Ethernet Controller
Front Panel Serial Port
Theory of Operation
Serial Over LAN
Utilities
Supported Usage Model
Configuring the Blade for SOL
SOL Configuration Reference Script referencecfg
Installation and Configuration
SOL Client ipmitool
Default Behavior
Bios and OS Configuration
Executing the Script referencecfg
Parameter Remarks
Ipmi V2.0 Set LAN Configuration Parameters Command Settings
SOL User Information
LAN Parameters
Channel Parameters
Command Line Options
SOL Configuration Reference Script Command-line Options
SOL Parameters
Executing the SOL Client ipmitool
Operating Environment
In-Target Probe ITP
Maintenance12
Diagnostics
Supervision
Thermals13
Power vs. Flow Rate
ICH3
Component Technology
Main Components
Code Name Brand Name Package Type
Returning a Defective Product RMA
Warranty Information
For Europe, Middle East, and Africa Emea
For the Americas
For Asia and Pacific Apac
167
Sales Assistance
Technical Support and Return for Service Assistance
Customer Support
Customer Support
Bsmi
Certifications17
English
Safety Instructions English and French-translated
Agency Information-Class a
North America FCC Class a
French
Taiwan Class a Warning Statement
Japan Vcci Class a Korean Class a Australia, New Zealand
North America FCC Class B
Agency Information-Class B
Japan Vcci Class B
Korean Class B Australia, New Zealand
Not the Main Disconnect
Safety Warnings
Mesures de Sécurité
178
Sicherheitshinweise
180
Norme di Sicurezza
182
Instrucciones de Seguridad
184
Chinese Safety Warning
Reference Documents
187
188
Ipmi 1.5 Spec Func
List of Supported Commands Ipmi Picmg
Ipmi 1.5 Supported Commands Sheet 1
Command NetFn
Ipmi 1.5 Supported Commands Sheet 2
SDR Device Commands NetFn
Ipmi 1.5 Supported Commands Sheet 3
SEL Device Commands NetFn
IPMI2.0 Spec Func
Picmg 3.0 Ipmi Supported Commands
Ipmi 2.0 Supported Commands
Command Net Function Interface
193
Material Declaration Data Sheets
Level B Materials and Substances
Level a Materials and Substances
Comments
197
198